Diseases immune system
A-Z A B C D E F G H I J J K L M N O P R S T U V X C CH W SCH E Y Z All sections Hereditary diseases Eye diseases Children's diseases Male diseases Venereal diseases Women's diseases Skin diseases Infectious diseases Nervous diseases Rheumatic diseases Urological diseases Endocrine diseases Immune diseases Allergic diseases Oncological diseases Vein and lymph node diseases Hair diseases Dental diseases Blood diseases Breast diseases Diseases of the respiratory system and injuries Respiratory diseases Diseases of the digestive system Diseases of the heart and blood vessels Diseases of the large intestine Diseases of the ear, nose and throat Drug problems Mental disorders Speech disorders Cosmetic problems Aesthetic problems
How do we evaluate your immune system disorder if it doesn't fit one of the lists? These lists are just examples of immune system disorders that we consider serious enough for you not to do anything beneficial. If your disorder does not meet the criteria of any of these lists, we must also consider whether you have a disorder that meets the criteria of the list in another body system.
We can evaluate these disturbances in the affected body's system. For example, we will evaluate. Musculoskeletal involvement, such as surgical joint reconstruction, under. Side effects such as dry eyes, under. Respiratory disorders such as pleurisy, under.
Immune system diseases include pathological conditions that develop against the background of changes in the effector mechanisms of immunity. Diseases of the immune system are classified taking into account the activity of immune reactions: in the case of a hyperreaction to external allergens, allergic diseases develop; in the case of a perverted reaction to one’s own (endogenous) tissue antigens, autoimmune diseases develop. When the immune system is hyporesponsive, immunodeficiency states occur, in which the body becomes vulnerable to various types of infections. The main organs of the immune system are the bone marrow, thymus, spleen, tonsils, lymph nodes, and lymphoid tissue of the mucous membranes.
Cardiovascular disorders such as cardiomyopathy. Genital disorders such as nephropathy, under. Hematological abnormalities such as anemia, granulocytopenia and thrombocytopenia, under. Skin disorders, such as persistent fungal and other infectious skin rashes, and photosensitivity, under.
Neurological disorders such as neuropathy or seizures. Mental disorders such as depression, anxiety or cognitive deficits. Allergic disorders such as asthma or atopic dermatitis, up to 00 or 00 or according to criteria in another affected body system.
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the immune system are carried out by doctors of various specialties: allergic pathology and immune deficiency are in the field of view of allergists-immunologists, autoimmune diseases (depending on the leading syndrome) are in the competence of rheumatologists, endocrinologists Louis-Bar syndrome, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome etc. Secondary immunodeficiencies can develop against the background of infectious, lymphoproliferative, metabolic diseases, intoxication, irradiation, intake medicines(immunosuppressants, corticosteroids). When they occur, the cellular and/or humoral immunity and the phagocytosis system may be damaged. The most famous form of secondary immunodeficiency is AIDS (HIV infection).
Syphilis or neurosyphilis according to the criteria for the system of the affected organism; for example, 00 Special Senses and Speech, 00 Cardiovascular System, or 00 Neurological. If you have a severe medical impairment that does not qualify for the listing, we will determine whether your medical impairment would qualify for the listing. If this is not the case, you may or may not have the residual functional capacity to engage in significant gainful activity.
Your immune system is your safety information. It's difficult to differentiate between what belongs to your body and what doesn't. When it spies on a medical device such as a virus, bacteria or parasite, it shoots to kill. Unfortunately, the system is not perfect. Sometimes it targets healthy tissue, a situation which, if persists under certain circumstances, can lead to autoimmune disease or autoimmunity.
Common manifestations that accompany various immunodeficiencies are recurrent infections - pneumonia, urinary tract infections, meningitis, generalized candidiasis, herpes, furunculosis, etc. Immunodeficiency states are often combined with allergic diseases - eczema, Quincke's edema. Today it has been proven that congenital defects or acquired deficiency of any immune factors play a leading role in the development of many cancers. Patients with severe immune deficiency often die from opportunistic infections.
"Auto" means I; so "autoimmunity" basically means that your immune system targets itself. More than 23 million Americans suffer from autoimmunity, making it the third most common category of disease in the United States, behind cancer and heart disease. Yet 90 percent of Americans can't name one autoimmune disease, writes Donna Jackson Nakazawa in her book The Autoimmune Epidemic. “It boggles the mind,” she says. The name deserves some blame. "Autoimmune disease" is an umbrella term for a variety of conditions, most of which do not actually use the word "autoimmune" in their names.
To identify or confirm immunodeficiency, a special laboratory study of the immune status is necessary: determination of the number and morphology of lymphocytes, the content of immunoglobulins in the blood serum, study of the complement system, determination of specific antibodies, etc. A biopsy of the lymph nodes, chest X-ray, ultrasound of the thymus and spleen. Treatment of diseases of the immune system that occur with immunological deficiency involves replacement therapy (administration of immunoglobulins, serums, bone marrow transplantation), immunocorrection, immunomodulation.
Some of the most common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, lupus, Hashimoto's thyroid disease, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and asthma. The National Institutes of Health currently labels more than 90 diseases as autoimmune disorders, and this number is sure to increase as scientists continue to identify and further understand the origins of other diseases.
At first, the medical establishment more or less missed the epidemic because specialists, who rarely spoke to each other, viewed individual diseases in a vacuum, Nakazawa says. Patients suffering from joint problems such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are commonly seen by rheumatologists; individuals with skin problems such as psoriasis turned to dermatologists; intestinal disorders such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome fall under the jurisdiction of gastroenterologists; and so on. There was no one standing at the top of the mountain saying, "Wow, look what's happening in all these valleys," says Nakazawa.
Autoimmune disorders constitute a special category of immune system diseases. In this group of diseases, cells of the immune system exhibit autoaggression towards the tissues of their own body. The prevalence of autoimmune diseases is extremely high - they affect about 5-7% of the world's population. Diseases of the immune system with an autoallergic mechanism are divided into organ-specific - in which autoantibodies are directed against a specific target organ (autoimmune gastritis, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hepatitis, etc.), non-organ-specific - in this case autoantibodies can attack different organs and tissues (scleroderma, SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.) and mixed.
However, the system learns the problem and adapts its protocols. One of the catalysts for this change is the ever-expanding scale of the problem. Today's doctors and scientists also have a more sophisticated understanding of how the immune system can go awry. Decades of research led him to the conclusion that every autoimmune disease has three main components: a genetic predisposition, an environmental trigger, and a leaky gut.
Identification of the first two components was easy. Scientists have long known that autoimmunity runs in families and that the onset of a disease can be caused, for example, by an environmental factor such as an infection. In particular, Fasano discovered zonulin, which regulates intestinal permeability.
Triggers that launch a cascade of immunopathological reactions can be bacterial and viral infections, radiation exposure, medicinal and toxic substances, and stress. A number of autoimmune diseases are caused by hereditary factors. Many immune system diseases in this group are characterized by pain in the joints and muscles, skin rash, weight gain or loss, fatigue, increased bleeding or a tendency to thrombosis, fever, and muscle weakness. Most autoimmune diseases have a steadily progressive course, and without appropriate treatment they can lead to severe disability.
“Zonulin works like a police officer from the tissues of our bodies,” he says. “It opens up the spaces between cells, allowing some substances to pass through while keeping harmful substances" Some people produce excess amounts of zonulin, which secretes the cells of the intestinal lining and allows toxins and undigested bits of food into the bloodstream - hence the term "gut leak".
How common are autoimmune diseases?
While clinical and integrative health practitioners have long stated that gut permeability is a major problem in chronic disease, including autoimmune disorders, many mainstream physicians have distanced themselves from this idea. However, the science of gut permeability is now too compelling to ignore.
The most valuable methods for diagnosing autoimmune diseases are laboratory tests aimed at identifying autoantibodies to various tissues, circulating immune complexes, acute phase proteins, components of the complement system, and genetic markers in the blood. Since many antibodies are not specific for a particular pathology, but are found in a number of diseases of the immune system, laboratory diagnostics are always supplemented by instrumental methods (radiography, ultrasound, endoscopy, scintigraphy, biopsy, etc.). In recent years, significant progress has been made in the treatment of diseases of the immune system. The traditional approach includes immunosuppressive therapy, anti-inflammatory therapy with corticosteroids, and efferent therapy (hemodialysis, hemosorption). Performed according to indications surgery(splenectomy for hemolytic anemia, pericardectomy for autoimmune pericarditis, thyroidectomy for autoimmune thyroiditis, etc.). Transplantation of CD34+ autologous hematopoietic stem cells offers very encouraging prospects.
Gut leakage is especially important in any conversation about autoimmune disorders because it is what allows environmental factors to trigger susceptibility genes. Certain gene clusters can directly influence them, making them hyper-responsive. Other genes play an indirect role, exposing the organ to attack.
Although the science of genetics and autoimmunity is in its infancy, researchers have discovered a combination of genes called human leukocyte antigens that may determine who develops an autoimmune disease and who does not. In short, the most important thing to understand is that genes determine how sensitive your immune system is to environmental triggers.
The “Immune diseases” section of the “Beauty and Medicine” reference book contains a detailed list of immunodeficiency and autoimmune pathologies. After reading them, the reader will receive comprehensive information about the causes, course, and modern possibilities for diagnosing and treating diseases.
Immune system diseases, listDiseases and disorders of the immune system are classified according to the activity of the immune system. An overactive immune system has just as much potential to create health risks as an underresponsive immune system. The surge in autoimmunity has been accompanied by the rise of consumer products made from plastics, man-made fibers and synthetic dyes. According to consumer advocates at the Environmental working group, the average person is exposed to more than 126 chemicals before even leaving the bathroom in the morning. Chemicals may be one reason why the majority of autoimmune sufferers—78 percent—are women. Nakazawa believes it's just a matter of time before scientists connect the dots between gender differences in autoimmune diseases and endocrine disruption in women's personal care products, such as phthalate esters and parabens in things like lotion, perfume and sunscreen. Below is a list of immune system disorders based on immune system activity Hyporeactive states of the immune system
Immune system hyperreactivity
Other immune system disorders
Immunodeficiency conditionsThis is the largest group of immune system diseases and includes various diseases that suppress the immune system. Often the cause of an immunodeficiency state is an underlying chronic disease. The symptoms of an immunodeficiency state are the same as those of the underlying disease. Which doctor treats autoimmune diseases?Research is currently underway to determine which chemicals are the most egregious. One that comes up again and again is mercury, which can cause autoimmunity by increasing the production of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell in the immune system. Infections can also cause autoimmunity. Some infections, such as group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, cause rheumatic heart disease, an autoimmune disease that affects the heart. You may be genetically susceptible and exposed to a variety of environmental triggers, but in most cases you will not develop autoimmunity unless you also have leaky gut. Combined immunodeficiency- hereditary disorders of the immune system. Combined immunodeficiency is caused by a number of genetic abnormalities, in particular the X chromosome. Several types of recurrent infections are common in people with combined immunodeficiency. In addition, they are also prone to contracting diseases such as meningitis, pneumonia, measles, chicken pox, oral candidiasis, herpes, blood diseases, etc. Diseases of the immune system in children suffering from combined immunodeficiency become apparent in the first 3 months after birth. Immune system diseasesThe fatty, slippery intestines, if they were fused and flat, would be carpet on a tennis court. The outermost lining is just one layer of cells and is home to trillions of bacteria. In a healthy gut, good bacteria outnumber bad bacteria. But maintaining a healthy ratio is very difficult. Years of eating junk food, pain management, and stress inflame the lining of your gut. Every bowel can occasionally leak from time to time. A leak may occur after an infection, virus, or stomach upset. Some people have symptoms such as bloating, gas, or upset stomach. If the intestines are healthy, the lining will heal. But if the intestines are in poor condition, they may not be able to close the cracks. AIDS: HIV/AIDS is a serious immune system deficiency and one of the leading causes of death worldwide. AIDS develops in the later stages of the progression of HIV infection, when the body's immune system, after slowly deteriorating, comes to a state of complete collapse. AIDS is considered a life-threatening disease transmitted through sexual contact, physical contact, blood transfusion, sharing needles and the like. The chances of survival for AIDS patients are negligible if the diagnosis is made at later stages. Immune system symptoms associated with AIDS range from common colds and flu to pneumonia and cancer. Excessive immune function - allergiesInside a leaky gut, zonulin opens the door for bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, chemicals and pollutants to enter the bloodstream. Faced with a steady stream of invaders, the immune system makes T helper cells, which speeds up its response. "Humans have evolved over 5 million years, during which our immune systems were designed to attack one enemy: infection," Fasano says. "Now the same mechanism is forced to fight thousands of enemies it has never seen before." Not every bleeding gut will lead to an autoimmune disease, but if you are genetically predisposed, the fight can be very dangerous. Substances produced by T cells can irritate and inflame the body and indirectly activate genes that can cause autoimmunity. Allergy: Allergy is a response of the immune system to substances that are usually harmless to life, called allergens. There are many allergens such as pollen, mold spores, latex and certain foods like peanuts or medications such as penicillin that can cause allergies. In many cases, there is more than one allergen responsible for inducing the allergic reaction. Although allergy symptoms are often mild, it is recommended to diagnose the underlying problem. The body's ability to resist autoimmunity is similar to a trunk's ability to retain water, Nakazawa says. The body barrel is half filled with factors you can't control, like your gender and your genes. The other half is filled with things we can control, like the amount of chemicals we put into our bodies. A healthy diet creates a healthy gut. It protects your body from autoimmunity. "When you heal your gut, you automatically reduce what's in the trunk," says Nakazawa. Eat all unprocessed foods such as vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds and whole grains. For two weeks, cut out gluten, dairy, yeast, corn, soy, eggs and other highly allergenic foods and see how you feel. Find a practitioner who can help you address these underlying issues before they get out of control. Replicate your internal ecosystem with prebiotic and probiotic foods such as plain yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, etc. Boost your digestive enzymes. Without enough enzymes, your intestines cannot break down food into the nutrients your body needs. Aiding broad-spectrum digestive fermentation with your food may help. Eat good fats. Specifically, research shows that omega-3 protects against autoimmunity by reducing inflammation and helping to heal leaky gut. Connect all leaks. Gut-healing nutrients like glutamine and zinc help rebuild the intestinal lining so it can no longer slip through.
Anaphylactic shock: Anaphylactic shock is a serious, extreme form of allergy. In this condition, allergens, such as food, medications, or insect bites, act as a trigger and cause a range of physical symptoms of discomfort in the person. Itching, rash, swelling of the throat and drop in blood pressure are some of the common symptoms of anaphylaxis. Anaphylactic shock can lead to an emergency if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Asthma: asthma, chronic lung disease, the basis of the disease is inflammation of the respiratory tract. Allergens, various irritants or even stimulants such as physical activity can initiate inflammation and cause various breathing problems in a person. Symptoms of asthma include wheezing, cough, shortness of breath, chest tightness, etc. Autoimmune diseases: Autoimmune diseases are a group of immune system dysfunctions in which immune system cells misinterpret signals and attack healthy cells in the body's own. Autoimmune diseases pose a serious threat to human health. Autoimmune diseases can be considered a special category of immune disorders. Chediak-Higashi syndrome: Chediak-Higashi syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by a mutation in the LYST gene (regulator of directional transmission). Common variable immunodeficiency: General variable immunodeficiency is characterized by a low level of antibodies in the body. Common variable immunodeficiency occurs mainly in adults. It may be present at birth but not appear until age 20. Symptoms of common variable immunodeficiency include bacterial infections of the ear, sinuses, bronchi and lungs. Painful swelling of the knee, ankle, elbow or wrist joints, general symptoms of inflammation. Some patients may have enlarged lymph nodes or spleen. hay fever: Hay fever is very similar to allergies, caused by particles suspended in the air such as pollen, mold spores, and animal dander. Hay fever, also called allergic rhinitis, is extremely common in the world. Symptoms include runny nose, watery eyes, sneezing, etc., which are very similar to a cold. The symptoms remain as long as you are in contact with the allergen. Urticaria (urticaria). Urticaria is an acute skin reaction to an allergen. .An allergen is either food or contact with a specific plant. Blisters appear on the surface of the skin. These blisters are often itchy and round or flat. In addition to increased itching of the skin and blisters, a rash, swelling of the lips, tongue and face appear. Human T-lymphotropic virus (retrovirus) and human T-lymphotropic virus (retrovirus) type II (HIV). They cause severe pathology of the human immune system. Most common among drug users and people who have multiple sexual partners. People with genital ulcers and survivors of syphilis are also prone to infection with lymphotropic viruses. The method of transmission of HIV is through sexual contact, blood transfusion, or during pregnancy from mother to fetus. Hyper-IgE syndrome: Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome or Jobe syndrome, Hyper-IgM syndrome: Hyper-IgM is a rare immunodeficiency disease. In hyper-IgM, the immune system cannot generate IgA and IgGj. This disease is caused by a defective gene in T cells. Due to this defect, B cells do not receive the signal to switch immunoglobulin synthesis genes from IgM to IgA and IgG antibodies, and thus continue to synthesize IgM antibodies. Primary immunodeficiency: Primary immunodeficiency diseases are a group of immune system diseases caused by genetic abnormalities. In this case, people are born with a faulty immune system. Selective IgA deficiency: This is a special immunodeficiency in which the immune system is unable to generate IgA antibodies. These antibodies protect the mucous membranes lining the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract from infections; a variant of IgA is secretory IgA. Obviously, in the absence of IgA, the mucous membranes are open to infections. Skin allergies: Skin allergies are similar to any other allergies, with the only difference being that the immunological reaction to the allergen is realized on the skin X-linked agammaglobulinemia: X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a genetic disorder in which The above list of immune system diseases reflects only some of the major immune disorders. Along with these diseases, there are several genetic and acquired immunodeficiencies that affect millions of people around the world. Since the immune system protects us from various infections and diseases, attempts are being made to strengthen it. |

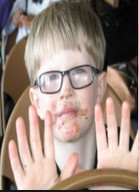 placement of lysosomes). This syndrome is manifested by recurrent purulent infections, partial albinism of the eyes and skin; neutrophils contain giant cytoplasmic granules. Bone marrow transplantation is effective. In addition, natural vitamins are indicated to help the immune system if the child's condition is not severe.
placement of lysosomes). This syndrome is manifested by recurrent purulent infections, partial albinism of the eyes and skin; neutrophils contain giant cytoplasmic granules. Bone marrow transplantation is effective. In addition, natural vitamins are indicated to help the immune system if the child's condition is not severe.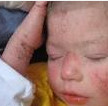 characterized by increased levels of IgE in the blood serum. Hyper-IgE syndrome is characterized by recurrent staph infections and a skin rash similar to eczema. This is a genetic disease and can be dominant or recessive. People with dominant hyper-IgE syndrome cannot lose their baby teeth and have two sets of teeth.
characterized by increased levels of IgE in the blood serum. Hyper-IgE syndrome is characterized by recurrent staph infections and a skin rash similar to eczema. This is a genetic disease and can be dominant or recessive. People with dominant hyper-IgE syndrome cannot lose their baby teeth and have two sets of teeth.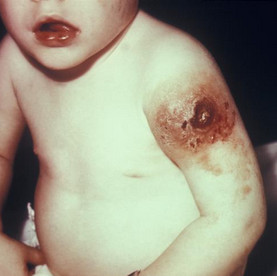 The symptoms and effects are the same as with AIDS, but unlike AIDS, the cause is not acquired, but congenital.
The symptoms and effects are the same as with AIDS, but unlike AIDS, the cause is not acquired, but congenital.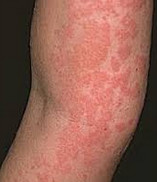 e. Allergy is a reaction of the immune system to certain harmless substances. Skin allergies are characterized by redness and itching of the skin, sometimes blistering and some lesions.
e. Allergy is a reaction of the immune system to certain harmless substances. Skin allergies are characterized by redness and itching of the skin, sometimes blistering and some lesions. The body's ability to fight infections is impaired. The immune system does not produce enough antibodies to fight infections. Naturally, the body becomes a victim of many infections.
The body's ability to fight infections is impaired. The immune system does not produce enough antibodies to fight infections. Naturally, the body becomes a victim of many infections.

