Psychological tests for schoolchildren began to be carried out in junior educational institutions relatively recently. At present, it has been proven that such an innovation helps to understand a number of serious issues and solve important problems.
Tests for schoolchildren are traditionally divided into three age categories: tests for junior schoolchildren for middle and high school students. Each of these age groups has its own characteristics. According to the intended purpose, they can be divided into intellectual and personal. The first type helps to understand the features of cognitive processes: thinking, memory, mindfulness. A striking example of such tests is the "School test mental development(SHTUR) ".

It helps to know how effectively absorbed educational material, as well as to understand the presence or absence of certain abilities in the student: mathematical, technical, linguistic. Teachers working in primary school often use so-called "thinking tests" in their work. Younger students are asked to solve a number of problems that clearly show how the child thinks. Very often, psychologists use "visual" tests in their work, where the child must draw something at the request of a specialist.
According to the resulting picture, the psychologist will be able to draw conclusions about the presence or absence of a small person creativity, out-of-the-box thinking. Drawings can tell a lot about the character of the student, about his state of mind. Such tasks very often help to identify "dysfunctional" families. A striking example of such tests are tasks for determining the general level of anxiety, which exist in several versions, including those adapted for elementary grades.

Psychological tests for younger students also help to identify certain problems that a student has when communicating with peers, teachers, and parents. Timely rendered psychological help will allow the child to feel more confident and more effective in confronting emerging difficulties. This kind of testing is important not only for elementary and high school students.
High school students also need to conduct similar surveys, only the proposed tasks will be completely different. Features of character, temperament, behavior - these most important characteristics will help determine any personality test. Choosing a profession for schoolchildren is a very responsible step. And psychological testing will help to figure out which occupation is suitable for a teenager and which one is not suitable.

Experts believe that all high school students should pass tests for "professional incompetence". This will save the teenager from choosing the profession in which he will not be able to achieve the desired results. It is much wiser to choose what is most suitable for the characteristics of character and temperament. In this case, a person has every chance for a brilliant career.
In order to better understand yourself, it is not necessary to visit a psychologist. To get started, you can simply buy psychology tests for schoolchildren with answers that can be purchased at any bookstore. High school students who are tested on the basis of high school should remember the principle of voluntariness. No one can force a person to take a test if they don't want to. The second principle of conducting surveys is the objectivity of their evaluation.

A competent specialist evaluates the result only in accordance with the available methods, and not on the basis of subjective reasoning. And most importantly, testing must be strictly confidential. Only the student himself, his parents and, if necessary, the teacher can get acquainted with its result. Dissemination of such information to any third parties is strictly prohibited.
Test "Are we able to listen correctly"
1 - I never do that;
2 - rarely act;
3 - almost always;
4 - always.
1. Do I give the speaker the opportunity to express his thoughts completely without interrupting?
2. Can I discover hidden meanings in words when talking to people?
3. Am I actively trying to develop the ability to remember what I hear?
4. Do I write down the most important details from the messages I hear?
5. When writing a message, do I concentrate on capturing the main facts and key phrases?
6. Am I repeating to the speaker in my own words the essential details of his message in order to better understand?
7. Do I refrain from stopping the speaker when I find their message boring, uninteresting, or when I personally dislike the speaker?
8. Do I avoid showing hostility or emotional arousal when the speaker's point of view is different from my own?
9. Do I notice when I'm distracted while listening?
10. Am I expressing genuine, sincere interest in what other people are saying?
Calculate your points:
32 or more points - you are the ideal listener;
27-31 points - the listener is above the average level;
22-26 points - need additional training and must consciously practice listening skills;
21 points or less - you perceive many messages in a distorted form, biased, without delving into the meaning.
You can discuss the most typical results for the whole class as a whole. To do this, mark four groups on the board based on the results of the survey and write down the number of students who fell into each of these groups.
Test "My optimism"
Self-confidence is the basis for enjoying life and having the strength to act.
F. Schiller
A sense of self-confidence and one's strengths, cheerfulness, cheerfulness, desire and the ability to see life in bright colors favorably distinguish an optimist. The main thing is that he is sure that he is able to change a lot in life for the better.
A pessimist is characterized by a constantly depressed mood, a lack of self-confidence and, as a result, there is no desire to change anything either in his own life or in the lives of those around him.
Let's check your level of optimism. After carefully reading the statements and answer options below, in the answer sheet, next to the number of each statement, put the letter that matches the option that is specific to you.
Then we will decipher these letters, assigning to each of them and according to the test key a certain number of points, and by the sum of these points we will determine the level of your optimism.
Statements:
1. What do you think about in the morning, just waking up:
a) about the activities that you like most of all;
b) about upcoming affairs that you do not like;
c) about a person who is nice and close to you;
d) about a person who is unpleasant to you.
2. During breakfast, do you usually:
a) take your time, calmly set the table;
b) grumble that there is not enough time, that you did not get enough sleep again;
c) like to talk with loved ones;
d) Hurry up to eat, as you are constantly late.
3. When you first meet a stranger, you:
a) immediately trust him;
b) wait for him to ask you something;
c) watch him with interest;
d) start a conversation yourself.
4. If you notice that someone is looking at you (at the theater, cinema, on the street...):
a) First of all, it seems to you that there is something funny in you;
b) you enjoy it;
c) look at yourself in some showcase, mirror;
d) don't pay attention.
5. If you are looking for an address in an unfamiliar area (city), then:
a) prefer to go directly to the information desk;
b) you will ask your friends;
c) try to find it yourself;
d) you will always be afraid that you will not be able to find it yourself.
6. Starting the school day, you:
a) hope that it will be successful;
b) wait for classes to end quickly;
c) enjoy the opportunity to see your friends;
d) hope that on this day you will not have trouble.
7. If you lose in any game, then:
a) it upsets you and you think: “This is a bad day for me”;
c) you think that the game is a game - someone has to lose, so why not you;
d) trying to think of a way to win.
8. When you quarrel with a person you like, then:
a) you are afraid of quarreling with him completely;
b) take it easy, and this has its own meaning;
c) you think that for sure you will quickly make peace and everything will be in order;
d) think that too “smooth” relationships are boring.
9. Waiting for results medical examination, You:
a) you are afraid that something serious will be found with you;
b) you know that the doctor will not tell you the truth anyway;
c) you think, since you have nothing, then why should you be afraid;
d) think that it is better for everyone to know the whole truth in time.
10. When making a decision, you expect:
a) luck and luck;
b) only on himself;
c) to “avoid meeting a black cat”;
d) fate.
Answer sheet
Last name, first name Date
|
Approval number |
||||||||||
|
Answer (letter) |
||||||||||
Results processing
Use the key provided to find your result. To do this, you need to translate all the letters of the answer options indicated by you in accordance with the key into numbers and find their sum.
Key to the test
Interpretation of results and psychotechnical exercises
11-17 points . You are an almost incurable, morbid pessimist. You need to do something with yourself!
All the time you hear inner voices that convince you that life is boring, people are not worth paying attention to, etc. Even the adoption of a more or less important decision is accompanied by a struggle of various inner voices that advise quite the opposite. One says, for example: “Don’t go for a walk today, it’s cold outside, you can catch a cold and get sick.” Another voice coaxes: “Go for a walk, fresh air is very good for health!”
This dialogue can go on indefinitely, and as a rule, you succumb to the persuasion of the first voice and stay at home. Learn to make a more optimistic decision. Moreover, this must be done as quickly as possible, in the very first minutes of this internal dialogue. And if you have made a decision, then you need to act in accordance with it, for example, go for a walk on the street.
18-24 points. Although from time to time you have some glimpses of optimism, pessimism most often takes over your mood. Try to look at the world more joyfully, do something pleasant for yourself.
On a large sheet of paper, make a list of "My virtues" and place it in a conspicuous place. Regularly (at first once a day, then less often) supplement the list of your virtues. To do this, you need to carefully study yourself, your characteristics, inquisitively peer into your habits, actions.
If you yourself cannot find another advantage in yourself, first contact the closest people, those whom you especially trust and whose opinion is significant to you. They will help you find your strengths. The same question can be (and probably, after some time it should be) asked by the most different people. All that kind and good things that they will say about you, include in the list “My virtues”.
25-30 points . You have a very sober view of the world, but you cannot completely abandon pessimistic moods.
At the first signs of a pessimistic mood, start praising yourself for every little thing: "I'm good, I'm very good." And so every time when it will be necessary.
31-41 points. You have a clear, realistic outlook on life, usually in any situation you remain optimistic. You are an optimist from birth. And you are right! But this quality of yours to a certain extent prevents you from correcting your mistakes. It's a pity!
Develop the habit of analyzing your optimism. What is happening, how do people around you feel, does your energy interfere with others, etc.? Ask yourself questions like this more often. And when you get two or three dozen answers, see which of the reasons are more common.
Now the most important thing remains - to eliminate the reasons why your mood and optimism interfere with others. Try not to get into those situations that lead to possible conflicts.
42-49 points . This is no longer optimism, but unbridled frivolity. You need to think about your attitude towards life.
Try to enter the image, for example, of a phlegmatic, calm person who has seen everything, knows everything, and live in this image for several hours in a row. No matter how difficult it is for you, no matter what reasons and reasons arise, you cannot leave the image.
React to what is happening the way your hero would react - a phlegmatic person. First calmly think about what actually happened, collect additional information for acceptance needed solution, put it aside for a while (suddenly something else happens), and only then act.
A comment. The list of statements of this test is open for additions, especially those directly related to the life of the schoolchildren themselves. The very process of discussing the available statements and possible answers is a good diagnostic of the children's real attitude to the realities of modern life.
During the discussion, it should be emphasized that today it is really difficult to remain optimistic, but only such an attitude to life will help to overcome the difficulties that almost every person experiences.
Test "My creativity"
Strive for the highest goal available to you and do not fight over trifles.
G. Selye
Man is by nature a creator who is in constant search for new ways to transform the world around him. But what is the creative potential of each of us?
The proposed test will help answer this question. For each question of the test, you need to choose only one answer option and write down the corresponding letter on the answer sheet.
Questions:
1. Do you think that the world around you can be significantly improved?
a) yes; 6) no; c) just a few things.
2. Do you think that you yourself can participate in changing the world around you?
a) yes; b) no; c) in some cases.
3. Do you think that some of your ideas would accelerate progress in the area you are in?
b) yes, but only under favorable circumstances;
c) only to some extent.
4. Do you think that in the future you will play such an important role that you will be able to fundamentally change something?
a) for sure; b) unlikely; c) maybe.
5. When you decide to undertake something, do you think that you will carry out your undertaking?
a) yes; b) no, c) yes, sometimes.
6. Do you feel like doing something you absolutely don't know?
b) the unknown does not interest me;
c) It all depends on the nature of the case.
7. You have to do something unfamiliar. Do you feel the desire to achieve perfection in it?
b) be satisfied with what I managed to achieve;
c) Yes, but only if I like it.
8. If you like something you don't know, do you want to know everything about it?
a) yes, of course;
b) no, I want to learn only the most basic;
c) No, I just want to satisfy my curiosity.
9. When you fail, then your actions:
a) I persist for some time, contrary to common sense;
b) give up on this idea;
c) keep doing it even when it becomes obvious that the obstacles are insurmountable.
10. Based on what will you choose a profession?
a) from their capabilities, prospects for themselves;
b) from the necessity of the profession;
c) of the benefits it will provide.
11. When traveling, could you easily navigate the route that you have already traveled?
c) yes, but only where I liked the area.
12. Immediately after the conversation, can you remember everything that was said?
a) yes, without difficulty;
b) I can’t remember everything;
c) I remember only what interests me.
13. When you hear a word in an unfamiliar language, can you repeat it syllable by syllable without error, even without knowing its meaning?
a) yes, almost without difficulty;
b) yes, if the word is easy to remember;
c) I can repeat, but not quite right.
14. In your free time, do you prefer:
a) stay alone, think;
b) to be in the company,
c) to be alone or in the company - it makes no difference to me.
15. You are doing something. You decide to stop this activity when:
a) the job is finished and seems to me perfectly done;
b) I am more or less satisfied with the result;
c) the job is not over yet.
16. When you are alone, your actions:
a) I like to dream about abstract things;
b) at any cost I try to find a specific occupation for myself;
c) sometimes I like to dream, but about things that are connected with my studies.
17. When an idea captures you, you think about it: a) no matter where and with whom I am;
b) only when I am alone;
c) only where it is not too noisy.
18. When you defend an idea, your actions:
a) I can refuse it if I listen to convincing arguments of opponents;
b) I will remain with my opinion, regardless of the arguments of opponents;
c) I will doubt the arguments of my opponents.
Answer sheet
Last name, first name Date
|
Question number |
|||||||||
|
Question number |
|||||||||
Total points: _____________
Results processing
For each answer "a" you get 3 points; for the answer "b" - 1 point and for the answer "c" - 2 points.
Interpretation of results
23 points or less. Your creative potential, unfortunately, is small. But maybe you just underestimate yourself?
You need to believe in your strengths and knowledge, in your abilities and talent. Believe that there are no non-talented people in the world. Each person has the makings of talent, it only needs to be discovered. In order for this to happen, look for your talent, start various businesses, try yourself in different areas of activity. And you will definitely find your talent, your place, yourself.
From 24 to 28 points. You have a good creative potential, but there are also problems that hinder progress.
If you want, you will succeed, only for this you need to understand yourself deeper, figure out what attracts you especially, find the area of activity in which you can show your talent to the maximum. Ask yourself the question more often: “Is this my business?”
29 points or more . You have significant creativity. If you can actually apply your abilities, you will achieve great success.
You are lucky, because you already know what your talent is and where you can show your abilities. But you have a difficult task ahead of you - to preserve and develop what you have. Therefore, constantly improve your memory, acquire new knowledge, create and invent new things.
Questionnaire for high school students
Target: determine the state of interaction between teachers and senior students in the team, as well as the dynamics of its development.
Progress
Respondents are asked to answer the following questions:
1. Which adults should be invited on the hike?
2. Who serves as a moral example for you:
a) comrades;
b) parents;
c) teachers;
d) heroes of books;
e) outstanding athletes;
f) members of youth ensembles;
h) add _________________.
3. In what areas of life are your students educational institution have real rights:
a) in improving the educational process;
b) in the organization of leisure;
c) in control over the quality of knowledge;
d) in encouragement;
e) in the organization of educational work;
g) Add _________________.
4. Where you can most fully express your personality (where you are most interested, where you are appreciated, understood):
a) in educational work;
b) in the classroom;
c) in the company of friends;
d) in public work;
e) in industrial training;
f) in leisure activities;
g) in the family;
5. Who can you be honest with:
a) with no one
b) with the guys from our company;
c) with the director of the educational institution;
d) with group mates;
e) with parents;
f) with the head of the circle, section, club;
g) with grandparents;
h) with class teacher;
i) with an old acquaintance; j) with a loved one; k) with a teacher;
l) Add _________________.
6. What would you do if the teacher, in your opinion, unfairly offended you:
a) keep silent
b) I will answer with impudence;
c) turn to parents for support;
d) turn to comrades for support;
e) calmly try to prove my case;
e) complain to the administration;
g) I will take revenge on occasion;
h) contact the group leader;
i) contact a teacher I trust;
j) ask to put my question at the group meeting;
l) add _________________.
7. In what cases do teachers of an educational institution participate on equal terms with students?
8. Add phrases:
“I want to go to a technical school when...”; “I don’t want to go to a technical school when…”;
“A model of moral attitude towards people in our technical school is...”;
"The relationship between teachers and students in our technical school can be called ...".
9. What systems of relations at school need to be improved:
a) teacher - student;
b) teachers - teachers;
c) teachers - administration;
d) teachers - parents;
e) parents are students;
f) students - students;
g) administration - students.
10. Who can you turn to in a difficult moment for help?
11. What cases in an educational institution, in your opinion, can be resolved:
a) one teacher;
b) jointly by teachers and students;
c) independently by students.
12. The following relations prevail in the team of employees of our educational institution:
a) hostile
b) unfriendly;
c) business;
d) group;
e) you - to me, I - to you;
e) complex;
g) all sorts;
h) friendly;
i) Add _________________.
Tasks:
1. Teach the basics of working with tests.
2. Stimulate students to know their own self.
Equipment: sayings written on the board.
Class hour progress
Teacher. A long time ago in ancient Greece, a temple was built in honor of the god Apollo (the god of light and arts). Seven sayings were written on the walls of the temple:
1. Know yourself.
2. Nothing beyond measure.
3. Measure matters most.
4. Everything has its time.
5. The main thing in life is the end.
6. There is no goodness in the multitude.
7. Vouch only for yourself.
These sayings were composed by 7 wise men. They were famous politicians and legislators of the time. One of these sayings - "Know thyself" - loved to repeat the great philosopher Socrates.
What do you think the expression "Know (understand) thyself" means? (Children answer.)
To know yourself means to understand what advantages and disadvantages you have, what you are capable of. How to do it?
Psychologists have developed a large number of tests - simple, but effective, with which you can find answers to almost all your questions. Moreover, with the help of tests, you can learn a lot of interesting things not only about yourself, but also about the people who surround you.
Today we will try to figure out what is close and clear to you - whether you feel good with your friends. At the same time, we will see what kind of activity you prefer.
1. Draw 8 circles. Look at them and determine where you are. Put a tick in the selected circle.
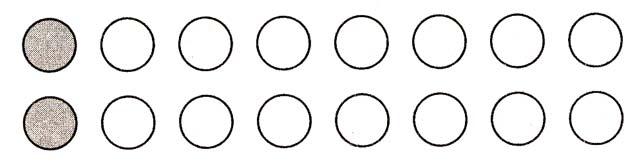
2. Draw two rows of circles, seven in each row. Do you live with your mom and dad? Write inside the first circle (it is specially painted over), suppose, "mother." Or "dad". If in the first "mom", then enter "dad" in the circle below.
Look carefully at the row of circles and determine where you are. First in the first row, then in the second. Check the boxes.
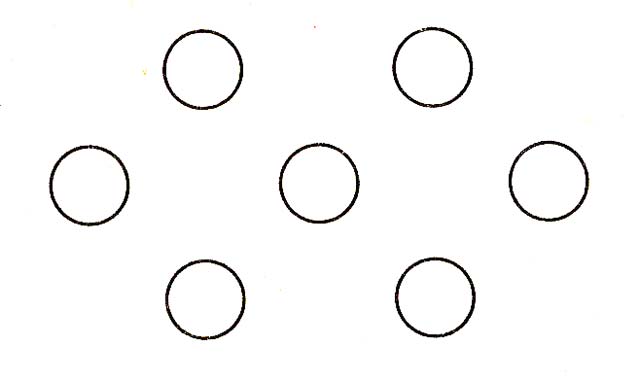
3. Draw seven circles. (Teacher should show how.) Tick where you are, sign where parents are.
4. There are three groups of people around each of you (parents, teachers, friends). There are three circles in front of you. Write where someone is. And mark where you are.
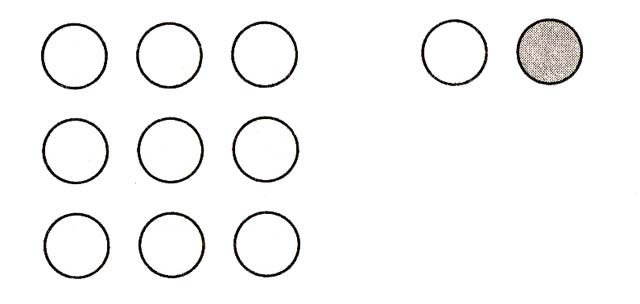
5. There are two groups of circles - nine and two. Find yourself among them. Mark with a checkmark or a cross.
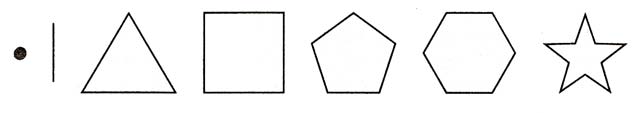
6. Before you is a point, a vertical line, a triangle, a square, a pentagon, a hexagon, a star. Which figure do you like the most? Which figure most resembles you?
7. And now - attention! There are five shapes in front of you - a square, a triangle, a rectangle, a circle and a zigzag. Choose from them the figure in relation to which you can say: "It's me!" - the one you liked the most. Then choose the one you don't like the most.
Evaluation of results
(Based on the test results, the class teacher can draw conclusions about relationships in the family, in the class. Therefore, it is not necessary to read all the results aloud).
If you quickly completed the task, then there is nothing difficult in your relations with people, you are a pleasant person to communicate with. You are rather focused on communication, i.e. your profession should be connected with people.
If you did not dare to put a tick for a long time, you can say that you are an indecisive person, you have few friends. It's time for you to get out of your shell. Of the professions, working with technology is more suitable for you.
1. A tick on the left - you feel good in a team, a sociable person and one on one with a complex machine (for example, with a computer or a disassembled vacuum cleaner) will not last long - you need company.
A tick on the right - you have a clear bad luck with the environment, you prefer loneliness, and if you are pulled out to an event, then you try to behave there unnoticed.
A tick in the middle - it all depends on the mood. In the class, you do not particularly stand out, do not strive to become leaders, but do not strive to get into outright outcasts either.
2. Whom they wrote first - that is the main thing for you in life.
They wrote "mom" - you are guided by your mother, more with her
communicate, with any question, first of all, go to her.
They wrote "dad" - it means that you are more comfortable with your father than with your mother.
If you checked the box next to their circles, then you have a trusting, sincere relationship with your parents. 3-4th circle from the beginning - you are on good terms, but everyone has their own secrets. Your relationship is unimportant if you see yourself in the circles farthest from your parents.
3. This is a question for the imagination. If, after reading the task, you introduced yourself, your relatives, or maybe friends and quickly put them in their places and ticked off, everything is clear in your relationship. If it was difficult to imagine, everything is not so simple for you.
If you put yourself above others (tick in the upper circles) - the world lies at your feet. You consider yourself sufficiently knowledgeable in this life. People as confident as you are drawn to. Next to your confidence and it becomes warmer. Perhaps you were the ringleader in the classroom, at any party you literally gush with ideas. You do a lot of things in time and try to keep up with others in your studies.
Did you tag your parents? And both in one circle? You have a good relationship - what is commonly called friendly.
Parents are one step down. Normal position. Your parents are still working for you, so they are in second place in your thoughts. You are the main person.
Parents on the third level, by a wide margin from you. You are in an unimportant relationship. With your problems, you would rather go to your friends than to mom and dad. common language you don't, you don't try to find it.
According to the arrangement of the circles, mom is closer than dad, and even mom is drawn before dad. Your authority is mom. Perhaps dad spends so much time at work that you hardly see or communicate with him.
You have chosen the middle row for yourself. It is convenient for you to be in the company. When asked who will volunteer for a cause, do not raise your hand. You do not like to stick out, although you are happy to accept invitations to all sorts of events.
Parents are standing nearby - you have complete peace and harmony. You even go hiking together.
Parents are above you - in your house you can hear a conversation in raised tones, and more often you have to obey, doing what you don’t want to do.
Parents are on the bottom row. You are more interested in school than at home. You get all the news from friends, not from parents.
You have selected the bottom row for your location. It is convenient for you to sit at the last desk by the window and be invisible. Now it doesn't really bother you.
Parents are nearby. As they say, the apple does not fall far from the tree. Quiet, calm parents often have equally quiet children. The very atmosphere of the family puts pressure on them, forcing them, so to speak, to bend down to the floor. But your little “revolutions” are still waiting for you when you try to “break through the blockade” and go free swimming.
Parents are one position higher. Your mom and dad adhere to the principle: while you live in their house, you are small and if you please do as it is said. With your "calmness" it is not so difficult to command you.
Parents are two positions higher. Your parents are the rulers of your little kingdom, and you occupy the most insignificant position in it. And all this is also superimposed on conflicts in the classroom, the absence of friends (or their betrayal) - in short, the streak in life is clearly dark.
4. Whom they wrote in the first place - he is the authority for you.
5. Test to determine how well you feel in the "pack".
You have found yourself among the nine circles - the "flock" accepts you, you can get lost in it and be one of its members. You feel a little above the “pack” (top row), an equal member (middle row), not the strongest and most popular fighter (bottom row).
You have chosen a circle to the side. The collective expelled you, or you yourself left. Or maybe you write poetry and soar far, far away? So, you are aware of your individuality.
Black circle. Not the best position.
6. The more complex you have chosen a figure, the more multifaceted person you feel. Creative people choose a star - she is all so intricate and mysterious. The pentagon is associated with the number five, which in itself says a lot. Straight line - you are a secretive nature, jealously keep your secrets. Or vice versa, you are too frivolous and simple. There are no difficulties in life for you, the horizon is clear. An enviable state.
Let's draw conclusions. If according to all the tests it turns out that you are a leader, you feel and evaluate yourself above everyone else, then you should look for a profession where you can express yourself. Any profession implies good performance and praise for success. Politician, speaker, organizer of his business, sociologist (a person who deals with the "laws of the crowd", who knows how to predict events in human society), teacher (this is where leadership qualities will appear), actor (applause, flowers ...).
If, according to the tests, it turns out that you are a quiet middle peasant (do not be offended by these words), you put yourself next to someone everywhere, you cannot live without a team, then distant expeditions, lonely winterings and trips around the world on a raft are not for you. In the future, work in a large corporation will smile at you, where everything is spinning, spinning, global events are taking place, where planets are leaving their orbits and supernovae are igniting.
7. Now let's see what kind of fruit you are, or rather, what kind of figure.
Square. Hello, excellent students and good students! You are an organized and hardworking person, at home there is always order on your desk. The pencils in the pencil case are sharply honed, the pens are all colors of the rainbow. But sometimes you fail too. If you get too carried away with the little things, you make big mistakes. You stubbornly go to your goal. It’s hard to ask for a loan from you - don’t give it. You love to learn. People like you make good businessmen and teachers.
Triangle. You are the instigator. In dreams, girls like you see themselves as great actresses, and boys like Napoleons. You like being the center of attention. You like to compete and win, but the principle “the main thing is not the finish, but the participation” is not for you. You need to win!
Circle. You easily get along with people. Approximately the same as Kolobok. Having set off to travel from the house of his grandparents, he immediately determined that neither the hare nor the wolf could interfere with him. Well, there was a mistake with the fox. Who doesn't make mistakes these days? You enjoy meeting new people. A favorite lesson in the lesson is to study the teacher's reaction to one or another irritant: to Sidorov's sniffling, to a slamming window, to Petrov and Ivanov whispering, to Borisov's creaky shoes. You know how to make people around you feel good. Your element is literature and history.
Rectangle. You are questioning everything. Where there is doubt, there is a desire to understand everything, which means that you are inquisitive and courageous. Until you find out what rustles there in a dark corner, do not calm down. You easily decide challenging tasks- you are interested in the decision process itself.
Zigzag. Such complex shape usually chosen by creative personalities. The zigzag is unusual, stands out from the crowd, is aggressive (that's why notorious hooligans can choose it). In the classroom, you rarely answer memorized phrases. The answer itself is born in your head, so you love literature that allows you to reason and argue. You are an interesting conversationalist.
Additional material
sociometric technique
The word "sociometry" literally means "social dimension". The technique was proposed by the American psychologist J. Moreno and is intended to assess interpersonal relationships: likes and dislikes, attractiveness and preference. Consider this technique in relation to the children's team.
The children are invited to list classmates with whom each of them would like to communicate and cooperate in various types activities. For example:
1. Which classmate would you invite to your birthday party?
2. With which classmate would you go on a trip around the world?
As a rule, children are invited to choose no more than three classmates. Their surnames are written in the nominative case.
The results are presented in the form of matrices (tables), which are compiled by the class teacher. A separate matrix is compiled for each question.
The first column of the matrix contains the names of the guys who choose. The first row of the matrix contains the names of those who are chosen. In both cases, the names are listed in the same order.
The number 1 is placed in the column of the student who was chosen first, the number 2 - in the column of the one who was chosen second, 3 - the third.
In summary rows and columns:
BC - the number of choices made by this person;
VP - the sum of the choices received by this person (i.e. how many people chose him);
BB - the number of mutual, coinciding elections.
The sum of the choices received by each child (VP) is a measure of his position in the class.
If the student received the most choices, he is considered to be a "star".
If you get an average number of choices - to the preferred ones.
If less than the average number of choices - to neglected.
If you have not received a single choice - to the isolated ones.
The satisfaction of the child with his own position in the class is determined by the coefficient:
BB (number of mutual elections) K.
BC (number of choices made by this person)
So, if the number of BB is 0, and the number of choices made by a person is 3 and K = 0/3 = 0, then it should be assumed that he may have problems in interpersonal relationships.
Average relationship well-being(BWV) in the class will be fixed in case of approximate equality: "stars" + preferred = = neglected + isolated.
The low level of well-being in the class is evidenced by the predominance of people with low status.
If “stars” + preferred > neglected + isolated, then this indicates a high WLW, which is characterized by fairly stable, even, friendly relations in the team. But at the same time, one should be very careful about the presence of isolated and neglected ones and try to make the necessary adjustments to interpersonal relations in the team, having previously understood the causes of the existing problems.
As an example, let's give a table in which the answers to the question are entered: "Who would you go on a trip around the world with?"
|
Smirnova |
Alekseev |
Danilova |
||||||
|
Smirnova |
||||||||
|
Alekseev |
||||||||
|
Danilova |
||||||||
The symbol "X" means that this field is not to be filled.
The sociometric methodology, in order to increase its effectiveness, involves the compilation of three matrices on three different questions, the results of which are evaluated jointly. To do this, it is necessary to summarize the obtained values of VP, BB, BC for all three matrices. It is likely that the overall picture may change.
As you can see, there is more than enough data for analysis and reflection. Take a closer look at the guys during collective games, creative activities, in free time. Your observations will complement the current picture and tell which of the children and what needs your help.
To prevent children from guessing about the research being conducted, it is better if you conduct sociometric research in the form of a game - for example, start forming a team for a round-the-world trip. Otherwise, they will expect results from you, which for many can become a source of worries, unnecessary psychological trauma.
The results of such tests, surveys and other methods focused on the study of interpersonal relations in a team, assessment individual qualities children, should not be brought up for discussion in the classroom and are used by the class teacher only in order to optimize their educational activities.
Psychological tests for diagnosis psychological readiness for school
Kern-Jerasek test - a technique for diagnosing the level of readiness for schooling. A significant advantage of the test is its versatility (the use of verbal, graphic methods of research, focus on a wide range of social factors that affect the child).
Test "Ability to study at school" G. Witzlak (1972) is intended to diagnose the psychological readiness for school in children aged 5-7 years.
Method N.I. Gutkina "House "Designed to diagnose the formation fine motor skills in children.
Methods A.L. Wenger's "Draw mouse tails" and "Draw umbrella handles" designed to diagnose the formation of fine motor skills in children.
Technique "Riding on the track" It is designed to identify the level of development of the child's psychomotor skills.
Methodology "Pattern and rule" (developed by A.L. Wenger) is aimed at identifying the ability to be guided by the system of the task condition, overcoming the distracting influence of extraneous factors. The results of its implementation also reflect the level of development of visual-figurative thinking.
Methodology " Graphic dictation" D. B. Elkonina is aimed at identifying the ability to listen carefully and accurately follow the instructions of an adult, correctly reproduce a given direction of lines on a sheet of paper, and independently act on the instructions of an adult.
Method "Politeness" is designed to diagnose voluntary attention and memory in determining the readiness of children for school.
Method "Labyrinth" is designed to identify the level of formation of visual-schematic thinking (the ability to use diagrams, conditional images when orienting in situations).
Methodology "Explanation of plot pictures"
Method "Sequence of events" designed to diagnose thinking.
The method of interpreting proverbs proposed B.V. Zeigarnik is designed to diagnose thinking.
Technique "Find the sound" serves to study the development of the speech sphere (checking phonemic hearing).
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS FOR DIAGNOSTICS OF COGNITIVE SPHERE
Technique "Recognition of figures" designed to diagnose the features of perception.
Method for determining short-term memory.
Technique "Random Access Memory".
Technique "Figurative memory".
Method A.R. Luria "Memorizing 10 words" is designed to determine the state of memory, attention, fatigue.
Technique "Reproduction of the story" is designed to determine the level of semantic memory, its volume, as well as the ability to memorize texts.
Technique "Mediated memorization" (proposed by L.S. Vygotsky and A.R. Luria, developed by A.N. Leontiev) is intended to determine the features of mediated memorization, thinking.
Method "Pictogram" is designed to study the features of mediated memorization and its productivity, as well as the nature of mental activity, the level of formation of conceptual thinking.
Method "Correction test" (Bourdon test) designed to study the degree of concentration and stability of attention.
Methodology "Schulte Tables" is designed to determine the stability of attention and the dynamics of performance.
Gorbov's technique "Red-black table" designed to assess the switching and distribution of attention.
Methodology for studying the level of attention (proposed by P.Ya. Galperin and S.L. Kabylitskaya)
is aimed at studying the level of attention and self-control of schoolchildren in grades 3-5.
Methodology "Intellectual lability"
designed to diagnose attention switching.
Methodology "Interpretation of proverbs" purpose for the study of the level of thinking.
Technique "Simple analogies" allows you to identify the nature of logical connections and relationships between concepts in children older than 10 years.
Technique "Complex analogies" designed to diagnose thinking.
Methodology "Comparison of concepts" is aimed at the study of operations of comparison, analysis and synthesis in childhood and adolescence.
Methodology "Identification of essential features" allows you to identify the features of thinking.
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS FOR DIAGNOSTICS OF INTELLIGENCE AND MENTAL DEVELOPMENT
Methods for determining the level of mental development of children 7-9 years old E.F. Zambiciavichene .
Verbal test G. Eysenck is designed to assess the intellectual abilities of persons aged 18 to 50 years with an education not lower than secondary.
D. Wexler test designed to study mental development. There are currently three forms of Wechsler scales designed to different ages. It is believed that the test can be used to diagnose school readiness and assess the causes of underachievement. In our country, the Wexler test was adapted by A. Yu. Panasyuk (1973) and later published in an updated edition in St. Petersburg (Yu. I. Filimonenko, V. I. Timofeev, 1992).
J. Raven test designed to study mental development."Raven's Progressive Matrices" - This is a non-verbal test developed by L. Penrose and J. Raven in 1936 in black and white and in 1949 in color. The black-and-white version of the test is designed to examine children from 8 years old and adults up to 65 years old. The test consists of 60 matrices or compositions with a missing element.
Culturally-free intelligence test by R. Cattell designed for level measurement intellectual development regardless of the influence of factors of the surrounding social environment.
Group Intelligence Test (GIT) by J. Wanda. The test was translated and adapted for a sample of Russian schoolchildren in LPI (M. K. Akimova, E. M. Borisova et al., 1993). Designed to diagnose the mental development of students in grades 3-6. The test reveals how much the subject at the time of the examination has mastered the words and terms offered to him in the tasks, as well as the ability to perform certain logical actions with them - all this characterizes the level of mental development of the subject, which is essential for successful completion of the school course. GIT contains 7 subtests: execution of instructions, arithmetic tasks, addition of sentences, determination of similarities and differences of concepts, number series, analogies, symbols.
School Test of Mental Development (SIT) developed by the team of K.M. Gurevich to diagnose the mental development of students in grades 7-9. The tasks of the STC include concepts that are subject to mandatory assimilation in the subjects of three cycles: mathematical, humanitarian and natural sciences.
Intelligence structure test by R. Amthauer. It was created in 1953 (last revised in 1973). The test is designed to measure the level of intellectual development of persons aged 13 to 61 years. The test consists of nine subtests, each of which is aimed at measuring different functions of intelligence. Six subtests diagnose the verbal sphere, two - spatial imagination, one - memory. The test contains 9 subtests: awareness, classifications, analogies, generalizations, arithmetic problems, numerical series, spatial representations (2 subtests), memorization of verbal material.
ASTUR (for Applicants and Senior Students Test of Mental Development). The test includes 8 subtests: 1. Awareness. 2. Double analogies. 3. Lability. 4. Classifications. 5. Generalization. 6. Logic circuits. 7. Number series. 8. Geometric shapes.
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS FOR DIAGNOSTICS OF EMOTIONAL STATES
Questionnaire for assessing the syndrome of mental burnout is designed to diagnose the manifestations of the burnout syndrome: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, reduction of personal achievements.
Depression scale (according to T.I. Balashova, O.P. Eliseev) designed to diagnose the presence and severity of depression.
Beck questionnaire designed to diagnose depression.
Tsung Depression Scale .
Test "Determination of a typical state" by E.E. Eidemiller, V.V. Yustitsky designed to measure professionally conditioned states: general dissatisfaction, neuropsychic stress, anxiety.
Luscher color test designed to study the features of the emotional state. The essence of the testing procedure is the ranking of colors by the test subjects according to the degree of their subjective pleasantness (cuteness).
Rosenzweig's pictorial frustration method is intended to study reactions to failure and ways out of situations that impede activity or satisfaction of the needs of the individual.
Methodology for assessing psychological activation, interest, emotional tone, tension and comfort (according to N.A. Kurgansky and T.A. Nemchin)is designed to diagnose states of mental activation, interest, emotional tone, tension and comfort.
Anxiety test C.D. Spielberger - Yu.L. Khanina . This test is a reliable and informative way to self-assess the level of anxiety at the moment - reactive anxiety and personal anxiety as a stable characteristic of a person.
Taylor's Anxiety Measurement Method.
Anxiety test according to V.M. Astapov designed to study the level of anxiety in preschoolers.
Phillips School Anxiety Test allows you to identify the nature and level of anxiety in schoolchildren.
Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS) is designed to measure the level of personality alexithymia.
The technique of emotional-color analogy (color painting) by A.N. Lutoshkin designed to study the characteristics of the emotional state of the subject.
Methodology for diagnosing neuroticism (T. Tashev's questionnaire) is designed to determine the presence and degree of neurotic personality disorder and its type.
Method for measuring the severity of the state of neuropsychic stress "(according to T.A. Nemchin) allows you to identify the level of neuropsychic stress.
A method for identifying the severity of reduced mood - subdepression (according to V. Zung-T.N. Balashova).
Drawing test by J. Book "House. Tree. Person" allows you to identify the degree of severity of insecurity, anxiety, self-distrust, feelings of inferiority, hostility, conflict, communication difficulties, depression.
Fairy tale test. This technique is a kind of projective test. The research procedure is as follows: a fairy tale is read to the child, and he must come up with its continuation. Depending on the child's answers, one can draw a conclusion about the features of emotional experiences (primarily anxiety, aggressiveness) and the sources that cause these experiences.
SAN - a technique that allows you to clarify the characteristics of well-being, activity, mood.
Color test of relationships (A. Etkind). This is a non-verbal compact diagnostic method that reflects both conscious and partially unconscious levels of human relationships. The methodological basis of this method is a color-associative experiment. During the experiment, the subject is asked to express his attitude towards the partner using color.
Method "Cactus" M.A. Panfilova designed to determine the state emotional sphere preschooler, the presence of aggressiveness, its direction, intensity.
Methodology for diagnosing the level of emotional burnout V.V. Boyko, which allows you to establish the leading symptoms, phases of emotional burnout ("tension", "resistance" and "exhaustion").
Methodology "Differential scales of emotions" (according to K. Izard) It is designed to identify dominant emotions that allow you to qualitatively describe the well-being of the subject.
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS FOR DIAGNOSTICS OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS
Sociometric game "Secret" (T.A. Repina) reveals the system of electoral preferences existing between children.
Method "Captain of the ship" is designed to diagnose the status of preschoolers and younger schoolchildren in a peer group.
Methodology "Mosaic" - a natural experiment that studies the features of interpersonal relationships between children in a group of peers, including: the degree of emotional involvement of the child in the actions of a peer; the nature of participation in the actions of a peer, the nature and degree of empathy with a peer, the nature and degree of manifestation of prosocial forms of behavior in a situation where the child faces a choice to act "in favor of another" or "in his own favor".
Rene Gilles technique allows you to explore the social adaptability of the child, the scope of his interpersonal relationships and its features, the child's perception of family relationships.
sociometric test is intended for diagnosing emotional connections, i.e. mutual sympathy between members of the group.
Methodology for diagnosing interpersonal relations T. Leary is designed to study the style and structure of interpersonal relationships and their characteristics, as well as the study of the subject's ideas about himself, about his ideal self, attitude towards himself.
Methodology for studying mutual relations "student-teacher" (according to Khanin-Stambulov).
Methods of studying the psychological atmosphere in the group (scale-questionnaire F. Fiedler). The methodology is designed to study the characteristics of the psychological (emotional) atmosphere in the work team.
Methodology for studying the psychological climate in the team of A.N. Lutoshkin.
Test "Psychological climate circle" designed to diagnose the psychological climate, measured through the business and emotional component
Methodology "Team management style" is designed to diagnose the style that the leader implements in managing the workforce (liberal, democratic or authoritarian).
K. Thomas test is designed to determine the behavioral strategies of the subject in conflict situations.
Methodology "Constructive quarrel" S.Kratohvil is aimed at determining the degree of constructiveness of the course of the conflict and its results (it is used in family psychology).
Methodology "Studying the cohesion of the team" (indicators of value-oriented unity) R.S. Nemova allows to identify the level of cohesion and value-oriented unity of the team by determining the frequency of distribution of positive positive and negative characteristics of a phenomenon significant for the group
Methodology "Analysis of family relationships" (DIA) E. Eidemiller, V. Yustitsky is designed to diagnose the characteristics of the relationship between parents and the child, the degree of satisfaction of his needs, the level and adequacy of the requirements applied
Marriage satisfaction test questionnaire by V. Stolin, T.L. Romanova, T. Butenko. The purpose of the methodology is to determine the level of satisfaction - dissatisfaction of spouses with marriage.
Methodology "Conflict in different spheres of family life". The methodology uses the predominant spread of conflicts in 8 areas family life, namely: a) problems of relations with relatives and friends; b) issues related to the upbringing of children; c) manifestation by spouses of the desire for autonomy; d) situations of violation of role expectations; e) situations of mismatch of norms of behavior; f) manifestation of dominance by spouses; g) manifestation of jealousy by spouses; h) differences in relation to money.
Methodology "Distribution of roles in the family" is designed to determine the practice of distribution of roles that has developed in a young family.
Methodology "Diagnostics of parental attitude" A.Ya.Varga and V.V. Stolin allows you to identify the features of the attitude of parents to the child, described in terms of the following five scales: 1) Acceptance - rejection of the child. 2) Cooperation. 3) Symbiosis. 4) Authoritarian hypersocialization. 5) "Little loser". This last scale shows how adults relate to the child's abilities, to his strengths and weaknesses, successes and failures. The parent sees the child as younger than their actual age. The child appears to be unadapted, unsuccessful, open to bad influences.
Drawing test "Family drawing" (T. G. Homentauskas) allows you to identify the features of intra-family communication.
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS FOR DIAGNOSTICS OF PERSONALITY
Sixteen factor personality questionnaire Cattell - allows you to get a lot of information about personality traits which are called constitutional factors. A factor is understood as a deep personal characteristic that determines a group of stable behavioral manifestations, relatively independent of other characteristics of the same series. The questionnaire contains 187 questions that the subjects are asked to answer.
G. Eysenck's personal questionnaire is designed to identify character traits that are called "extroversion", "introversion" and "neuroticism".
Questionnaire Mini-mult (abbreviated version of the MMPI questionnaire) designed to study the following personality traits: hypochondria, depression, hysteria, psychopathy, paranoia, psychasthenia, schizoid, hypomania.
Shmishek test questionnaire designed to diagnose the type of personality accentuation. The theoretical basis of the questionnaire is the concept of accentuated personalities by K. Leonhard.
Bass Questionnaire - Darkie – designed to diagnose the type and level of aggressiveness, including: 1. Physical aggression - use physical strength against another person. 2. Indirect - aggression, in a roundabout way directed at another person or not directed at anyone. 3. Irritation - readiness to display negative feelings at the slightest arousal (temper, rudeness). 4. Negativism - an oppositional manner in behavior from passive resistance to active struggle against established customs and laws. 5. Resentment - envy and hatred of others for real and fictional actions. 6. Suspicion - ranging from distrust and caution towards people to the belief that other people are planning and causing harm. 7. Verbal aggression - the expression of negative feelings both through the form (shout, screech) and through the content of verbal responses (curses, threats). 8. Guilt - expresses the subject's possible belief that he is a bad person that evil is doing, as well as the pangs of conscience he feels.
"Q-sort" technique is designed to diagnose the subject about himself, as well as to determine the ideal I of the individual.
Multilevel personal questionnaire "Adaptiveness" is designed to assess the adaptive capabilities of the individual, taking into account socio-psychological and some psycho-physiological characteristics, reflecting the generalized features of neuropsychic and social development.
Keirsey test for the diagnosis of communicative personality traits.
Questionnaire of the level of subjective control Rotter is designed to determine external or internal personality types.
Methodology "Motivation for success" by T. Ehlers
.
Motivation for success and fear of failure (A.A. Rean's questionnaire).
Methodology "Purpose-means-result"
is designed to study the features of the structure of activity.
Methodology for determining the orientation of the personality
It is designed to evaluate priority areas for the individual by focusing on oneself, on communication or on business.
Methodology for the study of empathic features of personality VV Boyko.
Methodology for determining the self-esteem of a preschooler (V.G. Shchur).
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS IN PSYCHOSOMATICS
Giessen Somatic Complaints Inventory reveals the intensity of emotionally colored complaints about the state of physical health.
Questionnaire Serdyuk to study self-assessment of the social significance of the disease.
Kellerman-Plutchik Questionnaire designed to identify defense mechanisms.
Sachs-Sydney's Unfinished Sentence Technique, modified for psychosomatic patients, is aimed at studying the following parameters: attitude to mother, attitude to father, attitude to family, attitude to women (men), attitude to sexual life, attitude to friends, attitude to superiors, attitude to subordinates, attitude to workmates, fears and concerns, consciousness of guilt, attitude towards oneself, attitude towards the past, attitude towards the future, attitude towards illness, goals.
Questionnaire Garbuzov to identify the dominant instinct.
K. Machover's test "Draw a person" is designed to explore ideas about the past, present, future, the specifics of human relationships with others.
Clinical Questionnaire to identify and evaluate neurotic conditions.
Rorschach test is aimed at studying the personality characteristics of the subject during the associative test.
Sodney test allows you to identify satisfied and unsatisfied needs of the subject.
TAT - thematic test of apperception is designed to diagnose the aspirations, needs of the subject, the impacts exerted on him, conflicts that arise in relationships with others.
Projective test "Image of yourself" It is designed to study the characteristics of the subject's perception of their physical parameters and self-image.
OTHER TESTS
Methodology for determining stress resistance and social adaptation of Holm and Ray
Methodology for studying the level of social frustration L.I. Wasserman is aimed at studying the level of satisfaction with various factors of the social environment.
The questionnaire of psychological difficulties is intended for express diagnostics of the level of experiencing one's own troubles in the sphere of interpersonal relations.
Method for diagnosing consistency family values and role attitudes in a married couple in both groups of A.N. Volkova. The method allows to determine: 1. Spouses' ideas about the importance of sexual relations in family life, personal community of husband and wife, parental responsibilities, professional interests of each of the spouses, household services, moral and emotional support, external attractiveness of partners. 2. Spouses' ideas about the desired distribution of roles between husband and wife in the implementation of family functions, united by a scale of role expectations and claims.
Test "Level of satisfaction with life" by E. Golizek.
The scale of loneliness D. Russell, L. Peplo, M. Ferguson is designed to study the level of a person's subjective feeling of his loneliness.
Sensation seeking scale It is designed to study the level of needs for sensations of various kinds in relation to adolescents and adults.
Methodology "Value Orientations" by M. Rokeach is based on a direct ranking of the list of values and allows you to explore the individual rank of values. M. Rokeach distinguishes two classes of values: 1) terminal - beliefs that some ultimate goal of individual existence is worth striving for; 2) instrumental - beliefs that some mode of action or personality trait is preferable in any situation.
PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF PROFESSIONAL SELF-DETERMINATION
Methodology "Motives for choosing a profession" is designed to determine which motives are leading when choosing a profession: internal individually significant or internal socially significant.
D. Holland test is designed to diagnose the type of personality depending on abilities, desires, hobbies, interests.
Differential-diagnostic questionnaire of E.A. Klimov "I prefer" aimed at determining the type of professional field of activity of the optant.
Questionnaire for the study of the cognitive sphere of personality in the context of professional orientation.
Determination of inclinations according to the method of L.A. Yovaishi.



