Logical thinking is one of the most complex shapes thinking that develops only at the beginning of the school period of development (6-7 years). It is based on imaginative thinking, the skills of which should already be quite well formed by this period.
Development logical thinking through educational games
The development of logical thinking operations in children aged 6–7 years is a complex and multi-stage process. Its achievement poses many challenges for the child, including:
- Enriching ideas about the world around us.
- Understanding the patterns that unite objects and phenomena.
- The ability to identify the most common and significant features of objects.
Thanks to the proper level of development of logical thinking, a child at the age of 6 will be able to more successfully master the school curriculum and acquire knowledge, skills and abilities that are significant in the future.

What is logic - definition
In particular, this will contribute to the internalization of many mental processes (including the development of mental arithmetic and internal speech).
Stages of development of logical thinking of a preschooler
The development of the foundations of logical thinking in children aged 6–7 years is carried out in several stages.
- The child learns the basic properties, quantitative and qualitative characteristics of objects, and also learns to use them in his daily life.
- Implementation of thinking operations with the replacement of real manipulation of an object with verbal reasoning.
- Replacement of verbal active accompaniment of activity with internal mental operations.
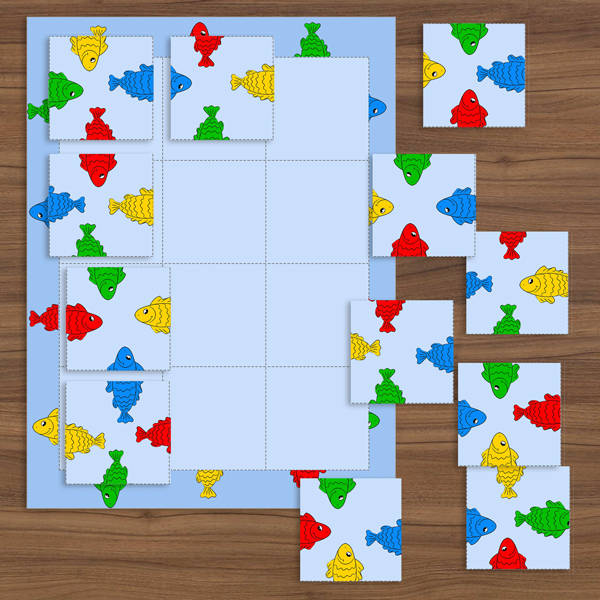
Jigsaw puzzles for 6-7 years old
Requirements for the logical development of a child
By the age of six or seven years, a child should successfully cope with the following thinking operations:
- The child must be able to find patterns that unite groups of objects according to one or another attribute, and also continue logical series independently, without using hints and leading questions.
- Find an extra item from the 5 offered to him.
- Compose stories independently from pictures and come up with a logical conclusion.
- Divide objects into groups, while specifying which feature was taken as a basis.
If to the right age the child has not yet acquired these skills; competent development of thinking in children from 6 to 7 years old can solve this problem.
Basic logical operations
The operations of logical thinking that a child should master by this age include:
- analysis;
- synthesis;
- comparison;
- classification;
- proof.
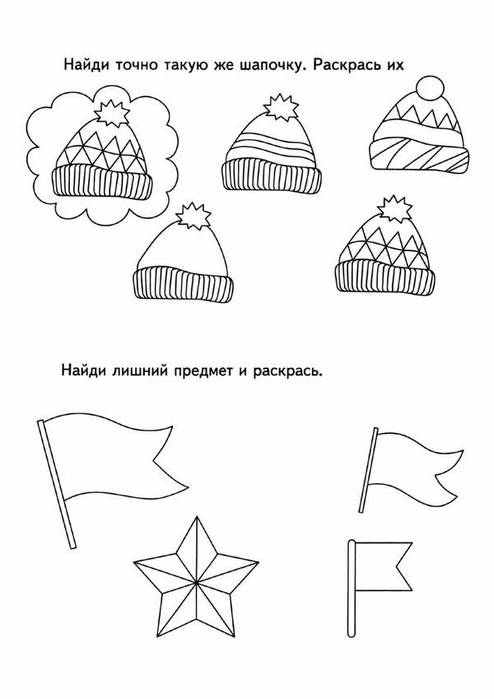
Task for attentiveness and logic
Development logical operations allows the child not only to successfully carry out most activities, but also:
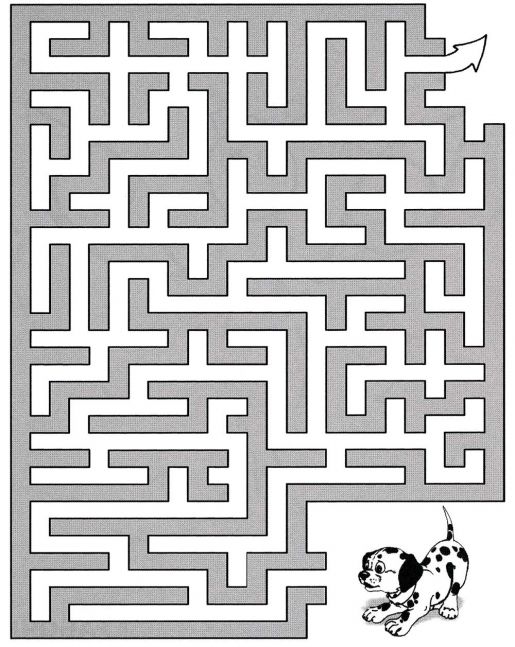
Types of games to develop logical thinking in children
Currently known games and tasks for the development of logical thinking in children can be divided into the following categories:
- Graphic games are aimed at improving fine motor skills and basic preparation of the hand for writing.
- Mathematical - games and puzzles based on teaching a child to mental arithmetic, logic and abstract thinking.
- Speech games – contribute to the development of active vocabulary child.
- Puzzles and board games teach the child to think consistently and strategically. In addition, they strengthen the child’s ability to work in a team and express themselves in joint activities.
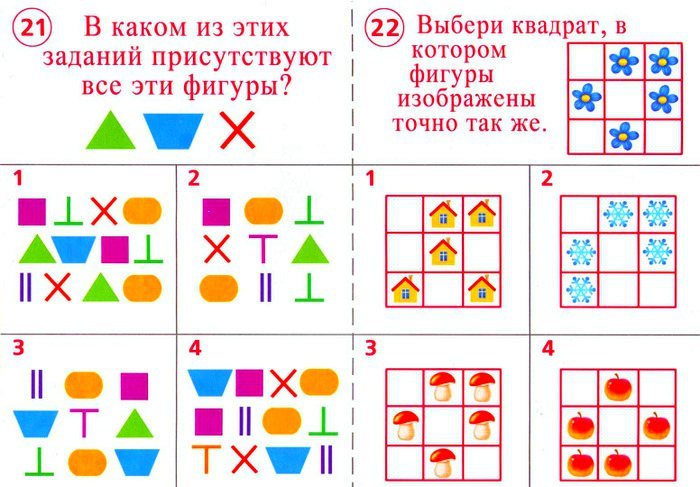
Test tasks for the level of logical thinking
Games and exercises to develop a child’s logical thinking
The logical development of children aged 6-7 years is impossible without special organized activities aimed at achieving a given result. Thematic games and exercises can provide considerable assistance to parents in this regard.

Logic games from the store
1. “I made a wish”
The parent thinks of an object in his mind. The child’s task is to guess it using clarifying questions. It is advisable that the child learns to correctly formulate leading questions, allowing him to identify the key features of the objects being guessed.
2. “I take it with me”
To play you will need cards with images of a variety of objects. The child is asked to choose those that will be useful in a particular situation (for example, outdoors, at the theater, visiting, at school, etc.). It is advisable that among the drawn objects there be a variety of objects - including those that may be useful in several situations at once or not useful at all.
The child takes out cards one by one and explains whether he will need this or that item, giving reasons for his decision.

An interesting game for logical thinking
3. “Seated in rooms”
Cards with images of people of different genders, ages, hair colors, eyes, etc. are laid out in front of the child. And also a sheet of paper divided into four equal rectangles (symbolic “rooms”). Its task is to “settle” people into rooms depending on one quality or another. And then answer the questions proposed by the parent (for example, which of the drawn people can enter two or more rooms, who is not suitable for any room and why).

Game extra object - complicated version for 6-7 years old
4. Comparison problems
The child is asked to compare, comparing several objects or phenomena with each other. For example:
- Birch is taller than oak, and oak is taller than pine. Which tree is the tallest and the shortest?
- Olya's hair is darker than Masha's, and Katya's is darker than Olya's. Which of the girls has the most dark hair? etc.
It is necessary to take into account not only the children’s answers, but also their reasoning for their choice.
The development of logic in children aged 6-7 years should be carried out in the most relaxed and comfortable environment possible. The more actively game teaching methods are used in classes, the more effective they will be.

By the age of 6, a child should be able to play chess
Taking into account the rapid fatigue of children, it is advisable to calculate the duration of the lesson so that it does not exceed 20-30 minutes.
It is very important that the child not only gives answers to the proposed questions and finds solutions to tasks, but also explains his answers in as much detail as possible. This will make sure that the child really sees logical patterns and understands them.
Watching a child develop is an amazing pleasure. Participation in the process of the baby’s learning about the world around them becomes even more exciting for parents.
Playing chess greatly develops logical thinking
The best time to develop your thinking
The baby learns to think with the help of objects, and then with the help of images. By the age of 6-7 years, the ability to logically comprehend information becomes more and more evident. You can't lag behind nature.

Teach children to solve puzzles
Adults must be proactive and train the child’s mind, because the first 7 years of life are the most favorable time for the development of natural potential.

To decide logic puzzles, children need to develop attentiveness
If adults take care of creating a developmental environment for the baby, then by the age of 7 he will be able to:
The game is an intellectual simulator
The ability to reason will help a child overcome various life difficulties. Play can be an excellent intellectual simulator, since this is the main activity of a child before entering school.

Play extra words with your kids
It is advisable to include a variety of tasks in a developmental complex for 7-year-old children: verbal, with objects, with images. The main thing is that they are interesting, understandable and not too easy. Then the correct decision will be perceived by the child as a desired victory.
Solve riddles
Logical actions with objects. We think and reflect
A 7-year-old child has good fine motor skills and can coordinate his movements. Therefore, you can safely offer logic puzzles based on actions with small objects.
- Exercises with sticks or matches (construct a specific image and change it using a specified number of movements of the sticks).
- Educational games with scissors and paper (cutting unusual parts according to a sample or according to instructions).
- Exercises with “smart” cubes. For example, B. Nikitin’s games: “Fold the pattern”, “Unicube”, “Cubes for everyone”. They develop children's ability to analyze and synthesize, as well as combination skills.
- Designers from different materials(including dynamic ones). The tasks force children to think about the purpose of various parts of the construction set, options for connecting them, and the reasons for the stability (instability) of the structure.
- Rubik's cube, game "15" and other puzzles.

Rubik's Cube is a great educational game
"Smart" pictures. Let's watch and talk
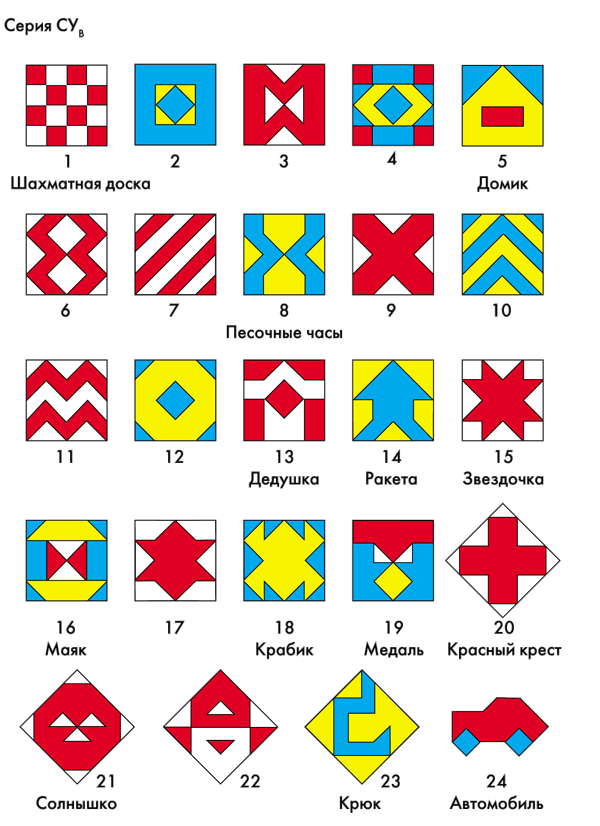
Visual-figurative thinking becomes the basis for developing the ability to reason and draw conclusions. At 7 years old, children enjoy completing tasks with images:
- continuation of a series of figures built according to a certain rule;
- finding a way out of the maze;
- comparison of pictures;
- completing the image (with selecting the missing element from several proposed ones);
- exclusion of an unnecessary image from the number of proposed pictures;
- combining images into a group based on essential characteristics;
- game “Nonsense” (search for illogical details of the image and explain your point of view).

Exercises to develop attention
Lotto cards, thematic sets of pictures for learning about animals, plants, professions, household appliances, modes of transport and others are excellent for performing many exercises.
For children 7 years old, buy Dienesh's logic problems
Verbal and logical tasks. Listen, read, draw conclusions
A seven-year-old child has the necessary experience and knowledge to perform simple reasoning tasks without the help of objects and images. Therefore, adults should offer children not only exercises from special manuals, but also word problems they themselves compiled based on the model. You can list 9 best views exercises for the development of verbal and logical thinking in children 7 years old.
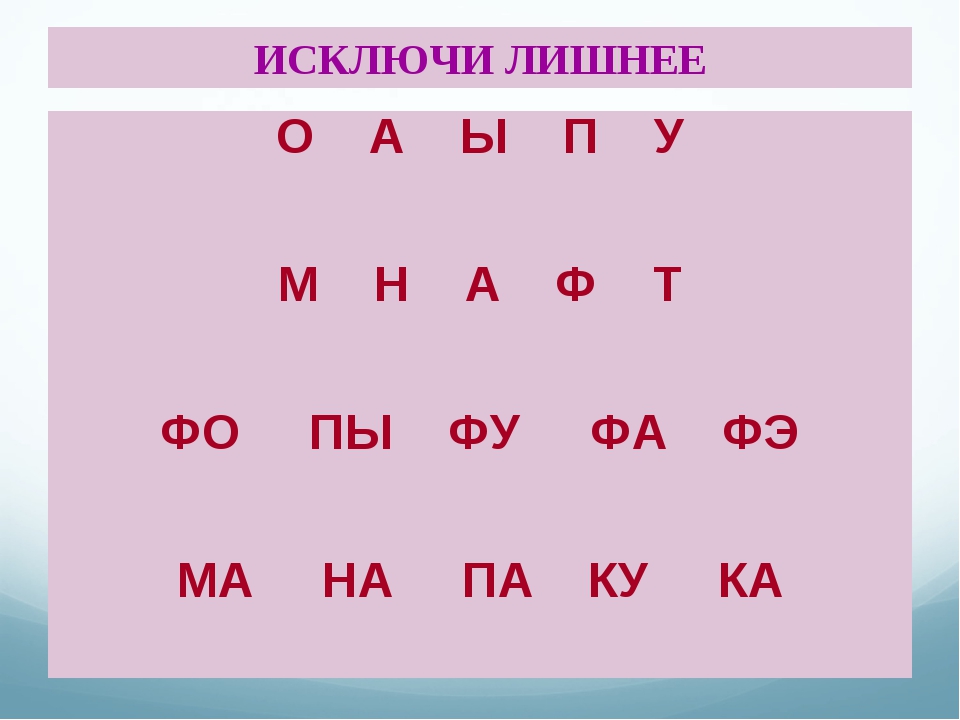
The game “Eliminate the Unnecessary” will help you quickly learn to read
- Elimination of unnecessary words. For example: birch, pine, berry, oak.
- Generalization. For example: a shovel, a rake, a broom – this is...
- Comparison. For example: plum and apple.
- Action by analogy. For example: lemon is sour, sugar...
- Classification. Distribution into groups. For example: boot, frying pan, tit, pigeon, shoe, pan.
- Explanation figurative meaning proverbs and metaphors. For example: golden hands.
- Conclusion. For example: Igor is taller than Dima, Dima is taller than Yura. Who is the tallest? Who's the shortest?
- Inventing “lost” parts of the story (beginning, ending, middle).
- Solving and inventing riddles.
- These are great exercises for developing logic. They can be used not only for seven-year-old children, but also for children 8-9 years old. You just need to complicate the examples.

Dienesh's logic blocks are designed for different age categories
The child has enormous development potential. But for its implementation, adults must create a developmental environment. Logic problems are a necessary element of intellectual training for children.
Let's remember a scene familiar from childhood. Malvina says to Pinocchio: “You have two apples in your pocket.” “You’re lying, not a single one...” answers the mischievous wooden boy. This scene fully reflects age feature children's thinking, namely concreteness. The ability of a child’s mind to perceive everything concretely, literally, the inability to rise above a situation and understand its general meaning is one of the main difficulties of children’s thinking, which is clearly manifested when studying such abstract school disciplines as mathematics or grammar. However, by the time children enter first grade, their imaginative thinking ceases to be purely specific and situational. The child is able not only to imagine an object in its entirety and variety of characteristics, but is also able to highlight its essential properties and relationships. He develops visual-schematic thinking. This special kind thinking, which is expressed in the fact that the child understands and successfully uses various schematic images of an object (plan, layout, simple drawing). Children begin to understand conventional representations of much more abstract relationships: relationships between words in a sentence, between letters in a word, between mathematical quantities, etc. This opens the way to teaching children literacy and mathematics based on visual and conditional displays of the basic patterns within educational material. The foundations of verbal and logical thinking begin to be laid. This type of thinking is finally formed only in adolescence (13–14 years old) and is the leading one in an adult.
The process of distraction at the age of 7–8 years occurs not only during the perception of a number of objects, but also under the influence of verbal descriptions and explanations. However, the child is still captivated by images of specific objects. Knowing from experience that iron objects sink in water, he says that the nail will sink, but he supports this conclusion not with a general statement (“All iron objects sink”), but with a reference to an isolated case: “I myself saw a nail sink.” .
The activity of children’s thinking is eloquently demonstrated by their numerous questions, in which the child expresses curiosity about what surrounds him: “Why is it night now? Why are the drops falling? Why is there fire in the match, where is it hidden? etc. The thought of why is now aimed at distinguishing and generalizing objects, phenomena, and events observed by them.
The way of thinking using the “short circuit” method, which has emerged in five- and six-year-old children, also appears in the course of the thought process. The child does not analyze the entire problem as a whole (everyday, spelling or mathematical), i.e. does not highlight all its conditions, all the data and does not see the connection between them. It picks out one condition and establishes a direct connection with any other condition or with by the question asked. Thus, when solving the riddle “I know everything, I teach everyone, but I myself am always silent,” a first-grader often answers that it is the teacher. The phrase “I know everything, I teach everyone...” is enough to find a solution, i.e. substitute a familiar image. And although this is followed by an addition - “...but I myself am always silent” - i.e. it seems that the exact opposite condition to the answer found is evident; the child simply rejects this condition.
Entering school changes the content of children's activities. The range of objects and phenomena about which they must think is significantly expanding, and the requirements for the thinking processes themselves are increasing. The teacher teaches children to carefully follow the course of reasoning, accurately express thoughts in words, think first and then do something, etc. Although thinking junior schoolchildren in general remains concretely figurative, elements of abstract thinking are expressed more and more noticeably. Children can think at the level of general concepts about what they know well, about familiar animals, plants, people and their work.
The rate at which school-age children develop their thinking largely depends on how they are taught. Experienced training of younger schoolchildren in special programs of increased difficulty proves that already in children 7–8 years old the ability for abstract reasoning and consistent performance of mental actions is quite high. The use of scientifically developed methods of teaching children accelerates the development of thinking.
Thus, in shaping the thinking of schoolchildren, decisive importance belongs to educational activities, the gradual complication of which leads to the development mental abilities students.
However, to activate and develop children’s mental activity, it may be advisable to use non-academic tasks, which in a number of cases turn out to be more attractive for schoolchildren. Tasks and exercises to find patterns, logical problems, and puzzles will provide invaluable assistance in the development of logical thinking. Let the child guess the riddles and come up with them himself. Introduce him to proverbs, but not in an abstract form, but in relation to life situation(for example, if a child has scattered toys, say: “If you like to ride, you also love to carry sleds,” and explain the general meaning of the proverb).
Make activities to develop your child’s thinking not only useful, but also fun. Our website will definitely help you with this!
Good luck and be proud of your child's achievements!
Logic problems for children 6-7 years old help develop correct thinking and create interest in mathematical education in preschoolers.
Age characteristics
It is in early preschool age that the foundations are laid mental development. Logical tasks for children 6-7 years old help to fully prepare them for their future life. Mental activity, as well as the processing and comprehension of information offered in tasks, contribute to the formation of certain ideas, as well as the acquisition of generalized and specific knowledge. The acquired skills will help children find the right solution in various life situations.
Where to start?
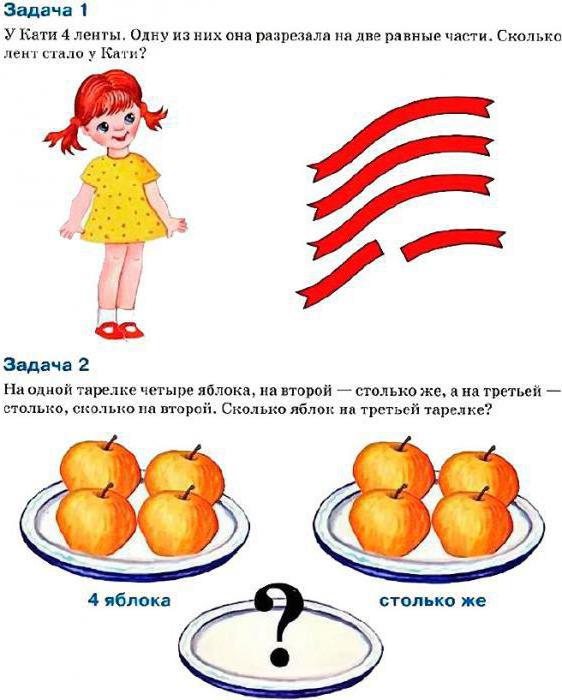
We offer ready-made logic problems for children aged 6-7 years with answers. The child is offered pictures that depict: a bus, a scooter, a bicycle, a car. It is necessary to determine the vehicle that is superfluous in the proposed list.
Problem 1: solution
The answer is a bicycle. The point of the task is that to travel by bus, car, scooter, you need fuel, so they can be classified as one group. When moving on a bicycle, a person’s muscular strength is sufficient, so this means does not fit into the general list.
Such logical tasks for children 6-7 years old not only develop thinking, but also form the horizons of preschoolers. Children master skills colloquial speech, reason freely, speak, plan their activities, ask questions, and draw logical conclusions.
Problem 2
There are also logic puzzles with a trick for children, which are aimed at developing the imagination of the younger generation. Petya is weaker than Kolya, but stronger than Misha. Which of the guys is the weakest?
Answer: Misha.
To resolve this, a comparison needs to be made between Misha, Kolya, and Petya. Kolya is the strongest, therefore Misha will be the weakest.
Psychologists call a variety of logical tasks for 6-year-old children the right direction for children’s development, which does not bring problems with their physical and mental state. Experts advise starting with simple tasks, gradually increasing their level of complexity.
Problem 3
We offer logical problems with answers for children, which adults will also have to think about.
There are as many blue parrots in the zoo as there are yellow birds. The number of red and blue parrots is the same; how many birds are there in the zoo if there are three red parrots?
Answer: 9 parrots.
In order to cope with this mathematical problem, you need to carefully listen to its condition. Since the number of all birds is the same, therefore, red, blue, yellow birds together will be nine birds.
By solving such a task, the child gains the skills of analysis and synthesis, comparison, learns to organize his actions, and navigate in space.

Types and examples of logic problems
Subject problems can be offered during tabletop or didactic games. For example, the guys must choose one item from the proposed list geometric shape, color, size. Such tasks perform a specific function - teaching the child to complete a given task, strive for results, the ability to find his mistakes, and correct them:
- 1st task. A chicken weighs two kilograms on one leg, how much will it weigh on two legs? (2 kg).
- 2nd task. Two dads, two sons, as well as a grandfather and grandson came into the cafe. How many men were in the cafe? (three).
- 3rd task. The family has five sons. Each has one sister. How many children are in this family? (Six).
- 4th task. Four girls played with dolls for an hour. How many hours did each girl play? (one hour).

Verbal tasks
Such tasks for the development of logical thinking for children can be of different topics:
Task 1. Kids must guess the description of pets or identify the animal based on the listed external signs.
Task 2. Five cones and four bananas grew on a pine tree. How many bananas are left if all the pine cones have fallen?
The guys who have developed creative thinking understand that bananas cannot grow on a pine tree, so they answer that there will not be a single fruit left on a pine tree.
Children solve logical problems much faster than adults; they are more likely to use logic and imagination.
Task 3. Masha lit six candles, and a little later extinguished 3. How many candles does the girl have left? (3 pieces, since the rest were completely burned).
Task 4. Seryozha broke a wooden rod into 3 parts. How many breaks did he make? (Two).
Psychologists are convinced that it is diversity that contributes to the formation harmonious personality child, therefore such exercises are included in the programs according to the new federal educational standards preschool education. Only when using educational tasks and games can we talk about the formation of the younger generation with full-fledged logical thinking.
Varied finger games help activate brain activity, stimulate the formation of speech skills, develop fine motor skills, have a positive impact on creative activity. For example, you can offer children dramatizations of fairy tales and stories using their fingers.
The success of schooling directly depends on the ability to solve logical mathematical problems for children in preschool age.

Task 5. Where can you jump from, but where can’t you jump? (On the plane).
Task 6. Seryozha found himself in a room in which there was a gas stove, a candle, and a kerosene lamp. What should a boy light first? (A match).
Task 7. What can Masha see with her eyes closed? (Dreams).
Task 8. Maxim saw the “little green man”. What should the boy do? (Cross the road when the traffic light is green).

Conclusion
In preschool age, play is used as the main activity. It promotes the rapid assimilation of skills, knowledge, concentration, and memory development. It is towards the end of the preschool period that the formation of verbal and logical thinking begins. It is associated with the development in children of the ability to use words, analyze and perceive the logic of reasoning. In order for a child not to have problems with social adaptation, it is necessary to pay attention to special attention the formation of his logical thinking.

Psychologists identify three types of conversations that contribute to the formation of logic in preschoolers. Introductory classes are designed to familiarize children with objects, phenomena, and processes. The main objective of this form of work is to obtain new knowledge and generate interest in the upcoming activity.
They are short-term, emotional, and without them the development of mathematical logic is impossible. The second version of the conversation involves the teacher asking questions, in order to find answers to which the child will have to engage in active mental activity.
Work is built on the basis of mobilization children's attention, thinking, memory. The child constantly monitors the progress of the conversation, looking for answers to the questions asked by the teacher. Heuristic conversations are suitable for older preschool age. For example, the conversation can be concluded with a riddle or a proverb that stimulates the subsequent activities of preschoolers. When building a conversation, it is important to update the experience that children have and direct them to the upcoming mental activity. For example, during a heuristic conversation, the teacher identifies contradictions that children are forced to resolve.
Exactly preschool age is the most important point in the formation of a logical and ecological culture. At this time, the foundations of personality are being laid, including a positive and caring attitude towards living nature and the people around us.
Logical tasks that help a preschooler learn and understand the phenomena and processes occurring in living nature contribute to the development of an emotional and value-based attitude towards plants and animals, and an awareness of the connection with the living world.
At this age, children are happy to join in the process of solving logical problems The main thing is to make the lesson interesting and exciting.
On intelligence for older preschoolers1. Seven brothers have one sister. How many sisters are there?
(One)
2. Two mothers, two daughters and a grandmother and granddaughter. How many are there?
(Three: grandmother, mother and daughter)
3. There are three apples in the basket. How to divide them between three children so that one apple remains in the basket?
(Give one along with the basket)
4. One and a half pike perch cost one and a half rubles. How much do three pike perch cost?
(3 rubles)
5. Five candles were burning in the room. Two candles were extinguished. How many are left?
(Two, the rest burned)
6. You can jump off it while moving, but you cannot jump on it while moving. What is this?
(Airplane)
7. Born twice, dies once.
(Chicken)
8. Liquid, not water, white, not snow.
(Milk)
9. What grows upside down.
(Icicle)
10. Who can’t be lifted off the floor by the tail?
(Ball of thread)
11. The pencil was divided into three parts. How many cuts were made?
(Two)
12. Five knots were tied on the rope. How many parts did these knots divide the rope into?
(At 6)
13. When can you cut your hand on water?
(If you turn it into ice)
14. Is it possible to fill an empty bucket three times in a row without emptying it once?
(Yes: large stones, sand, water)
15. You entered a dark room where there is a candle, a gas stove, and a kerosene lamp. What will you light first?
(Match or lighter)
16. The predictor undertakes to predict with 100% accuracy the score of any match before it begins. What is the secret of his unmistakable prediction?
(Before the start of the match the score is always 0:0)
17. Is it possible to throw a ball so that, after flying for some time, it stops and starts moving in the opposite direction?
(Yeah, throw it up)
18. How to transport a wolf, a goat and a cabbage from one bank to another if one person (the carrier) can fit in the boat, and with him either a goat, or a wolf, or a cabbage?
(First transport the goat, then the cabbage, and on the return trip take the goat, leave the goat on the opposite bank, transport the wolf, return for the goat)
19. Two boys played checkers for two hours. How long did each of them play?
(2 hours each)
20. The two went and found five nails. If four go, how many will they find?
(Not a single one, everyone has already been found)
21. One man has four sons and each of them has sister. How many children does he have?
(Five people)
22. Six trees grow near the post office: pine, birch, linden, poplar, spruce and maple. Which of these trees is the tallest and which is the shortest, if it is known that the birch is lower than the poplar, and the linden is higher than the maple, the pine is lower than the spruce, the linden is lower than the birch, and the pine is higher than the poplar?
(Spruce, pine, poplar, birch, linden, maple)
23. Which is heavier: a kilogram of cotton wool or half a kilogram of iron.
(1 kg cotton wool)
24. Kolya and Sasha bear the surnames Shilov and Gvozdev. What surname does each of them have if Sasha and Shilov live in neighboring houses?
(Kolya Shilov and Sasha Gvozdev)
25. Two fathers and two sons, and a grandfather and grandson were walking down the street. How many people were walking down the street?
(Three)
26. There were sweets on the table. Two mothers, two daughters, and a grandmother and granddaughter each took one piece of candy. How many candies were on the table?
(Three)
27. When a goose stands on one leg, it weighs 7 kg. How much will a goose weigh if it stands on two legs?
(7 kg)
28. In the running competition, Yura, Grisha and Tolya took prizes. What place did each of them take if Grisha took neither second nor third place, and Tolya did not take third?
(Grisha – 1, Tolya – 2, Yura – 3)





