DTP vaccination may not have the most unpleasant consequences. Given this, many parents are wary of it, despite the fact that it is designed to protect the body from viruses that can cause an epidemic.
So what should you be prepared for when going with your baby for vaccination, and what should be the correct preparation for this manipulation should be sorted out. Parents should be aware of the appropriateness of the vaccine and its possible alternative.
Each vaccination and its revaccination is aimed at promoting the production of protective antibodies in the child’s body. DPT can be considered one of the most complex vaccinations, because the serum that is injected during the injection consists of three components.
In a three-component vaccine (whooping cough, tetanus, diphtheria), the component that can cause a strong reaction in the body is whooping cough. This can be explained by the fact that this particular component is made on the basis of living bacteria that have undergone pre-treatment (partial).
The effect of whooping cough on a child’s body is quite strong. For example, it can have a negative effect on the baby’s brain and disrupt its functioning. nervous system, due to their immaturity. As for the other components that make up the vaccine, they rarely contribute to the appearance of negative reactions in the body. After all, they are used in the form of a completely adsorbed substance that the body absorbs well.
There are cases when a baby has contraindications for a vaccine consisting of three components. These include acute respiratory infections, chronic diseases, complications or a strong reaction to a previous vaccine; the baby has been diagnosed with a disease of the nervous system.
In such cases, it is better not to vaccinate or to use two-component serum (ADS), but only after a complete examination of the baby by a doctor and the necessary tests.
What consequences are considered normal?
After DTP vaccination, parents should be prepared for the fact that they may face certain consequences. Not all children are affected by them, but in most cases those with weak immunity. In other cases, the child’s behavior and condition remains unchanged. Side effects that may occur after vaccination and are normal include:
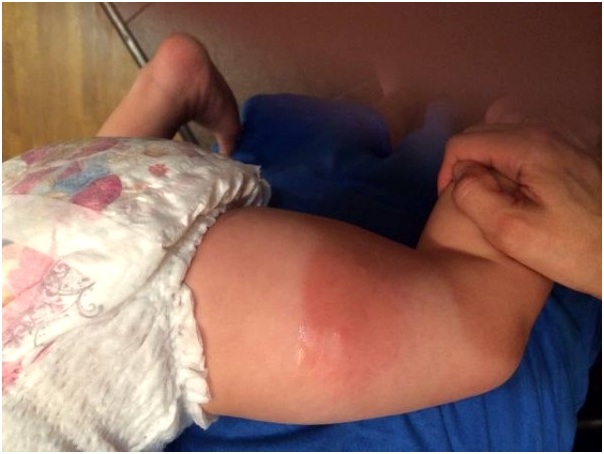
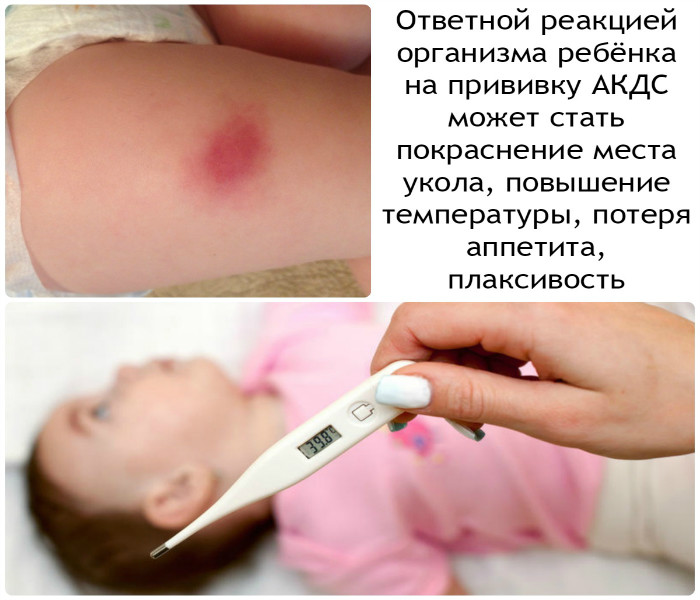
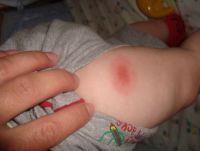
- The appearance of redness in the place where the vaccination was given. If this spot is not hot, its diameter does not exceed 10 centimeters, then there is no need to panic. It is important to ensure that it does not increase in size or change its shape, because this can cause swelling and suppuration, and this can no longer be called a normal reaction of the body.
Due to the inflammatory process, the baby may experience painful sensations, causing moodiness and tearfulness, sleep disturbances, and appetite. You can help the baby using painkillers, which were discussed with the doctor the day before.
- Increased body temperature. This happens due to the fact that the body struggles to produce antibodies. If the temperature exceeds 38 degrees, then it should be brought down, which ensures the normal condition of the child, and the process of formation of protective antibodies in the body is carried out properly.
- The baby's coughing and runny nose are another common consequence that can be encountered after DPT. Symptoms may be caused by one of the components of the serum - whooping cough.
If the baby has the consequences listed above, then you can help him by reducing the pain. It is allowed to give a light massage to the inflamed area of skin, use a compress or product (ointment, cream) that will reduce discomfort. It is also necessary to carefully prepare antipyretic drugs; today, most of them can not only reduce body temperature, but also provide the proper analgesic effect.
Serious consequences
The consequences of DTP vaccination can be dangerous for the baby’s health. Parents who plan to give it to their child should know about this. Serious consequences include:
- Spasm. Its appearance is due to the fact that the baby’s body temperature rises after the administration of the serum. In this case, neurological abnormalities occur in the body. Therefore, even increasing it to 38 degrees may well provoke this condition and lead to brain hypoxia.
- Allergy. Depending on the degree of its manifestation, skin rashes may be short-lived and disappear a few days after the administration of the serum, or they may develop into more serious complications. We are talking about atopic dermatitis and diathesis. All this causes discomfort to children and requires special treatment.
- Swelling of internal organs, which is associated with the appearance of an allergic reaction. Anaphylactic shock is also noted among the serious consequences of this group.
- Brain encephalitis is a fairly serious complication that can make absolutely healthy child disabled person (Downism). This can happen due to the fact that the component of the vaccine, whooping cough, has a negative effect on the meninges.

In the first three days after the three-component vaccine is introduced into the baby’s body, there is a possibility of the above-mentioned consequences occurring. In this regard, every year more and more parents decide to refuse it, not understanding the risk they are exposing their baby to.
After all, everything that was mentioned above is just a partial manifestation of the reaction exerted on the body by the components of whooping cough, tetanus and diphtheria. It’s scary to think about how the virus itself can affect a child’s body. Therefore, it is necessary to get vaccinated, but it should be done correctly.
Proper preparation
Having decided to vaccinate their baby, parents should understand that proper preparation and actions that should follow after the serum is introduced into the body play a huge role. And if after vaccination it is enough to give the baby an anesthetic and antipyretic, then the preparation process will take more time and effort.
But at the same time it will provide confidence that the child is healthy and negative consequences even if they appear, they will be minimized. You can get vaccinated after:
- The child was examined by a doctor and ordered a blood test, which was taken.
- A preliminary consultation followed with specialists, who fully explained to the parents the need for this vaccination, what consequences it could cause and what to do if they occur. After this consultation, they should not have any questions left.
- There was a consultation with the doctor. If the previous vaccine caused complications in the baby, this should not be kept silent. In this case, the doctor will select and advise an alternative to DTP.
A few days before and after DTP, it is recommended to minimize walks with your baby in places where there are a huge number of people. This will prevent viruses from entering the body, which can weaken the immune system and lead to consequences after vaccination. Special attention You should also pay attention to the baby’s nutrition. In the next week after vaccination, it is not advisable to introduce new foods into his diet.
As for the baby’s condition, within 3 days after the serum is introduced into his body, it should normalize - the body temperature will return to normal, swelling and redness will decrease, and lameness, if any, will disappear. The baby's condition will also improve.
He will become cheerful, smiling, calm, the regime will normalize, because nothing bothers him anymore. This means that the components present in the serum are absorbed by the body.
The decision as to whether a child needs a vaccination or not is, of course, made by the parents. But they must understand that the vaccination schedule was invented for a reason. After all, the health of children depends on their timeliness.
If you don’t trust the free vaccinations that often appear in children’s clinics and kindergartens, then the vaccine can be purchased with all the relevant documentation at the pharmacy. You should also be interested in the availability of documentation when you plan to use a free vaccine.
This is the most effective way protecting the human body from serious diseases of an infectious nature. One of the first vaccines used in childhood, is DPT. The uniqueness of this vaccine lies in the fact that it protects the child’s body from the development of several serious infectious diseases at once.
Decoding
The abbreviation DPT stands for adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine. This drug is universal, since its administration protects the child’s body from several severe infectious diseases at once. The pharmaceutical market offers this vaccine as in pure form, and in combination with other drugs for vaccination.
The following vaccine options are available:
- Polio vaccine + DTP + Haemophilus influenzae vaccine (Pentaxim);
- Hepatitis B vaccine + diphtheria vaccine + tetanus vaccine (Bubo - M);
- Hepatitis B vaccine + DTP (Tritanrix);
- Polio vaccine + DPT (Tetracok).
The anti-pertussis component of the DTP drug causes a high risk of side effects during the administration of the vaccine. If a child is prone to allergic reactions, or requires revaccination only against tetanus and diphtheria, then it is recommended to use the following vaccines:
- AD-m (d) - anti-diphtheria drug;
- ADS - a combination of vaccines against tetanus and diphtheria;
- AC - pure tetanus vaccine;
- ADS-m is a diphtheria-tetanus vaccine used for vaccination of adults and children over 6 years of age.

Purpose of the vaccine
Vaccination of children with this drug is mandatory in all developed countries. Thanks to this drug, it was possible to save millions of children's lives and prevent outbreaks of tetanus, diphtheria and whooping cough. Some countries have tried to remove the pertussis component from the vaccine. As a result of such experiments, a serious epidemic of whooping cough arose, claiming the lives of thousands of children.
From the moment a child is born, young parents are faced with the question of the advisability of vaccination. Refusal to vaccinate can be argued as fear of possible complications. But the real reason for the refusal is the lack of information regarding what function the DTP vaccine performs.
When the vaccine components enter the child’s body, they contribute to the production of specific antibodies (immunity), which will protect the child’s body from tetanus, whooping cough and diphtheria throughout his life. The load that the drug puts on a child’s body is not comparable to the risk to which an unvaccinated child is exposed.
A serious advantage of the DTP drug is that it combines 3 vaccines that are administered simultaneously. In this case, there is no need to give several injections and take the child to the clinic several times.

Consequences of refusing DTP vaccination
In order to understand whether this vaccine is necessary for a child or whether it can be ignored, it is recommended to study morbidity statistics. Before the invention of the DTP drug, constant outbreaks of epidemics of diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough were observed in our country.
At least 25% of children fell ill with diphtheria. The mortality rate for this pathology was 50%. People with tetanus died from it in 90% of all cases. Before the invention of the vaccine, there was a widespread incidence of whooping cough. These disappointing statistics speak for themselves.
DTP vaccination acts as a reliable protector of the child’s body, despite the possible risk of complications. To reduce the risk of complications, parents are advised to pre-examine their baby.
Vaccination schedule
In order to form the necessary immunity, the child will need vaccination in several stages. The frequency of administration of DTP is 4 times. Primary vaccination is carried out at the age of 3 months. Secondary - 4-5 months, and tertiary - 6 months. An increase in the frequency of vaccinations is associated with the need for revaccination and maintaining immunity at the proper level.
The first DPT revaccination is carried out at the age of 6 years, and the rest at 7 and 14 years. Subsequent revaccinations are recommended every 10 years.

If the child has no contraindications for the administration of the DTP drug, then the vaccination schedule is as follows:
- 3 months from birth;
- 4-5 months:
- Half a year:
- 18 months;
- Revaccination at 6-7 years;
- 14 years old;
- 24 years old;
- 34 years old;
- 44 years old;
- 54 years old;
- 64 years old:
- 74 years old.
The interval between the first three vaccinations should be at least 30 days. The remaining vaccines are administered at intervals of 1 month. If the child falls ill on the eve of the next vaccination, it is recommended to postpone vaccination. It is recommended to resume the vaccination schedule immediately after the baby recovers.
If a child gets sick after the first vaccination, then at the time of recovery, the 2nd and 3rd vaccines should be administered, with an interval of 30 to 45 days.
Primary vaccination
The first vaccine is administered when the child is 3 months old. This period is due to the fact that until the age of three months, the mother’s antibodies, transmitted to the child through the umbilical cord, retain their influence in the child’s body.

In some countries, DPT vaccination is practiced from 2 months. If at the time of administration of the drug contraindications were found in the child, then primary vaccination can be carried out at any age, up to 4 years.
If the child is over 4 years old, he is recommended to receive the ADS vaccine containing anti-diphtheria and anti-tetanus components.
To reduce the risk of complications, the child must be healthy and prepared. A serious obstacle to DTP vaccination is an increase in the size of the thymus gland.
Both the domestic drug and its imported analogues can be used for vaccination. The drug Infanrix has a mild effect and is easily tolerated by the child’s body compared to other vaccines.
Secondary vaccination
A month after the first administration of the vaccine, the child can be vaccinated for the second time. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a previously administered drug, however DTP vaccines are interchangeable.
The reaction of the child's body to repeated immunization is more pronounced. This should not be a cause for alarm. This phenomenon is caused by the fact that the entry of microbial particles into the child’s body provokes the development of an immune reaction. If the secondary vaccination was missed, it should be carried out as soon as possible.
If the baby reacted severely to the introduction of the first vaccine, then it is recommended to choose another drug (Infanrix) for the second vaccination.

Tertiary vaccination
The administration of the DTP vaccine in the third round is carried out 30-40 days after the second vaccination. It is recommended that each vaccination be performed with the same drug. If for a number of reasons it was not possible to obtain it, then you should use analogues.
Vaccine administration technique
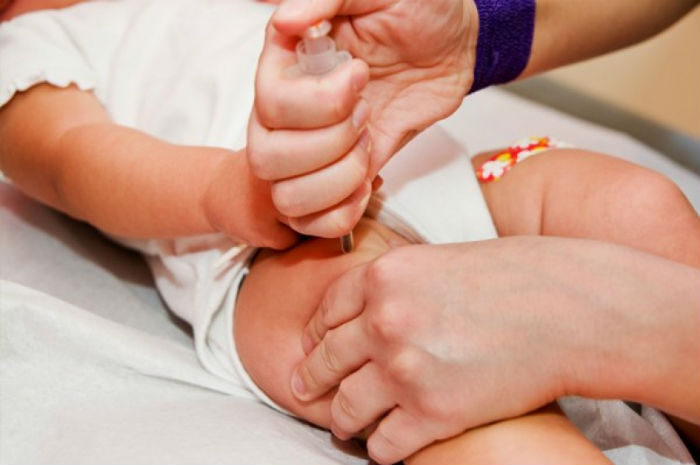
In order for the vaccine components to quickly spread throughout the body, the drug is recommended to be administered intramuscularly. Subcutaneous administration slows down the rate of spread and formation of immunity. For young children, the vaccine is given in the thigh muscle. In older children, the drug is injected into the shoulder area.
It is strictly forbidden to administer the vaccine into the gluteal region, as this risks getting into the sciatic nerve or large vessel. According to research, maximum antibody production is achieved when the vaccine is administered into the thigh area.
Contraindications
The entire list of restrictions for DTP vaccination is conditionally divided into absolute and relative contraindications. Absolute contraindications include:
- individual intolerance to one or more components of the vaccine;
- acute course of any disease;
- pathological conditions associated with immunodeficiency.
Vaccination of a baby is unacceptable if there is at least one contraindication.
If a child suffers from a neurological pathology that is accompanied by a convulsive syndrome, then he is recommended to receive the ADS vaccine, which does not contain an antipertussis component. Vaccination of pregnant and lactating women, as well as children suffering from leukemia, is strictly prohibited. It is recommended to postpone vaccination if the child has an allergic diathesis in the acute stage.
Relative contraindications for DTP vaccination include:
- birth before the due date (prematurity);
- neonatal encephalopathy;
- cases of severe reaction to the drug in close relatives of the baby;
- adverse reactions to the vaccine in close relatives of the child (convulsions, allergies).
These contraindications are not a reason to completely refuse vaccination, but the child must be thoroughly examined. The baby's parents must obtain permission for vaccination from a neurologist. For children with relative contraindications, it is recommended to administer drugs with a gentle effect (Infanrix).
How to prepare your child for vaccination
Considering the high risk of developing adverse reactions, the issue of preparation should be approached very responsibly. There are a number of key conditions that must be met:
- vaccination takes place on an empty stomach;
- at the time of vaccination the child must be absolutely healthy;
- on the eve of going to the clinic, the child must empty his intestines;
- Parents are advised to dress their baby according to weather conditions.
Vaccination of a child should be carried out against the background of the use of antipyretic drugs. For this purpose, use Ibuprofen or Paracetamol. Both drugs help reduce the risk of negative reactions.

- If a child is prone to developing allergies, then 2 days before vaccination he is recommended to take Erius or Fenistil.
- After returning from the clinic, parents are advised to give their baby an antipyretic rectal suppository. During the first day after vaccination, you should regularly measure the baby's body temperature and give him antihistamines.
- The day after vaccination, it is recommended to monitor the child’s body temperature. If increased, Paracetamol or Ibuprofen should be given. Antihistamines should be continued.
- 2 days after vaccination, the use of antihistamines should be continued.
- On the third day, it is recommended to stop using antihistamines, as the child’s condition returns to normal.
The dosage of antipyretics and antihistamines is selected by the attending pediatrician individually for each child.
Restrictions after vaccination
After vaccination, parents are advised to walk with their baby for 30 minutes, without leaving the clinic. This is necessary to monitor the child’s condition. If the child feels well and there are no signs of allergies, then you can go home.
Arriving home, parents should give the baby an antihistamine and an antipyretic.
It is strictly forbidden to overfeed a child after vaccination. Fluids should be given more than usual. On this day, the consumption of fruit juices and food products previously unknown to the child’s body is prohibited.
Bathing the baby is permissible only if he is in good health.
Consequences and complications
When DTP is administered, complications such as fever, skin rash, cough and general malaise may develop. Each symptom is caused by the pertussis component of the vaccine. To prevent and treat complications, antiallergic and antipyretic drugs are used. They eliminate both general manifestations of allergies and local ones in the form of compaction and pain in the injection area.
Modern medicine in all developed countries practices DTP vaccination. Having deciphered this term (adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccination), you can immediately understand that such a vaccination is clearly necessary in order to avoid these three, in most cases, fatal diseases.
And thanks to her, millions of lives around the world have been saved. Children up to the age of fourteen are given DTP 6 times.
It should be recognized and accepted as an unequivocal fact that the DTP vaccination is the most difficult to tolerate of all the vaccines that are included in the vaccination calendar. It is not surprising that a large number of questions that mothers ask doctors are associated with this vaccine.
Consequences of DTP vaccination
It is always worth remembering that the human body reacts in 100% of cases when an injection is given intramuscularly, even with sterile water. The substance included in this vaccine is very painful and children react to it with prolonged and loud crying.
This is where the normal consequences of DPT vaccination arise in the form of redness of the area, a tumor (up to eight centimeters in diameter) and an increase in temperature, which indicates the formation of immunity. Panic in such cases is extremely inappropriate and at such a moment you can only help the baby with a soothing game or hug.

Of course, if there is a strong increase in body temperature, the doctor should prescribe an antipyretic drug for the baby and valerian for the mother. High temperature after DPT is also considered a normal reaction of the body, it’s just that everyone’s body is different and the reaction, accordingly, too.
Very often, mothers can confuse the natural consequences of DTP with diseases that are not related to the vaccine.
When should you not worry?
Typical side effects after DTP vaccination:
 Let's figure it out in order. The baby can actually limp on his leg, because after a swelling forms at the injection site, the leg may swell a little. There may even be a slight inflammatory process.
Let's figure it out in order. The baby can actually limp on his leg, because after a swelling forms at the injection site, the leg may swell a little. There may even be a slight inflammatory process. Cold it can actually be caused by DTP, because after its administration the immune system may weaken and the child is more likely to catch a cold. That's why If your child gets sick after receiving DTP vaccination, then this is quite normal.

Since vaccines cannot protect 100% from the disease (but only 95-98%), the appearance of whooping cough after vaccination may indicate a lack of developed antibodies to the disease.
Nowadays, it is almost impossible to encounter the formation of an abscess after DTP vaccination. Now it is done in the child’s thigh, mainly in the front part. Therefore, many mothers complain that after DPT the leg is swollen. But there was no abscess, which past generations encountered very often!
 Abscess after DTP was very common when the vaccine was given in the gluteal muscle, where the baby has a lot of fat deposits. Their presence is simply necessary for the child in order to make it easier to fall on the fifth point. In these fatty deposits, the substance cannot be fully absorbed and simply stagnates, leading to a possible abscess and not bringing any benefit.
Abscess after DTP was very common when the vaccine was given in the gluteal muscle, where the baby has a lot of fat deposits. Their presence is simply necessary for the child in order to make it easier to fall on the fifth point. In these fatty deposits, the substance cannot be fully absorbed and simply stagnates, leading to a possible abscess and not bringing any benefit.
Chickenpox after DTP cannot be caused by vaccination, but if the baby gets sick after the injection, you should definitely consult a doctor as soon as possible. Because weakened immunity after DTP vaccination can lead to a severe course of chickenpox.
– this is when the vaccination is repeated. If your baby is approaching the revaccination period, we recommend reading our article and being fully prepared.
And if you have not yet been vaccinated and want to learn more about this vaccine, then we talk about it in detail.
What are the complications after DTP vaccination?

Considering that humanity has not yet invented medications that are indifferent to the body, it is always exposed to the dangers of their consequences.
So, your one and a half month old baby was vaccinated and after it the first signs of the body’s reaction to the injected substance appeared. Complications after an injection can be local or general.
A local complication can be in the form of compaction and a significant increase in swelling at the injection site with a diameter of more than 8 centimeters. This phenomenon can last 1-2 days.
Common complications are characterized by a high-pitched and prolonged cry from the child(can last even more than 3 hours), which sometimes reaches the point of screeching. Restless behavior and fever may also be present after DTP, but should go away on their own after a couple of hours.
Baby's seizures
 The appearance of a convulsive syndrome cannot be ruled out. Febrile seizures, caused by high fever (over 38 ºC), may appear in the first few days after vaccination.
The appearance of a convulsive syndrome cannot be ruled out. Febrile seizures, caused by high fever (over 38 ºC), may appear in the first few days after vaccination.
More severe complications occur in the form of afertile convulsions (with body temperature not exceeding 38 ºС), which may indicate organic damage to the central nervous system.
Allergy appears
Complications after DPT also occur in the form of an allergic reaction:
- Hives;
- Anaphylactic shock (this is the rarest and most serious complication, manifesting itself immediately or after 20-30 minutes).
Children's immunity after DPT
 In the first year of life, the child must be vaccinated with DTP three times, and upon reaching the age of one and a half years, he is given a revaccination. The first three immunization shots are enough to fight this infection. Revaccination allows the immune system to resist diseases (whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus) for another 6-8 years.
In the first year of life, the child must be vaccinated with DTP three times, and upon reaching the age of one and a half years, he is given a revaccination. The first three immunization shots are enough to fight this infection. Revaccination allows the immune system to resist diseases (whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus) for another 6-8 years.
As for the general state of immunity, it weakens after all vaccinations. But in a couple of days it should return to normal.
What to do after DPT vaccination and how to help your child
Depending on how hard the baby tolerates the vaccine, there are several options to ease the symptoms:
- After vaccination, get a massage;
- Apply a compress;
- Use special ointments.
Such help definitely requires consultation with a doctor, because everything depends on the severity of the reaction occurring and its type. But what you absolutely cannot do is apply an alcohol compress.
Results
- DTP vaccination is necessary in most cases, but each parent can refuse it.
- DPT is the most difficult vaccine to tolerate.
- Before all vaccinations, the child must be absolutely healthy and not have any allergies.
- Side effects and complications after DTP are local and general. The most difficult complications are allergic reactions.
- You can help your baby ease the symptoms that appeared after vaccination by giving a massage, applying lotions or anointing with a special ointment. But such actions should be performed only on the recommendation of a doctor and only under his supervision.
- The first three DPT vaccinations provide immunity support for the first year. Further revaccination at one and a half years of age ensures immunity to these diseases (whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus) for 6-8 years.
Video
Watch the report about a serious case of post-vaccination complications - seizures and what happened next:
It can be dangerous or not dangerous. Fever or redness, for example, are not considered a cause for concern. But there are also manifestations of reactions that require medical attention. Read about them in our separate article.
Do you know how the polio vaccine can be dangerous? This is one of those vaccines that is given to all children at a very early age.
And we will tell you about the test for the tuberculosis bacillus, the so-called Mantoux reaction and its norm.
Did you like this article?
Tell your friends! Like us using the floating button bar on the left. You will support our work and tell your friends on your favorite social network about this useful article.
We have new materials coming out almost every day! To stay updated, subscribe to our RSS feed or follow us on social networks.
Graft is an immunobiological drug that is introduced into the body with the aim of forming stable immunity to certain, potentially dangerous infectious diseases. It is precisely because of their properties and purpose that vaccinations can cause certain reactions from the body. The entire set of such reactions is divided into two categories:1. Post-vaccination reactions (PVR).
2. Post-vaccination complications (PVC).
Post-vaccination reactions represent various changes in the child’s condition that develop after administration vaccines, and go away on their own within a short period of time. Changes in the body that qualify as post-vaccination reactions are unstable, purely functional, do not pose a threat and do not lead to permanent impairment of health.
Post-vaccination complications are permanent changes in the human body that occurred after the introduction of vaccination. In this case, the violations are long-term, significantly exceed the physiological norm and entail various problems with human health. Let's take a closer look at the possible complications of vaccinations.
Post-vaccination complications can be toxic (unusually strong), allergic, with symptoms of disorders of the nervous system and rare forms. A post-vaccination complication should be distinguished from the complicated course of the post-vaccination period, when various pathologies are identified that occur simultaneously with the vaccination, but are in no way connected with it.
Complications after vaccinations in children
Each vaccination can cause its own version of complications. But there are also complications common to all vaccines that children can develop. These include the following conditions:- anaphylactic shock, which develops within 24 hours after the vaccine is administered;
- allergic reactions involving the entire body - Quincke's edema, Steven-Johnson syndrome, Lyell's syndrome, etc.;
- serum sickness;
- meningitis;
- neuritis;
- polyneuritis – Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- convulsions that develop against the background of low body temperature - less than 38.5 o C, which are recorded throughout the year after vaccination;
- sensory disturbance;
- vaccine-associated polio;
- thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- hypoplastic;
- collagenoses;
- decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood;
- abscess or ulcer at the injection site;
- lymphadenitis – inflammation of the lymphatic ducts;
- Osteitis – inflammation of the bones;
- keloid scar;
- baby screaming for at least 3 hours straight;
- sudden death.
Complications and side effects of vaccinations in children - video
Main causes of complications after vaccination
Complications after vaccination can be caused by one of the following reasons:- administration of the vaccine if there are contraindications;
- improper vaccination;
- poor quality of the vaccine product;
- individual properties and reactions of the human body.
That is why the basis for the prevention of vaccination complications is the careful identification of contraindications, adherence to the technique of using vaccines, quality control of drugs, compliance with the rules of their storage, transportation and transportation. Poor quality vaccines are not necessarily inherent in them initially. The pharmaceutical plant could produce normal, high-quality drugs. But they were transported and then stored incorrectly, as a result of which they acquired negative properties.
Complications after vaccination with DTP, ADS-m
 DPT vaccination is done to create immunity to whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus. In this case, K is a component against whooping cough, AD is against diphtheria, AC is against tetanus. There are also similar vaccines: Tetracok and Infanrix. The vaccine is given to children, three doses are administered, and the fourth one a year after the third. Then children are revaccinated only against diphtheria and tetanus at the age of 6–7, and at 14 years old with the ADS-m vaccine.
DPT vaccination is done to create immunity to whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus. In this case, K is a component against whooping cough, AD is against diphtheria, AC is against tetanus. There are also similar vaccines: Tetracok and Infanrix. The vaccine is given to children, three doses are administered, and the fourth one a year after the third. Then children are revaccinated only against diphtheria and tetanus at the age of 6–7, and at 14 years old with the ADS-m vaccine. The DTP vaccine provokes the formation of various complications in 1 child per 15,000 - 50,000 vaccinated. And the Infanrix vaccine has a significantly lower risk of complications - only 1 child per 100,000 - 2,500,000 vaccinated. The ADS-m vaccine almost never leads to complications, since it lacks the most reactogenic pertussis component.
All complications from the DTP vaccine are usually divided into local and systemic. The table shows all possible complications of DTP and ADS-m and the time of their development after vaccination:
| Type of complications DPT, ADS-m | Type of complications | Type of complications |
| Significant enlargement and hardening at the injection site | Local | 24 – 48 hours |
| Swelling of the injection site greater than 8 cm in diameter | Local | 24 – 48 hours |
| Allergy | Local | 24 – 48 hours |
| Skin redness | Local | 24 – 48 hours |
| Screaming continuously for 3 or more hours | Systemic | Up to two days |
| Increase in body temperature above 39.0 o C | Systemic | Up to 72 hours |
| Febrile seizures (at a temperature of 38.0 o C and above) | Systemic | 24 – 72 hours |
| Afebrile seizures (at normal temperature) | Systemic | 1 year after vaccination |
| Anaphylactic shock | Systemic | Up to 24 hours |
| Lymphadenopathy | Systemic | Up to 7 days |
| Headaches | Systemic | Up to 48 hours |
| Irritability | Systemic | Up to 48 hours |
| Digestive disorder | Systemic | Up to 72 hours |
| Severe allergic reactions (Quincke's edema, urticaria, etc.) | Systemic | Up to 72 hours |
| Reduced blood pressure and muscle tone | Systemic | Up to 72 hours |
| Loss of consciousness | Systemic | Up to 72 hours |
| Meningitis or encephalitis | Systemic | Up to 1 month |
| Sensory impairment | Systemic | Up to 1 month |
| Polyradiculoneuritis | Systemic | Up to 1 month |
| Decreased platelet count | Systemic | Up to 1 month |
Local complications of DPT and DPT-m vaccinations usually resolve on their own within a few days. To alleviate the child’s condition, you can lubricate the injection site with Troxevasin ointment. If the baby develops complications after DPT vaccination, then the next time only anti-diphtheria and anti-tetanus components are administered, without whooping cough, since it is this that provokes most of the complications.
Complications after tetanus vaccination
 Tetanus vaccination can lead to the development of the following complications within the specified time frame:
Tetanus vaccination can lead to the development of the following complications within the specified time frame: - increase in body temperature for 3 days;
- redness at the injection site – up to 2 days;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes – up to a week;
- sleep disturbance – up to 2 days;
- – up to 2 days;
- digestive and appetite disorders – up to 3 days;
- allergic rash;
- long, incessant screaming – up to 3 days;
- convulsions due to elevated temperature – up to 3 days;
- meningitis or encephalitis – up to 1 month;
- auditory and optic nerve – up to 1 month.
Complications after diphtheria vaccination
Vaccination only against diphtheria is not very reactogenic, so it is relatively easily tolerated. Complications can develop in the form of anaphylactic shock at the injection site, pain at the injection site and the entire limb as a whole, and neurological disorders.Complications after vaccination Pentaxim
 The Pentaxim vaccine is a combination vaccine, it is administered against five diseases - diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio and Hib infection, which is caused by Haemophilus influenzae. According to observations of children who received all 4 doses of the Pentaxim vaccine, complications developed in only 0.6%. These complications required qualified medical care, but not a single death was recorded. Since Pentaxim contains a component against polio, there is no risk of this disease, but it does occur when using the oral vaccine.
The Pentaxim vaccine is a combination vaccine, it is administered against five diseases - diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio and Hib infection, which is caused by Haemophilus influenzae. According to observations of children who received all 4 doses of the Pentaxim vaccine, complications developed in only 0.6%. These complications required qualified medical care, but not a single death was recorded. Since Pentaxim contains a component against polio, there is no risk of this disease, but it does occur when using the oral vaccine. Pentaxim, despite its five components, rarely causes reactions and complications, which mainly manifest themselves in the form of high fever, irritability, prolonged crying, thickening and a lump at the injection site. In rare cases, seizures, mild neurological symptoms, digestive disorders, and severe pain at the injection site and the entire limb may develop. The most severe reaction usually occurs on the second dose, while the first and third are easier.
Complications after hepatitis B vaccination
Vaccination against B can cause the following complications, which develop within the specified time frame:- Increase in body temperature – up to 3 days.
- Severe reaction at the site of vaccine administration (pain, swelling more than 5 cm, redness more than 8 cm, induration more than 2 cm) – up to 2 days.
- generalized BCG infection – after 2-18 months;
- osteomyelitis – after 2-18 months;
- osteitis – after 2-18 months;
- inflammation of the lymphatic ducts – after 2 – 6 months.
Complications after BCG vaccination
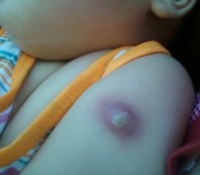 It is necessary to understand that BCG is given not with the goal of making the body immune to tuberculosis, but to reduce the severity of the disease in case of infection. This is especially true for children under 1 year of age, in whom tuberculosis infection does not affect the lungs, but results in generalized blood poisoning or meningitis. However, BCG itself is a low-reactogenic vaccine, which can provoke a rise in temperature within 2 days, an abscess under the skin at the injection site or more than 1 cm after 1.5 - 6 months, as well as a keloid scar after 6 - 12 months. In addition, the following are registered as complications of BCG:
It is necessary to understand that BCG is given not with the goal of making the body immune to tuberculosis, but to reduce the severity of the disease in case of infection. This is especially true for children under 1 year of age, in whom tuberculosis infection does not affect the lungs, but results in generalized blood poisoning or meningitis. However, BCG itself is a low-reactogenic vaccine, which can provoke a rise in temperature within 2 days, an abscess under the skin at the injection site or more than 1 cm after 1.5 - 6 months, as well as a keloid scar after 6 - 12 months. In addition, the following are registered as complications of BCG: Complications after flu vaccination
Vaccines against domestic and imported production are available in Russia, and they all have approximately the same properties and can cause similar complications. In general, the flu vaccine is extremely rarely accompanied by complications, the spectrum of which is very narrow. Most often, complications appear in the form of allergies, especially in people who have allergies to the drug Neomycin or chicken egg white. Several cases of hemorrhagic vasculitis have been reported, but the connection between this pathology and the influenza vaccine has not been established for certain.Complications after vaccination against chickenpox, measles, rubella, combined
MMR and Priorix vaccines
Priorix is a combination vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella. Vaccinations against these infections cause almost identical reactions and complications. Thus, a rise in temperature can be observed only on days 4–15 after vaccination, and a strong local reaction is observed in the first two days, and is expressed in the formation of severe swelling of more than 5 cm, redness of more than 8 cm, and thickening of more than 2 cm. In addition, vaccinations against chickenpox, measles, rubella and combined MMR can cause the following complications in the appropriate time frame: – from 4 to 15 days.
Complications after rabies vaccination
Rabies vaccination very rarely provokes the development of complications, and they are mainly manifested by allergies, especially in people suffering from reactions to chicken egg white. Neurological symptoms were also noted, such as neuralgia, attacks of dizziness, neuropathy, which, however, after a short period of time pass independently and without a trace.Complications after the Mantoux test
 Mantoux is a biological test that is necessary to detect whether a child is infected with the pathogen - Koch's bacillus. The Mantoux test is used in children instead of fluorography, which is done for adults. As complications, the Mantoux test may be accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes and ducts, as well as malaise, headache, weakness or fever. The severity of reactions to the Mantoux test depends on individual characteristics human body. For example, some children have severe arm pain or vomiting.
Mantoux is a biological test that is necessary to detect whether a child is infected with the pathogen - Koch's bacillus. The Mantoux test is used in children instead of fluorography, which is done for adults. As complications, the Mantoux test may be accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes and ducts, as well as malaise, headache, weakness or fever. The severity of reactions to the Mantoux test depends on individual characteristics human body. For example, some children have severe arm pain or vomiting. Statistics of complications after vaccinations
Today in Russia, official recording and control over the number of complications as a result of vaccination has been carried out only since 1998. Such work is carried out by national specialized scientific institutes and experts from the World Health Organization, but they are able to study the situation only in a limited number of settlements, mainly in large cities. According to US statistics, every year 50 children suffer from severe neurological symptoms and central nervous system dysfunction as a result of vaccination complications. The table shows various severe post-vaccination complications from various vaccinations according to the World Health Organization:| Vaccine | Complication | Frequency of development complications |
| BCG | Inflammation of lymph vessels | 1 in 1000 – 10,000 |
| Osteitis | 1 in 3000 – 100,000,000 | |
| Generalized BCG infection | 1 in 1000,000 | |
| Hepatitis B | Anaphylactic shock | 1 in 600,000 – 900,000 |
| Measles, mumps, rubella | Cramps due to fever | 1 in 3000 |
| Decreased platelet count in the blood | 1 in 30,000 | |
| Severe allergies | 1 in 100,000 | |
| Anaphylactic shock | 1 in 1000,000 | |
| Encephalopathy | Less than 1 in 1,000,000 | |
| Oral vaccine against polio (mouth drops) | Vaccine-associated polio | 1 in 2000,000 |
| Tetanus | Brachial neuritis | 1 in 100,000 |
| Anaphylactic shock | 1 in 100,000 | |
| DTP | Long continuous scream | 1 in 1000 |
| Convulsions | 1 per 1750 – 12500 | |
| Decreased blood pressure, muscle tone, loss of consciousness | 1 in 1000 – 33,000 | |
| Anaphylactic shock | 1 in 50,000 | |
| Encephalopathy | 1 in 1000,000 |
The variation in frequent complications is caused by differences in different countries. A greater number of complications are due to neglect of vaccination rules, ignoring contraindications, improper storage and transportation of vaccines, the use of spoiled batches of drugs and other similar factors.
March 20, 2012, 10:40 pm
Girls, yesterday I wrote a post about the fact that I received DTP, information about DTP was sent to my wild child, read it, maybe someone will find it useful. DTP vaccination or inhibition of children's development DTP is the most terrible of vaccines. An explosive mixture of diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus cells. And this miracle vaccine is injected into the baby’s body four times, starting from the age of three months. This is a very painful vaccination, and some children react to it with a long continuous scream. DTP causes the greatest number of complications and a greater percentage of the risk of allergic reactions in the child’s body. This vaccine is responsible for numerous child deaths, lawsuits, and it was banned many times in European countries, but not in Russia. Japan and Europe abandoned DPT By the early seventies, 37 children died from DTP vaccination in Japan. The Japanese stopped giving this vaccination to their children, then moved it from infant to 2nd age summer age. As a result, Japan dropped from 17th place in the world in child mortality to last place. In the 1980s, they began to vaccinate against whooping cough with a new acellular vaccine, which led to a fourfold increase in sudden infant death syndrome over the next 10-12 years. A similar situation occurred in England, Germany, and Holland. Vaccinations against whooping cough killed and disabled dozens of children, after which the population began to refuse this vaccination. With a decrease in vaccination coverage, the number of visits to hospitals sharply decreased, and where vaccination was not abandoned, there was an increase in the number of diseases, that is, vaccination did not save us from the epidemic. What does this mean? The fact that the DPT vaccine is deadly harmful, and at best, simply useless, and remains in the vaccination calendar for some reason that is beneficial only to him, and not in the interests of people. This vaccine is poisonous. DTP is not even called a vaccine, but a chemical and biological conglomerate that contains many chemical components that are harmful to human health, causing irreversible changes in the nervous system, affecting kidney and brain cells, causing cancer when ingested. All these components make the DTP vaccine the most dangerous vaccine, which leads to autism and paralysis in children. Not many people know about this, and they have no idea about the danger until they themselves encounter trouble. In addition to whole whooping cough cells, what makes this drug terribly dangerous is the organomercury pesticide called merthiolate or thiomersal, which is used as a preservative, and formaldehyde - all these poisons are present in the dose of the vaccine in quantities sufficient to poison the body little man! Merthiolate in our country is not considered a medicine; it has not been properly tested; its use in a vaccine was approved based only on the results of testing on five guinea pigs, which were given one dose each. During vaccinations, a child is given a dose five times larger! Merthiolate is not excreted from the body, accumulates in the nervous tissue, and in combination with aluminum hydroxide its toxicity increases tenfold! It is not difficult to guess that aluminum hydroxide is also contained in the dose of DPT. Merthiolate is a technical pesticide that Europe not only does not consider a medicine, but also refused to even produce this poison on its territory. But in our country it is successfully used in a vaccine, and our Ministry of Health is not even going to conduct research on the dangers of this drug! Benefit or risk? According to data recognized by the World Health Organization, DTP vaccination causes persistent brain damage, various neurological seizures, and even death (5 deaths per million population). In the 70s, Swedish scientists proved a direct connection with the introduction of the whole-cell DPT vaccine and encephalopathies (convulsions). Scientists have decided that the benefits of vaccination are not worth the risks. Despite the ban on use in many countries, the United States continues to produce and sell DTP containing whole-cell pertussis to third world countries, while within their own country the Americans have abandoned this form of the vaccine. And the trouble is that no one can ever say in advance whether this vaccination will cause some kind of complication in this particular child, or whether everything will go well. Doctors reassure that this is a safe vaccination, complications are extremely rare, and most often all this is not discussed either before or after vaccination, only if an accident happens to the child. But even in this case, they will tell you that vaccination has nothing to do with it, and it will be difficult to prove that the diseases that appear are related to the vaccination. Please note what complications this vaccine can cause: huge purulent tumors on the skin that have to be opened, damage to the central nervous system, joints, gastrointestinal tract, heart, various allergic reactions, asthma, diabetes, awakening of hidden diseases - tuberculosis, hepatitis; anaphylastic shock, sudden death. Vaccination during an epidemic of other diseases can be fatal! So, is it worth it, fearing a whooping cough epidemic in advance, to agree to introduce such a dangerous dose of pathogenic cells and toxic substances into the child’s body, thereby greatly increasing the risk that the child will then become disabled or, even worse, die? Or maybe it’s worth finding alternative ways to preserve the child’s health and strengthen his immunity? Parents have the right to refuse vaccination or agree, but in any case, it is worth first obtaining complete information from reliable sources, which, fortunately, are already available to everyone today. But now the question is: how not to do it? After all, it is necessary!!! It's better to be insured!!! We now have children in the city who have fallen ill with whooping cough, we had never heard of this disease before, but now they have begun to appear, I am a mother of 3 children, two daughters, I received DTP, I just don’t deny the heavy vaccination. Your opinion is it worth it or not to do it? ??



