In the 5th century BC e. Latin (self-name Lingua Latina) was one of the many Italic languages spoken in central Italy. Latin was used in the area known as Latium (modern name is Latium), and Rome was one of the cities in this area. The earliest inscriptions in Latin date back to the 6th century. BC e. and are made using an alphabet based on the Etruscan script.
Gradually, Rome's influence spread to other parts of Italy, and through them to Europe. Over time, the Roman Empire conquered Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. Throughout the empire, Latin came to be used as the language of law and authority, and, increasingly, as the language of everyday life. The Romans were literate, and many of them read the works of famous Latin authors.
Meanwhile, in the eastern Mediterranean, Greek remained the lingua franca, and educated Romans were bilingual. The earliest examples of Latin literature known to us are translations of Greek plays and Cato's agricultural manual into Latin, dating back to 150 BC. e.
Classical Latin, which was used in early works of Latin literature, differed in many ways from colloquial, so-called Vulgar Latin. However, some writers, including Cicero and Petronius, used Vulgar Latin in their writings. Over time, the spoken variants of the Latin language moved further and further away from the literary standard, and gradually, on their basis, Italic/Romance languages (Spanish, Portuguese, etc.) appeared.
Even after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in 476, Latin continued to be used as a literary language in Western and Central Europe. A huge amount of medieval Latin literature appeared in a variety of styles - from scientific works of Irish and Anglo-Saxon writers to simple tales and sermons intended for the general public.
Throughout the 15th century. Latin began to lose its dominant position and title as the main language of science and religion in Europe. It has been largely replaced by written versions of local European languages, many of which are derived from or influenced by Latin.
Modern Latin was used by the Roman Catholic Church until the mid-20th century, and currently continues to exist to some extent, especially in the Vatican, where it is recognized as one of the official languages. Latin terminology is actively used by biologists, paleontologists and other scientists to name species and preparations, as well as by doctors and lawyers.
Latin alphabet
The Romans used only 23 letters to write Latin:
Didn't exist in Latin lowercase letters. The letters I and V could be used as consonants and vowels. The letters K, X, Y and Z were used only to write words of Greek origin.
The letters J, U and W were added to the alphabet later to write languages other than Latin.
The letter J is a variant of I and was first introduced into use by Pierre de la Ramais in the 16th century.
The letter U is a variant of V. In Latin, the sound /u/ was represented by the letter v, for example IVLIVS (Julius).
The letter W was originally a double v (vv) and was first used by Old English scribes in the 7th century, although the runic letter Wynn (Ƿ) was more commonly used to represent the /w/ sound in writing. After the Norman Conquest, the letter W became more popular and by 1300 had completely replaced the letter Wynn.
Reconstructed phonetic transcription of classical Latin
Vowels and diphthongs
Consonants
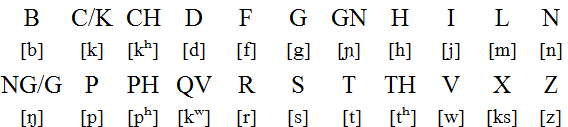
Notes
- Vowel length was not shown in writing, although modern editions of classical texts use a macron (ā) to indicate long vowels.
- The pronunciation of short vowels in the medial position is different: E [ɛ], O [ɔ], I [ɪ] and V [ʊ].
Phonetic transcription of ecclesiastical Latin
Vowels
Diphthongs
Consonants

Notes
- Double vowels are pronounced separately
- C = [ʧ] before ae, oe, e, i or y, and [k] in any other positions
- G = [ʤ] before ae, oe, e, i or y, and [g] in any other positions
- H is not pronounced except in words mihi And nihil, where the sound /k/ is pronounced
- S = [z] between vowels
- SC = [ʃ] before ae, oe, e, i or y, and in any other positions
- TI = before the vowel a and after all letters except s, t or x, and in any other positions
- U = [w] after q
- V = [v] at the beginning of a syllable
- Z = at the beginning of a word before vowels, and before consonants or at the end of a word.
The long-ago Latin spoken by the Romans has left behind an indelible mark. We are talking about all European languages, which are divided into Romance and Germanic. As for the Slavic peoples, a fundamentally new writing was developed especially for them, in which echoes of Europe and the Balkans could be traced. Thus, the main alphabets among the Slavic-European peoples became the Cyrillic and Latin alphabets, which we still use today.
Origin of languages
The sources by which one can calculate the birth of a particular language are very vague. To this day, ancient linguistics and etymology constitute one of the greatest challenges for researchers. However, the Cyrillic and Latin alphabets are an exception, since the origin of these alphabets is more or less clear.
Latin
We will start with the language that was spoken in Ancient Rome, and which today, although dead, is widely used in medicine, history and philology. The prototype of Latin was the Etruscan unwritten language, which existed mainly in oral form and was used among the tribes of the same name inhabiting the center of modern Italy.
The new Roman civilization systematized all the dialects and developments of its ancestors, forming a full-fledged latin alphabet. It consisted of 21 letters: A B C D E F H I K L M N O P Q R S T V X Z. After the collapse of the Roman Empire, Latin spread widely throughout Europe and assimilated into various tribal languages (Celtic, Welsh, Gothic, etc.).
This is how the languages of the Romance-Germanic group appeared - French, Italian, German, English and many others. Today, a single alphabet consisting of 26 letters is used to write them.

Old Church Slavonic
For the Slavic peoples, Latin was alien and unacceptable. But given the fact that some lands were subject to papal authority, while others adopted Orthodox Christianity, it was necessary to teach people the Holy Word. The Greek brothers Cyril and Methodius created an alphabet of 43 letters, which became understandable to the Slavic people.
It was named after his older brother Cyril, and it became the basis for the new Old Church Slavonic language. Later, the number of letters was reduced, and the language itself spread over very vast territories. Of course, it underwent changes due to various dialects, and as a result it split into many independent languages. This alphabet became the basis for Eastern European, Southern European and Russian scriptures.
Modern international writing systems
Nowadays, the Cyrillic and Latin alphabet are used to exchange information internationally, even in eastern countries. These are two universal alphabets that have similar structure and symbols, and they are also able to replace each other. But it is worth noting that each of them has its own advantages.
Undoubtedly, the Latin alphabet is more common on the globe. With its help, many Chinese and Japanese words are written, it is widely used in banking documents (even in Russia) for recording personal data. But any linguist will tell you for sure that the Cyrillic alphabet is a much richer and more convenient alphabet due to the fact that its symbols convey a greater range of sounds.

"Alphabet" reforms
Replacing the Cyrillic alphabet with the Latin alphabet is a very important issue that has repeatedly arisen in many Slavic states. For the first time, Latin writing replaced Slavic in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Principality of Lithuania. Until now, Lithuania and Poland, despite the Slavic roots of their languages, use the Latin alphabet.
The translation from Cyrillic to Latin also affected South European countries. For example, Romania, which used the Cyrillic script, adopted the Latin alphabet in the 19th century. They did the same in Montenegro, Serbia and the Czech Republic.
What Russia went through
On the territory of our state, the Cyrillic and Latin alphabet have repeatedly fought for a place in the sun. Undoubtedly, the Cyrillic script was native to the Russian people, but repeated attempts to Catholicize the country suggested abandoning it and introducing the Latin alphabet as the basis of written speech.
First from Slavic alphabet Peter the Great wanted to refuse. He even carried out a language reform, throwing out many letters from the alphabet and replacing some of them with European ones. But later he abandoned this idea, returning everything to its place.

The second attempt to Latinize Russian society occurred after the revolution. At that time, Lenin carried out a unification reform. European units of measurement were adopted, a transition to the European calendar took place, and it was assumed that the language would also be translated.
Linguists have done a tremendous amount of work to change all Russian sources that were written in Cyrillic. But Stalin, who soon came to power, realized that the idea was devoid of common sense, and returned everything to normal.
Latin and Cyrillic: the difference
It is impossible not to notice that these two alphabets are incredibly similar to each other. They even contain absolutely identical letters: A, B, E, K, M, N, O, R, S, T, U, X. But as was rightly noted above, the functionality of the Cyrillic alphabet is much wider. Due to letters such as “Ш” or “Ш”, for example, a sound is transmitted, which is written in Latin using two, three or four characters.
It is worth mentioning separately about the letters “S” and “K”, which in our writing are strictly distinguished by sound. And in groups, their transcription depends on the vowel in front. Well, the most important thing that distinguishes the Latin alphabet from the Cyrillic alphabet is that each sound has a corresponding letter.
The combination of letters in a word does not affect their sound, doubling consonants are pronounced clearly, there are no silent vowels or silent syllables.
The idea of translating all languages into Latin script was repeatedly put forward. The letter Z was removed from the alphabet in 312 BC. e. (later it was restored). In the Middle Ages, the Scandinavian and English alphabets used the runic letter þ (name: thorn) for the th sound (as in modern English the), but this later fell into disuse. At about the same time, but only in northern Europe, the digraph VV, which arose in the 11th century and was used in writing Germanic languages, began to be considered a separate letter.
The oldest discovered Latin inscriptions date back to the 7th century BC. e. The direction of writing in archaic inscriptions could be either left to right or right to left. According to one hypothesis, the Latin language borrowed alphabetic letter from Greek directly, according to another version, the Etruscan alphabet turned out to be a kind of intermediary in this.
The letters Θ, Φ and Ψ were not used to write words, but were used as symbols for the numbers 100, 1000 and 50. These functions were subsequently transferred to the letters C, M and L, respectively (see Roman numerals). The Latin script for epigraphic monuments is also called monumental, square or lapidary.
Latin alphabet
Epigraphists sometimes distinguish another type of Latin script - actuarial, used for documents (acts). Special view Latin writing arose in the 3rd century in North Africa - the so-called uncial (that is, “hooked”) letter. This alphabet coincides with the modern one English alphabet. During the Middle Ages, Latin writing shortened commonly used prefixes, suffixes, and even roots of words using ligatures and special characters, some of which are still used today.
what are latin letters?
Most artificial languages are based on the Latin alphabet, in particular Esperanto, Interlingua, Ido and others. For example, sometimes in Russian text Japanese names are written in Latin, although for the Japanese language there are generally accepted rules for transliteration into the Cyrillic alphabet.

Pronunciation of Latin letters
The Latin alphabet is used throughout the world to romanize languages that use non-Latin alphabets in order to simplify communication. Most languages with non-Latin alphabets have official transliteration rules based on the Latin alphabet.
Attempts to use the Latin alphabet in records in Russian were noted back in the 1680s - 1690s. The modern Latin alphabet, which is the basis for writing Germanic, Romance and many other languages, consists of 26 letters. Letters in different languages are called differently.
The Latin alphabet comes from the Etruscan alphabet, based, in turn, on one of the variants of the Western (South Italian) Greek alphabet. In a number of countries, the Latin auxiliary letter is standardized and children study it at school (in Japan, China). On the other hand, in texts in a non-Latin alphabet, foreign names are often left in Latin due to the lack of a generally accepted and easily recognizable spelling in their system.
The Russian language uses the Cyrillic script for writing, and it is also used by some other Slavic peoples, such as the Bulgarians and Serbs. But, more than half of European languages use the Latin alphabet for writing.

Where are Latin letters and numbers currently used?
But both language and writing are always the result of centuries of work by the people. Nomadic tribes and warring parties had no need for writing. Probably, it was in one of these moments of calm that the ancient Phoenicians began to think about how to graphically display the necessary information.
Latin language (Latin)
But Greek civilization fell under the onslaught of the Roman conquerors, who received the alphabet and writing as trophies. Many of these fonts are still used for decorative purposes. This is exactly how the evolution of writing took place, introducing new signs, styles, and methods of writing. Many people wonder: “ Latin letters“What are these?” In fact, everything is extremely simple. In essence, the Latin alphabet is the alphabetic characters of modern English language. The only difference is the pronunciation.

You don’t have to look far for an example; just take out your foreign passport and look at it. Under the surname written in Russian, you will definitely see its Latin version. Speaking about the Latin alphabet, it is difficult not to mention the influence Greek language, since he made a huge contribution to the development of modern Latin spelling.
All words written in it are read not only from right to left and vice versa, but, what is most interesting, the characters can also be read diagonally. Very often, when submitting documents such as visas, you are required to indicate your personal data using exclusively the Latin alphabet, the letters of which must correspond as closely as possible to Russian.
The letter C was used to represent the sounds [k] and [g]; in 234 BC e. a separate letter G was created by adding a crossbar to the C. This standard 26-letter alphabet is documented by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as the "Basic Latin Alphabet".



