After birth, up to six months, the baby's food will be the mother's breast milk or, if not available, infant formula. To track the development of the child, pediatricians weigh him every month and measure the same parameters as the neonatologist at birth - height, skull volume and chest volume.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has set standards for infant weight gain, but practice shows that each child is special and develops at his own pace - not all children grow "correctly". We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the weight gain table, which presents the weight of newborns by month.
Table of weight gain and growth of a child up to a year
| Month | Weight gain/month in grams | Increase in growth / month. in centimeters |
| 1 | 600 | 3 |
| 2 | 800 | 3 |
| 3 | 800 | 2,5 |
| 4 | 750 | 2,5 |
| 5 | 700 | 2 |
| 6 | 650 | 2 |
| 7 | 600 | 2 |
| 8 | 550 | 2 |
| 9 | 500 | 1,5 |
| 10 | 450 | 1,5 |
| 11 | 400 | 1,5 |
| 12 | 350 | 1,5 |
When discharged from the maternity hospital, the mother receives a form in which the very first information about the child is recorded, and most importantly, its weight. Later, the pediatrician will be guided by this value in the future. A newborn in the first days of life loses 10% of its weight. This happens because during childbirth he experiences severe stress, and then in a short time he is forced to adapt to new conditions. All this leads to the loss of calories and the rapid burning of fat mass gained in utero. In addition, immediately after the birth of the mother, the precursor of milk, colostrum, is secreted from the breast. It is still too little, because the baby, although it receives the necessary nutrients to activate digestion, does not receive enough carbohydrates. Transient states of newborns may appear, which are characterized by a physiological loss of body weight.
The day of discharge comes, the baby has already begun to adapt to the new world, the first vaccinations have been made, the weight has stabilized and has ceased to decrease. The weight at discharge, of course, will also be recorded on the form, which will be given to the mother in her arms. By this day, the mother already has milk, and the baby sucks it with appetite every three hours and gradually gains weight. So that the milk does not stagnate, the mother must always express it completely. In order for the milk to have the desired fat content, the mother needs to eat more meat products - in this case, the baby will gain weight even faster.
The child may be born ahead of time and underweight. Doctors can put him in an incubator for control, and at discharge recommend special mixtures to his mother that will help the baby gain weight faster. For the first month every week, the pediatrician will come to the child's home to once again not expose him to the danger of contracting diseases, and examine him, at the same time controlling his weight.
Previously, we gave a weight gain table approved by WHO. The doctor is guided by this table, determining the correct weight gain, and will let parents know if the child gains too much or vice versa, does not gain enough.
The kid has not yet learned to speak, therefore he cannot report his poor health or lack of appetite in any way. While the mother is breastfeeding, there is no way to measure, except with the help of scales, how much milk he drinks and whether he is full at the same time. As already mentioned, mom needs to eat well so that the milk is nutritious, but good does not mean fat. Foods that are too high in fat can cause diarrhea in a child, and this will lead to weight loss. That's right, if mom eats a lot of boiled lean meat, lean fish, you can also buckwheat and rice groats. A couple of weeks after returning home from the hospital, it will already be clear for sure whether the child eats well and whether it is necessary to supplement him with the mixture.

The child who is on artificial feeding may gain weight more slowly. It is easier for mom to control how much the baby eats and, if necessary, switch to a more nutritious mixture. At the same time, the diet of the mother does not affect the child in any way. The method of preparation is indicated on the packaging of each mixture, and inside each pack there must be a measuring spoon. Be sure to boil the bottle and nipple before making the mixture. Remember to watch your baby's reaction to formula very carefully, as some babies may be allergic to ingredients in the formula. In this case, you need to consult a doctor, and together with him choose the right mixture for your child.
What can affect the rate of weight gain
There are factors that affect weight gain in infants, these include:
- Features of genetics- just look at the parents to understand what the physique of the child should be. If parents have a naturally accelerated metabolism, then the child will gain weight slowly.
- Bad habits of parents- if there are smokers in the house where the child grows up or the mother drank alcohol during pregnancy, the child will be born small and will slowly gain weight, in addition, there may be developmental delays.
- Mom's stress and illness- If during pregnancy the mother was often nervous or very ill, the child may be born weak and slowly gain weight. The same applies to changes in the hormonal background in the body of a pregnant woman. Some medications can affect weight gain or make it jumpy. In this case, immediately consult an endocrinologist. If a mother is sick while breastfeeding, the effectiveness of lactation may decrease, which will not affect the baby's weight in the best way. With a deterioration in the quality of milk, the baby may even lose his appetite.
- gender- girls gain weight less intensively, although there are exceptions.

- Appetite and activity level Every child has their own habits and appetite from birth. There are kids who love to eat tightly, and there are those who will eat a little, but often. In the second case, the weight is added more slowly. When the baby grows up, learns to roll over, sit, crawl and walk, a lot of calories will go away during the games, because weight gain will slow down. Babies who are still lying on their backs, but are already receiving a massage, also gain weight more slowly.
- Weight at birth Babies who are born underweight will gain weight more slowly and vice versa.
- Type of feeding- provided by nature breastfeeding the baby quickly recovers, does not get sick and does not suffer from colic. Breast milk is always the first freshness, the right temperature and completely sterile. In addition, when breastfeeding, the baby is applied to the breast on demand, and not on a schedule. In the second case, it may be that the baby is not yet hungry enough and therefore will eat little, hence the underweight.

The most important thing to know is that every child develops according to their own individual scenario. This means that slight fluctuations in weight should not be a cause for concern and a visit to the doctor. You should not immediately change the mixture if the child gained 300 grams less than last month.
If suddenly your baby stopped gaining weight or suddenly doubled in weight at once - this is already serious and requires an early visit to the doctor. Thinness is always easier to fix than obesity, so in no case do not overfeed the baby. No child will deliberately starve himself, so if he does not want to eat, in any case, do not shove food into him.
Look at your little one. Is he cheerful? Is he actively playing with you? Turns around in his name and pulls his hands? Then he's all right. All WHO standards remain guidelines that should be guided by, but not strictly adhered to.
Good afternoon, my dear readers - moms and dads! You just had a baby, I congratulate you on this! Exciting moments, joy, anxiety and uncertainty - all in one. For some time these feelings will prevail over you, but still you need to tune in to new way and life will take its course. Along with thousands of questions, in the head of young parents there is an urgent question about how much a newborn should normally weigh and how soon he should gain weight and height. The classic table of newborn weight gain by months will help you with this.
Girls and boys are usually born in different weight categories: boys tend to be slightly larger. However, how much should a newborn weigh?
The weight of a baby at birth depends on the following factors:
- Gender of the child;
- Date of birth;
- The composition of the parents;
- Mom's nutrition during pregnancy;
- The presence of fetal pathologies or problems with the passage of pregnancy;
- The presence bad habits mother during pregnancy.
A healthy full-term boy weighs normally (on average) - 3.5-3.7 kg. Girl, respectively 3.2-3.5 kg.
In the maternity hospital, a newborn is weighed two control times - immediately at birth and at discharge.
This is done in order to compare how much the baby will lose in weight over these few days. And there will certainly be losses.
2. Why does the baby lose weight after birth?
Physiological weight loss of a newborn is a normal phenomenon, in no case should you be afraid of this.
Natural weight loss in a newborn comes from:
- Natural fluid loss through the skin;
- Sudden change in diet;
- The amount of food in the first days;
- Stress due to environmental change.
After the birth of a child, a shock occurs, a real stress, and this is understandable. This shock is one of the reasons for the slight weight loss. Nutrition also becomes new for the baby, the umbilical cord no longer supplies him with all the necessary substances, you have to “get” food on your own, which are still so fragile.
In the first three days, the mother adjusts lactation, colostrum begins to stand out, milk will arrive later. This colostrum is not enough for the baby to eat. Despite its quantity, the nutritional properties of colostrum are about the same as those of concentrated milk, and even more.
All these factors lead to the fact that the baby in the first days of life slightly loses weight. As a rule, he makes up for this weight loss very quickly already in the first month.
When discharged from the hospital, the weight of the baby is again measured. The allowable amount of weight loss from birth to discharge from the hospital is 5-10 percent. From this, and count the weight gain by week and by month.
3. Norms of weight gain and growth of a newborn up to a year by months
Normally, in the first 4 months, the baby grows most intensively. Every month it grows by 2-3 cm, the rate of weight gain per month, on average, is 600-800 grams.
By 6 months, the baby will already weigh twice as much as it was when it was discharged from the hospital, and by the year - three times.
Do not forget that weight gain, as well as height, depends on the initial build of the newborn. An increase in a large child may not go the same way as in a small one, everything is individual.
Meanwhile, I present to you a table with averaged data on the increase in height and weight of babies up to a year by months: 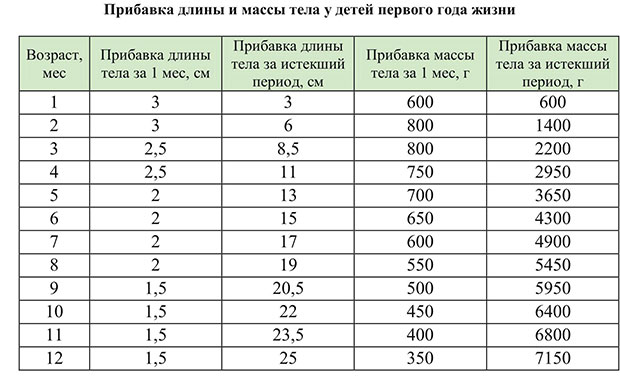
4. Factors affecting weight gain in newborns
The schedule of weight gain and growth in girls and boys is somewhat different. As a rule, girls gain more weight and height in the first month than boys. In the following months, the curve of the ratio of height / weight for both girls and boys goes smoothly and proportionally.
Weight gain in newborns is affected by:
- Type of feeding - breast or artificial;
- Feeding method - by the hour or on demand;
- milk quality;
- Baby health.
So, if the baby is artificially fed, he will gain more weight than the one that is breastfed.
Feeding on demand also results in more weight gain than timed feeding.
If the baby is healthy and adapts well to the new environment, he will develop correctly, that is, gain weight and grow within the normal range:
If the baby is underweight in the first two months, the pediatrician will draw your attention to this and may prescribe supplementary feeding.
It happens that the mother does not have enough milk, then the baby is constantly hungry and does not grow well. By choosing a supplemental formula, you can easily fix this problem.
With a critically low weight of the baby, an examination is prescribed to identify possible pathologies. After six months, weight gain and height is slower and depends on the baby's nutrition. At this time, complementary foods are introduced, so it becomes easier to regulate the amount of food that the baby receives per day:

Also, if the baby is sick, there is a lack of weight. With recovery, everything usually falls into place. Dear moms, do not worry, any deviations in weight gain or height are correctable. Most importantly, see your pediatrician and guide healthy lifestyle life.
And in this video you can see what a neonatologist says about weight gain in babies:
For today I say goodbye, do not forget to subscribe to updates and share information on social networks.
Height, body weight, head and chest circumferences are the main anthropometric measurements with which the pediatrician evaluates the physical development of the child. The norms for increasing the height and weight of the child are established by WHO. However, not all children develop according to the average. Gain in weight and height depends on many factors, including genetic characteristics, type of feeding, etc. As a rule, children who are breastfed develop more harmoniously, and children who receive milk formula often have an excess set masses. In the first three months of life, the increase is the largest, then the rate of gain in both height and weight decreases.
The growth (length of the body) of a newborn depends not only on heredity, but also on the quality of the mother's nutrition, the sex of the child, etc. The body length of newborns normally ranges from 45 to 55 cm. The growth of the baby after birth occurs according to certain patterns:
The baby grows most intensively in the first 3 months of life, "stretching", on average, by 3 cm per month.
From the 3rd to the 6th month, the baby adds 2.5 cm every month,
From the 6th to the 9th month, the increase is 1.5-2 cm per month
From the 10th to the 12th month - 1 cm per month.
During the year, the baby grows on average by 25 cm, and in a year his height is already about 75 cm.
Weight - the average weight (or weight) of a full-term newborn is 2600-4500 g. In recent decades, there has been an acceleration of biological development, and therefore babies are “getting heavier”: now the birth of 5-kilogram heroes is not uncommon.
Babies grow and gain weight "by leaps and bounds." True, this does not happen immediately:
In the first week, body weight may decrease slightly (but not more than 5-10%): the baby loses fluid, and the feeding regimen has not yet been established.
Then, during the first month, the baby becomes heavier by an average of 20 g per day.
Every day of the second month adds 25-30 g to the body weight of the baby.
By 4-5 months, the weight of the child doubles, by the year it triples.
From the age of 2 to puberty, the weight of the child increases by an average of 2 kg per year.
To assess the weight of the baby, doctors calculate the so-called due body weight using special formulas. For example, the body weight of a child in the first six months of life is determined by the formula: Body weight = body weight at birth (g) + 800*N, where N is the number of months. From the beginning of the second half of life, the rate of weight gain decreases, and the formula becomes more complicated: Body weight \u003d birth weight + 800 * 6 (weight gain in the first 6 months) + 400 * (N-6), where N is the number of months (from 6 to 12). Simplified, this formula can be reduced to the following scheme:
at 6 months, the average weight of an infant is 8200 g;
for each subsequent month, add 400 g;
and for each "extra" - subtract 800 grams.
Mass is a more dynamic indicator, in contrast to growth, and therefore the mass is “tied” to growth in order to determine the harmonious development of the child. Large babies at birth are usually heavier than their peers throughout the first year of life. The same babies, whose birth weight was less than 3300 g, from the second month of life should catch up with their peers, and, therefore, in the first month grow faster than them, i.e. add 100-300 g more than normal.
Examining the baby during the first year of life, the pediatrician measures not only height and weight, but also the circumference of the head and chest.
The newborn looks touching: a big head and a fragile little body. But this is the norm. The head circumference of a newborn is 2-5 cm larger than the circumference of the chest and is 34 cm. At the age of 3-5 months, the circumferences of the head and chest are compared, and then the chest begins to grow faster and outstrips the growth of the baby's head. If this does not happen, the doctor may suspect the presence of a pathology. When evaluating proportionality physical development child, the doctor also focuses on the data of special tables, which determine the correspondence of body weight and chest circumference to the height of the child. Most often, modern pediatricians use fairly objective centile tables. Normal performance physical development lie in the range of 25-75 centiles. If the baby's indicators fall in the range of 3-10 or 90-97, the child needs an additional examination.
Young parents are usually very sensitive to the anthropometric indicators of their child. And this is absolutely correct, because these indicators to a certain extent reflect the state of health of the child, his appetite and other features of the body. What I would like to warn parents against is independent conclusions. If in any doubt, it is best to consult your doctor. So, the features of breast augmentation are as follows.
Usually the baby adds a lot in the first three months of life, sometimes even up to 2 kg per month. The minimum increase of this period is 115 g per week, or 460 g per month.
At 4-6 months, children begin to actively learn new skills - they move a lot, try to sit down, some even try to crawl, and then infant gains are usually 400-600 g / month. In the second half of the year, the gains become even smaller: at 6-9 months - 300-500 g, and after 9 months, when many begin to walk, it is quite common to add 100-300 g / month.
Most often, it is not necessary to weigh the baby daily; the dynamics of the increase is clearly visible with a weekly measurement, and after eight weeks it is enough to weigh the child once a month.
Insufficient weight and height gain Insufficient weight and height gain: One of the main causes of stunted weight and height in infants is malnutrition. Such problems can occur in breastfed babies with hypogalactia (reduced secretion of breast milk). In this case, it is necessary to take measures to stimulate lactation, and if they are ineffective, supplement the child with mixtures. The causes of insufficient weight gain and growth are clarified by the doctor after appropriate examinations.
Every baby is born with a certain body weight. The norm is 2700 - 3700 kg. However, small deviations from these numbers do not yet say that the child is sick or something is wrong with him.
The weight of a newborn depends on:
- health;
- heredity;
- gender;
- mother's nutrition during pregnancy;
- the physical and psychological state of the mother;
- the presence of a woman's bad habits;
The baby loses some weight in the first days after birth. This is due to the fact that the body loses a lot of fluid and adapts to the new environment. At discharge, the baby will weigh 6-10% less than at birth. It is from the second digit (at discharge) that they begin to count the indicators of weight gain.
Features of weight gain in newborns
In the first four weeks of life, the rate of weight gain in newborns is 90-150 grams in seven days. From the second to the fourth month, the child gains 140-200 grams per week. Then the increase drops to 100-160 gr.

Thus, by six months, the mass will double. Further, the set slows down, and by the year the newborn weighs about three times more than at birth.
Some children gain weight quickly, some slowly. Why is this happening? This is influenced by a number of factors:
- Health;
- Appetite;
- Type of feeding (artificial or breastfeeding). With artificial feeding, weight is gained faster;
- Daily routine and meals. When feeding on demand, weight grows faster than when feeding by the hour;
- The quantity and quality of milk from the mother;
- Mobility and activity of the newborn.
Scientists have established conditional average rates of weight gain in children under the age of one year.
Average rates of increase
The table contains approximate figures for the weight gain of children under one year old. Remember that every baby is different and recruitment rates may vary from those shown.

Please note that a similar table was compiled for children who are on artificial feeding. With natural nutrition, the baby develops the way nature intended. And indicators in this case depends on genetics and compliance with the rules of feeding. However, the table will guide you and help you get an idea of the formation of the mass of the child.
Please note that, the larger the baby, the faster the weight increases. So, a newborn with a height of 52 cm adds 170 grams, and a height of 58 cm - already 210.

How to calculate the proper weight of the baby
On average, for the first six months, weight gain in newborns is 800 grams, and after six months - 400. Therefore, to calculate the approximate weight of the child for this period, use the following formula:
Body weight of a child up to six months = weight at discharge + 800 x age (months)
For example, the baby was 4 months old, and he weighed 3000 grams after birth. Then the proper weight = 3000 + 800 x 4 = 6200 grams.
To determine the weight after 6 months, use the following formula:
Body weight of a child after six months = weight at discharge + increase for the first six months + 400 x (baby's age in a month - 6)
To calculate the addition for the first six months, then just 800 x 6 and we get 4800 grams. Use the finished figure to calculate the mass of an infant over six months old.
If the baby is 8 months old, and initially he weighed 2900 grams, then the proper weight \u003d 2900 + 4800 + 400 x (8-6) \u003d 2900 + 4800 + 800 \u003d 8500 grams.

Overshoot and Undershoot
Mom may face two problems - weight loss or overweight. If the child is not feeding, then, first of all, determine whether the feeding is taking place correctly. The baby should receive milk 10-12 times a day and stay at the breast for as long as he wants. The number of trips to the toilet also affects. Diapers should get wet at least 12 times a day.

Excess is also a problem. Unfortunately, many mothers worry only when the baby is not getting enough. However, the problem of overweight is also dangerous if the rate of increase does not decrease after six months, and the baby at 6 months corresponds to the parameters of a one-year-old. This may be due to genetics, but it will not be superfluous to seem to an endocrinologist. Excess weight may be the result of health problems.
If there are no problems, then excess weight can lead to diseases.
Watch your baby's weight carefully. Remember that the table is conditional, each child develops individually. So don't panic if the numbers differ.



