Why are logic and thinking games so important for children 9-10 years old? This is due to the peculiarities of the development of thinking in younger schoolchildren. It is at the age of 9-10 years that a qualitative change occurs in the child’s mental activity.
Visual-figurative thinking, which was the main focus of the entire previous period in children, is finally replaced by conceptual, verbal and logical thinking. Now a 9-10 year old schoolchild can already assimilate knowledge, relying not only on what he sees and feels, but also masters abstract concepts, identifying the internal connections of objects.
Well prepared - depending on age with rubber boots and dirty pants or raincoats and sturdy shoes - presumably bad weather should not be an obstacle. The Idea Basically, all treasure hunts have a common similarity that children follow a specific route to finally find the treasure or a link to where it is hidden.
Often the route is indicated by a chalk arrow. Another possibility is to hang or take out paper in hidden places, which in turn reveal a link to the next station on the route. Who is afraid that someone is faster than the birth group and notes, despite the fact that carefully selected hiding places can come, of course, also without a completely “paper economy”!
How quickly and completely the formation of this way of understanding the world occurs depends on how successfully your child will study in the future. If by this point children have not developed full-fledged mental activity, they will not be able to fully master school subjects and the gap in mathematics and other sciences will only accumulate.
In general, of course, there are no limits to your imagination when it comes to preparing a treasure hunt, and new or complementary ideas are likely to arise entirely on their own! Here are some tried and tested suggestions. Preparation Most children kindergarten not yet read. Read the FAQs, find the answers, and maybe even expect them!
The one with with open eyes, the planned treasure hunt route, will find many questions, for example. “Stop time and take into account exactly: how many cars are driving under the bridge in 2 minutes?” “What numbers do you find by the lantern in front of the bakery?” . Which are individually written down by card type or together on a sheet for treasure hunters. Don't forget to add a little space for answers!
What should parents do to help their child at this important stage? You need to play with him! Play educational games with children yourself and encourage them to independently master logic and thinking games. It trains the growing brain the same way sports trains muscles.
Graphic games to develop logic
Additional materials such as a stopwatch or compass will be organized in time and, if necessary, a “real” treasure map will be created! Forward! Once the prepared questions are handed over to the little treasure hunters, the fun can begin!
With the help of an adult, search for answers and answers to questions. Clip and spare pencils - good service; in case of rainy weather, transparent films in which labels or cards can be placed. To ensure that every child comes on the train, it is advisable to create two groups that are accompanied by one adult, especially for large birthday parties. Both groups ask the same questions and go in different directions.
To print, click on the picture, it will open in a special window, then right-click on the picture and select “Print”
Graphic games for the development of logic in children begin to be used from the age of 5, but younger schoolchildren also willingly play them, choosing more complex shapes games they already know. Tabletop educational graphic games There are several types.
Often there are some children, others hardly leave the opportunity to answer at least once! Asking questions on individual cards ahead of time and assigning the same number to each child in advance increases the likelihood that all children will get the answers.
Questions answered - and then? Already on the road or later at home, children receive a piece of a prepared treasure map for each correct answer. Back at the birth child's home, all questions are read again by the parent, and each problem solved is rewarded with a piece of the treasure map.
If all the map pieces have been collected, you can play together! A thick cross on a simple sketch from a garden, playground or apartment shows where the treasure is hidden! All questions are read again to adults upon return and children present their collected answers.
- Paired pictures between which you need to find the differences. This game has been familiar to children since preschool years, but now the tasks are more complex, there are more differences and they are better disguised. There is a large selection of subjects of such drawings for both girls and boys.
- Mazes in which children must draw lines from the beginning of the task to the center or exit, finding the only correct path. They also differ from the labyrinths of previous years for children in a more complex structure and plot design.
- If, for example, for preschool girls it was necessary to draw a line from a kitten to a bowl of milk, then a younger schoolgirl will have to help Alice or Cinderella find a much more intricate path to a fairy-tale goal.
- and other educational games in which you need to connect dots or numbers located on a sheet, resulting in some kind of drawing.
- These board games It is also better to select according to the gender of the child, since different stories seem interesting and attractive for girls and boys of these years. Moreover, they sometimes deliberately emphasize this difference. Games where you need to complete the missing part are also close to them.
- Various graphic ones, where the solution is related specifically to the drawing.
Logic and thinking games
At that time, by the way, dinner can be prepared very well! The sample map shown does not allow you to complete your search for a child's birthday, but at the nearest playground. For schoolchildren questions and puzzles for schoolchildren Of course, questions for schoolchildren can be somewhat more demanding, for example.
“What is shown on the playground sign and up to what age can children play there?” When was the church built? . Additionally, one-bit thinking, small puzzles, and answers that require action prevent boredom from setting in. Then walk three big steps forward, turn left, take ten big steps back, and go south from there until you can't go any further. If a piece of paper is hidden under a swing, the word "swing" may be puzzled by a puzzle: You float in it!
- To find the next treasure link, the slide slides across the playground.
- Take the first letter.
- It's best in summer!
- Take the second letter.
- What is the name of the small horse?
- Children receive a leaf from a tree or other plant.
- The question is natural: “What plant is the leaf from?”
- Additionally, children can search for this plant and they can bring a leaf with them.
- It is not clear that this is not "cleared" in the yard!
- Ivy or chestnut leaf will also be found "wild".
Matches: puzzle
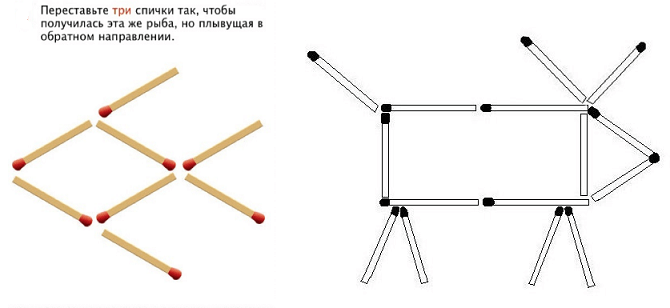
Educational board games have been known for a long time and they often use a variety of objects - matches, pencils, paper. One of the most popular are puzzles with matches. Matches are affordable and compact. You can play with them at home, on the road, and on the street.
For each problem to be solved, children receive a written word or solution sentence prepared on small notes. For simple words or phrases they can sort them into the correct order depending on their age. Otherwise, each letter can be marked on a colorful slide. The solution sheet, with letter positions marked in the same colors, allows little tinkerers to quickly reach the goal and the treasure chest!
Why are word problems so difficult for poor kids?
And the justification for this harsh judgment is usually the way in which the affected child deals with the most difficult area of mathematics primary school for all children: word problems. For example, a ten-year-old girl is faced with the following problem at the end of her fourth school year: A carpenter saws boards 3 m20 long into 4 equally long pieces. How long is each part? The girl immediately begins to count. Answer: “Each piece is 56 meters long!”
They are convenient for games and riddles, providing a huge number of options with a minimum of funds. Puzzles with matches develop spatial thinking in children and consolidate knowledge geometric shapes, cultivate patience and perseverance.
Logic problems
This seems a plausible explanation for such events. On the other hand: Dieselbon's parents who accept the "logical deficit" know their child and know exactly how to wake him up often in other contexts. And with all the undeniable differences in so-called “intelligence” in psychology: a child who has acquired something logical, like language; which can be found in its complex environment; a child who has already learned a lot at school - so the child demonstrates day after day that he is, in principle, very good at recognizing logical contexts and drawing conclusions.
Logical tasks train thinking, often forcing you to find unexpected solutions in a humorous manner, and to be attentive to the words that indicate the conditions of the task. They require not knowledge, but the ability to think logically. Basically, logical problems are formulated verbally, but there are also more visual ones, using available objects.
But then what about “headless” adaptations of word problems like the ones described above? In my opinion, research into mathematics didactics in dealing with children with so-called “captain's problems” is part of the explanation; classic example. There are 26 sheep and 10 goats on the ship.
What do students do when they are faced with such “problems”? with texts, therefore, that do not allow for reasonable calculation? This obviously depends entirely on how long they've already been taught: a study of 333 children in preschool through fifth grade found that such "meaningless problems" accounted for about 10% of first grade, about 30% of second grade, and about 60% of third and fourth grades. classes are "solved".
6 glasses
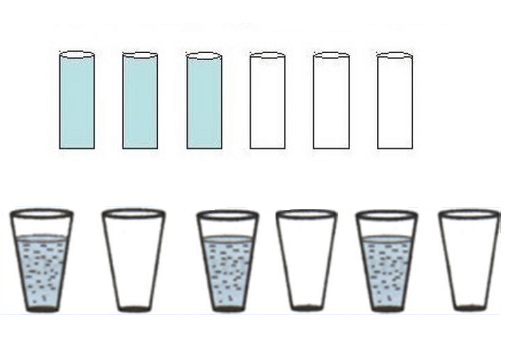
One of the popular logical tasks “6 glasses” is interesting and accessible to players of the most different years, both adults and schoolchildren. Six glasses are placed in a row on the table. The first three are full of water, and the next three are empty. It is necessary to make sure that full and empty glasses alternate, but you can only pick up one.
Once again, these studies were conducted with a completely normal student. So, should we now conclude that not only poor children, but in general, the majority of four-year-olds cannot “think logically”? The already increasing frequency of apparent "voicelessness" from class to class suggests that something very different from a "logical deficit" is at play here: it is clear that children have learned a certain deal with mathematics in general over many years, and text-based ones in particular tasks.
But this is by no means just for poor children! Here, on the one hand, we can recognize the danger that mathematics teaches for all children, and which naturally requires “preventive” measures. On the other hand, it is easy to explain why children who are "poor" children are especially susceptible to this seemingly arbitrary danger.
Application games for developing logic

Today, all these types of traditional logic games also exist in online versions, on various websites and portals. You can choose from them logic games and puzzles for girls and boys. A large number of games-applications have been developed for the development of logic, which can be downloaded for tablets and smartphones. These include puzzles, puzzles, and educational games.
Numbers do not mean numbers, not as "How many?", but as "stations" of a "chain of numbers". “69” is not in the mind as “six tens and 9 more,” but rather as “a ball in a ball chain.” How would this child recognize, on the basis of such “operational understanding,” whether the word problem now requires “double dot calculation”? Therefore, the problem of these children does not begin with " logical problem” to “recognize” the four main discourses in different situations. Rather, they have not yet understood the four main discourses for what they are. Therefore, recognition is generally impossible - at least not in accordance with the content criteria. It's like a question - but in a language you don't understand. It doesn't matter how smart you are: in such a situation you are hopeless. If, on the other hand, you have no chance, on the other hand, you cannot escape the task - what do you do then? There are certainly different possibilities; we find them all in children who are poor in calculation.
- "Numerative weakness" usually means: insufficient numerical understanding.
- However, on this basis the types of arithmetic cannot be understood as what they are.
If parents of children should think about at what age they can be allowed to use computers and gadgets, then schoolchildren have already fully mastered the most different games. So let their passion modern technologies will serve the development of logical thinking.
Logical mice

Or even like this: “These are, of course, times, because before we also expected time!” Finally, and above all, by a child trying to remember certain types of problems in a "pattern" sense: This is one with minutes. The bus leaves at 12 o'clock. Competence in “solving mathematical problems” does not arise.
The relationship between "prevention" and "cure"
The possibilities for combating “disturbed” attitudes towards word problems are not fundamentally different from the didactic aspect of mathematics measures, which are suitable for children with the help of tools for solving material and word problems from the very beginning. Thus, the suggestions given below for the first lesson are equally suitable for subsequent treatment of existing difficulties.
An example of such a computer game that develops logic in children is logic mice. The game belongs to the class of strategies and the player’s task is to click on the mouse standing on a piece of cheese and make it jump to the next free piece of cheese. Despite its apparent simplicity, the game is not so simple and allows you to understand how developed the player’s logical abilities are.
Of course, there is a big difference: for children who have already experienced failure, it often takes special educational and psychological skills to convince them to return to the hated topic. In such cases, it is often not enough to work with the child and “with the child.”
It goes without saying that prevention is better than cure. For this reason, the following, in this inevitable brevity, is an outline of the “text of the construction course”; course, which should begin in the first months of the first academic year. However, depending on the area of deficit, as already mentioned, the measures described above are also suitable for accompaniment or retrospective support in individual and remedial training.
Children's educational cartoons Logic games Cartoons for children
Games are a unique way for a child to get distracted, relax, and at the same time learn how to game form concentrate your attention and develop your thinking. Educational games can be regular games that need to be played offline, or they can be computer games that can be found online.
In any case, parents should supervise:
- That the game has clear and precise rules;
- The child alternated his play activity and didn't play one game too much or for too long.
- The game revealed the child's talents.
- Promoted goodwill.
- It had a bright picture.
- The game could be played, if desired, with peers and without the help of an adult.
For children 8-9 we have selected educational games. It will be like online games, as well as tasks that you can try to guess and solve together with your friends offline.
Children will find educational crossword puzzles very useful. Children eight or nine years old will be able to have fun answering simple but ambiguous questions on various topics that are given in the crossword puzzle.

A game in which you need to make a sentence out of words will also be entertaining. It will allow you to consolidate the skills acquired in the lessons. native language, and will perfectly develop thinking. A similar game could be “Insert the word in the sentence”, where the child will need to put the missing word in the proposed version of the sentence.
Excellent didactic and educational games for children who are already in second grade are puzzles and pictures in which you need to find the differences. They perfectly develop visual memory and thinking, and children simply like them.
Mathematics and logic
Didactic tasks that involve mathematics are a way to entertain a child of eight or nine years old, but at the same time also strengthen his counting skills and develop his abilities in mathematics.
The simplest one might be a game where some animals or, for example, fruits are drawn in the picture, and a child of eight or nine years old will need to count them and write the number in a special window.
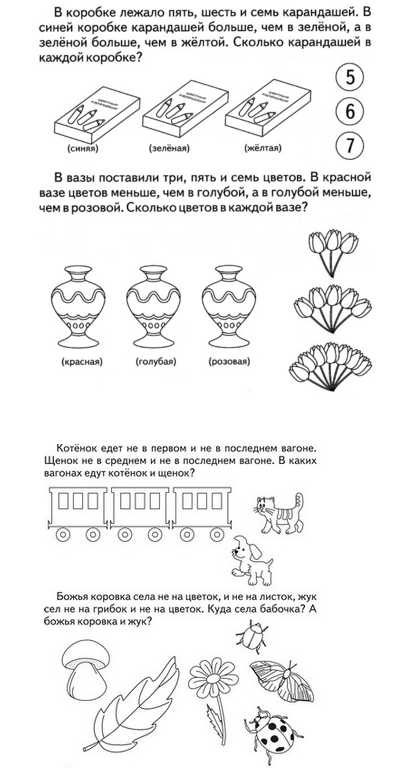
The educational and entertaining task will be a game in which you will need to arrange the proposed numbers in ascending order, and then in descending order. This game reinforces the concepts of more and less and trains thinking for eight- to nine-year-old children. A similar game could be a version of an educational and entertaining task where you need to count by tens in ascending and descending order.
An excellent counting task that definitely involves real mathematics would be a game in which eight- to nine-year-old children are asked to add and subtract some numbers. But the numbers will not be indicated by the usual boring numbers, but will look like the sum of stars, hearts or other figures. So a child of eight or nine years old will first need to count the figures, and only then complete the task. This will be educational mathematics that will be interesting and fun to do.
Educational game “For children 8 years old”
for children eight or nine years old, they are usually presented in the form of riddles. When children solve such a riddle and find the correct answer, they are usually completely delighted. The main thing is that such cognitive didactic tasks are selected exactly according to age and are not too difficult for children.
The seamstress has a roll of fabric 18 meters long. She cuts 2 meters from this piece every day. In how many days will she cut off the last piece?
“Look at this,” said Olya, “in this problem all even numbers are red.” “And all the even ones are black,” Zhanna added. What color is the number that is the sum of an even number and an odd number?
For boys
For boys, any educational exercises should be interesting and it is advisable that they be about their favorite characters. An example of such a task would be the task below.
Spider-Man fell asleep at two o'clock in the afternoon and woke up at three o'clock and fifteen minutes. How long did Spider-Man sleep?
Advice: For children at this age, it is very important that the exercises are not boring and fuel interest in development, entertainment and learning, so try to choose modern puzzles for your child, which involve characters familiar to them, and not abstract heroes.
But at the same time, ordinary funny exercises will be interesting for boys:

Compose and write words from the letters A, C, T, K, R, O, A in columns, in accordance with the number of letters in the word:
3 letters, 4 letters, 5 letters, 6 letters, 7 letters.
For girls
Educational - for girls they should also be attractive and interesting. Children of primary school age are very interested in puzzles that involve their favorite fairy tale characters or favorite animals.
The little fairy had 6 stars. She gave one star to her older fairy sister Marcel, who also had her own stars. After that, the fairy sisters had an equal number of stars. Think about how many stars the fairy Marcel had from the very beginning?
Of course, you can use the most ordinary cognitive didactic games, they will also be interesting to children.

Group the following animals into groups: wild, domestic, farm.
Cow, tiger, cat, pig, hippopotamus, rooster, dog, guinea pig, wolf.
Game "Wild and Domestic Animals"



