MBKG mastic is a plastic, homogeneous viscous mass of black color, it is an economy class product. Its main component is high-level oil-based bitumen and mineral fillers. And also the composition includes various additives and modifiers that improve the performance of hot bituminous roofing mastic. The material of the improved formula has unparalleled physical and chemical properties.
The mixture was widely used in roofing and waterproofing works. It can be used for the following operations:
- on flat roofs;
- on sloped roofs.
With the help of putty, rolled roofing products with waterproofing properties, which are reinforced with fiberglass, are glued. Also, roofing polymer mastic is used as a coating agent to provide the necessary waterproofing and anti-corrosion coating. Coated with a mixture of various metal structures, concrete pillars, reinforced concrete piles, building foundations, which will later be in contact with the ground.
Ways to use MBK mastic
Before manipulation, the material is properly heated and thoroughly mixed, after which it is applied to the surface with a roller, brushes or spatulas. For better adhesion, the surface must be cleaned and primed before application. If roofing operations using MBK 65 mastic are carried out on the roof of a building with an old roofing material, but in a still tolerable state, then it can not be removed, however, the mixture should be applied in 2 layers so that the first layer is not visible after the completion of the procedures.
Popular brands include: mastic MBK G 55, 65, 75 and 85. They are the most widely used, and you can order them from us with confidence in the quality of the products offered. remember, that given substance is a combustible material, therefore, all work must be carried out by persons from among specialists, subject to the rules of personal and fire safety.
Technical characteristics of mastic MBK G
The numerical indicator in the brand name means its heat resistance for a period of 5 hours, ºC, not less. Therefore, you should choose a brand, focusing on this factor, depending on the conditions at the facility, where work will be carried out using this material in the future.
For example, let's take the characteristics that bitumen mastic MBK G 55 has:
- Heat resistance after 5 hours - not lower than 55ºC;
- The softening point is between 55 and 60ºC;
- The flexibility of the substance for t 18±2ºC on the rod - 10mm;
- Pulverized filler, % by weight - 25-30;
- Water saturation - traces;
- Consumption - 1.5-2 kg / m 2.
Mastic MBK X is able to repeatedly freeze and thaw, being in an environment with high humidity, without collapsing and without reducing strength. The material has increased heat resistance due to strong crystalline structures, which means it retains its rigidity even when exposed to elevated temperatures. The elasticity of hot bituminous roofing mastic is increased with the help of additives - plasticizers. The addition of talc elements does not allow the putty to cake, and the various antiseptics and herbicides included in the composition increase its anti-corrosion properties. Such a mixture belongs to the products of hot application, therefore, the main requirement at the beginning of the procedure is the heating of the HB roofing polymer mastic to a temperature of at least 90 ° C.
MASTIC BITUMEN
ROOFING HOT
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
GOST 2889-80
STATE R EST COMMITTEE OF THE USSR
CONSTRUCTION
Moscow
DEVELOPED by the Central Research and Design and Experimental Institute of Industrial Buildings and Structures (TsNIIpromzdaniy) of the USSR State Construction Committee
PERFORMERS
M.I. Povalyaev, cand. tech. Sciences, OK. Mikhailova, L.G. Gryzlov, cand. tech. Sciences, L. M. Leibengrub
INTRODUCED by the Central Research and Design and Experimental Institute of Industrial Buildings and Structures (TsNIIpromzdaniy) of the USSR State Construction Committee
Deputy directors S. M. Glikin
APPROVED AND INTRODUCED BY Decree of the USSR State Committee for Construction of March 24, 1980 No. 39
STATE STANDARD OF THE UNION OF THE SSR
By the Decree of the State Committee of the USSR for Construction of March 24, 1980 No. 39, the deadline for the introduction was established
from 01.01. 1982
Non-compliance with the standard is punishable by law
This standard applies to bitumen roofing hot mastic, which is a homogeneous mass, consisting of a bituminous binder and filler, and is used in a hot state.
Mastic can be made with additives of antiseptics and herbicides.
Mastic is intended for the installation of rolled roofs, as well as mastic roofs, reinforced glass materials.
The scope of the mastic is given in this standard.
1. STAMPS
1.1. Mastic, depending on heat resistance, is divided into grades indicated in table. one.
T ab face 1
1.2. The conventional designation of mastic brands consists of its name hot bituminous roofing mastic and a number indicating the heat resistance of a mastic of a certain brand.
In the designation of brands of mastic with the addition of antiseptics, silt and herbicides, after the designation of heat resistance, the letter A or G is added, respectively.
Etc name symbol mastic and heat resistance 55 °С:
MBK-G-55
Same with antiseptic additive:
MBK-G -55A
The same, with the addition of herbicides:
MBK-G-55G
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Mastic must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Depending on the brand, the mastic must comply with the requirements of Table. 2.
5.2.3. Carrying out the test
After 2 hours of exposure, samples with mastic grades MBK-G-55 or M BK-G-65 are placed in a heated oven on an inclined stand (20% ). and with mastic brands M BK -G -75, MBK-G-85, M BK -G -100 - on an inclined stand (100% at an angle of 45 °).
The samples are kept in a cabinet for 5 hours at a given temperature, after which the samples are taken out and inspected.
The mastic is considered to have passed the test if it does not flow and does not begin to slide.
5.3. Flexibility Definition
The method is based on bending a glassine sample coated with mastic along a semicircle of a rod of a certain diameter at a given temperature.
5.3.1. Equipment and accessories
Thermometer according to GOST 2823-73
Rods with a diameter of 10, 15, 20, 30, 40 mm.
Vessel for water.
5.3.2. Preparing for the test
On a sample of glassine with dimensions of 50x100 mm, 8-10 g of mastic, preheated to 140-160 ° C, is applied in a uniform layer.
After that, the sample is kept for 2 hours at a temperature of 18 ± 2 °C in air. Then water is poured into the vessel, the temperature of which should be 18 ± 2 °C.
The samples and the rod are placed in this vessel with water and kept in it for 15 minutes.
5.3.3. Conducting a test
After soaking in water, the sample is slowly and bent along the semicircle of the rod for 5 with the front surface (mastic) up. The time from the moment of taking the sample out of the water and bending it along the semicircle of the rod should not exceed 15 s.
The mastic is considered to have withstood the test if cracks do not form on the sample surface.
5.4. Determination of adhesive properties of mastic
The essence of the method is to determine the load required to break two glued specimens of a certain length and width.
5.4.1. Equipment and accessories
Breaking machine of the brand RT-250M-2 or similar machines, and having a working part of the scale from 0 to 100 kgf with a division value of not more than 0.2 kgf, with an allowable error of readings within the working scale ± l% .
Laboratory drying cabinet with perforated shelves, ventilated, allowing automatic temperature control.
The plate is metallic.
5.4.2. Preparation of samples for testing
Two samples of glassine 50x140 mm in size, cut from a roll in the longitudinal direction, are glued together with mastic on an area of 50x60 mm. Heated to 140-160 °C mastic in the amount of 4-6 g is applied to the surface of both samples so that one end of each sample remains uncovered with mastic. The glued samples are pressed with a weight of 1 kg through a metal plate and kept for 2 hours at a temperature of (20 ± 2) °C. 3 samples are prepared for testing.
5.4.3. Conducting a test
Two hours after gluing, the samples are placed in the clamps of the tensile testing machine without distortion.
The specimen is tested at a constant moving jaw speed of 50 mm/min until rupture is to occur against the glassine.
5.5. Determination of filler content after heating.
After cooling to room temperature, the mastic is removed from the cylinder and samples (from the bottom and in the middle of the cylinder) are taken, each weighing at least 1 g. The test results must meet the requirements.
5.6. Determination of the mastic softening temperature - according to GOST 11506-73.
5.7. Determination of the filler content - according to GOST 2678-76.
5.8. Determination of water content in mastic - according to GOST 2477-65.
6. PACKAGING, LABELING, TRANSPORT AND STORAGE
6.1. Mastic can be packed in steel barrels with a removable bottom, in wooden barrels or drums, paper bags with anti-adhesive layer.
To construction sites located near the places of centralized production, the mastic should be transported heated to 160-180 ° C in special vehicles equipped with mixers. Travel time should not exceed 3 hours.
6.2. On the packaging of the mastic must be indicated with indelible paint:
name or trademark of the manufacturer;
mastic brand;
name of the filler;
batch number.
6.3. Each shipped batch of mastic must be accompanied by a document certifying the quality, which indicates:
name or trademark of the manufacturer;
the number of seats in the party and their mass;
mastic brand;
name of fillers and their percentage in mastic;
the name of the antiseptic or herbicide and their percentage in the mastic;
test results;
designation of this standard.
6.4. Packed can be transported by any means of transport.
6.5. Mastic should be stored separately by brands indoors.
7. MANUFACTURER WARRANTY
7.1. The manufacturer guarantees the compliance of the mastic with the requirements of this standard, subject to the conditions of transportation and storage.
Warranty period of storage of mastic - one year from the date of production. After the expiration of the warranty period of storage before use, the mastic must be checked for compliance with its requirements of this standard.
ATTACHMENT 1
1. The scope of mastic, depending on the construction area and the slope of the roof, is indicated in the table.
|
Construction area |
Mastic for the device |
|||
|
roofs with slope, % |
junctions |
|||
|
less than 2.5 |
2.5 - less than 10 |
10 - 25 |
||
|
North of geographic latitude 50 ° for European and 53 ° for the Asian part of the USSR |
MBK-G-55 |
MBK-G-65 |
MBK-G-75 |
MBK-G-85 |
|
South of these areas |
MBK-G-65 |
MBK-G-75 |
MBK-G-85 |
MBK-G-100 |
2. Mastics of the MBK-G-55 and MBK-G-65 brands should be used for gluing antiseptic roofing material, glass roofing felt and roofing materials, and mastics of the MBK-G-55A and MBK-G-65A brands - for gluing non-antiseptic roofing material; mastic brands MBK-G-55G and MBK-G-65G - for the installation of a protective layer on roofs.
APPENDIX 2
1. Hot roofing bituminous mastics should be prepared in the factory (for example, at asphalt concrete plants), at centralized installations of building trusts in heated tanks equipped with agitators. It is allowed to manufacture mastics in construction conditions.
2. The process of preparation of bituminous binder consists in dehydration and melting of bitumen, in fusion of bitumen, in the introduction of surfactants and plasticizing additives into bitumen or alloy.
3. Initially, fusible bitumen is loaded into the container, which is dehydrated at a temperature of 105-110 ° C, after that, bitumen grade BNK 90/30 (BNK 90/40) is loaded and, with constant operation of the mixer, the temperature of the bituminous binder is adjusted to 160 - 180 ° FROM.
4. The amount of roofing bitumen grade BNK 90/30 (BNK 90/40), introduced into the molten low-melting bitumen, depends on the softening temperature of the mixed bitumen and is determined by the formulas:
![]() (2)
(2)
where BT- the content in the alloy of more refractory bitumen (grade BNK 90/30),%;
B m - the content of low-melting bitumen in the alloy, %;
t- the softening temperature of the bituminous binder for the preparation of mastics, assigned in accordance with this standard;
t T ,t m - softening temperature, respectively, of refractory and low-melting bitumen.
5. To prevent foaming of bitumen when heated, defoamer grade SKTN-1 should be added at the rate of 0.01 g (2-3 drops) per 1 ton of bitumen.
6. Surfactant additives introduced to reduce the sedimentation of the filler during the transportation of mastics at a temperature not exceeding 130 ° C, should be injected directly into the bituminous binder or with filler.
Surfactants are introduced into the bituminous binder in the amount of 1.5 - 2% by weight of the bituminous binder.
Surfactants are introduced into the filler during grinding in the amount of 0.15 - 0.2% by weight of the filler.
7. By agreement with the consumer, for work in winter conditions, it is allowed to introduce plasticizing additives in the amount of 3-8% by weight of the bituminous binder. With the introduction of plasticizing additives, surfactants should not be introduced into the bituminous binder.
8. After sampling and determining the softening point of the bituminous binder, the filler is introduced in separate portions with constant stirring.
9. The amount of loaded filler in each portion should be 1/3 - 1/4 of the required calculated amount. With an intensive rise of the foam, the introduction of the filler is stopped until the level of the foam drops, after which the backfilling of the filler is resumed.
10. After loading the last portion of the filler, mastic cooking is continued at a temperature of 160 - 180 ° With constant stirring until a homogeneous mixture is obtained and the foam is completely settled.
11. Antiseptic additives in the amount of 4 - 5% or herbicides in the amount of: simazine 0.3 - 0.5%, amine (sodium) salt 2.4D 1 -1.5% by weight of the bituminous binder is administered in separate portions in 2 - 3 reception with constant stirring before the final preparation of the mastic.
APPENDIX 3
Reference
LIST OF PRODUCTS USED AS SURFACTANTS
|
Product name |
Regulatory document |
|
Anionic types of higher carboxylic acids: |
|
|
gossypol resin (cotton tar) |
OST 18-114-73 |
|
fat tar |
OST 18-114-73 |
|
synthetic fatty acids C 17 - C 20 |
OST 38-7-25-73 |
|
Cationic: |
|
|
type of higher aliphatic amines (BP-Z) |
TU 382-01-170-74 |
|
type of four substituted ammonium bases (alkyltrimethylammonium chloride) |
TU 3840798-78 |
Oil construction bitumen BN 70/30 GOST 6617-76
General information
Brand (type) BN 70/30
GOST, TU GOST 6617-76
OKP code 0256200001
Characteristics
Specifications Depth of needle penetration at 25°C, 0.1 mm - 21-40 mm. The softening temperature for the ring and ball is 70-80°C. Extensibility at 25°C - not less than 3 cm. Solubility - not less than 99.5%. Weight change after warming up - not less than 0.50%. Flash point - not less than 240°C. Mass fraction of water - traces.

Oil construction bitumen BN 90/10 GOST 6617-76
General information
Brand (type) BN 90/10
GOST, TU GOST 6617-76
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ, CJSC Soft Roofing
OKP code 0256200001
Characteristics
Specifications Depth of needle penetration at 25°C, 0.1 mm - 5-20 mm. The softening point according to KISH is 90-105°C. Extensibility at 25°C - not less than 1 cm. Solubility - not less than 99.5%. Weight change after warming up - not less than 0.50%. Flash point - not less than 240°C. Mass fraction of water - traces.
Description Building oil bitumen is obtained by oxidation of residual products of direct distillation of oil. It is a combustible substance. Packed in paper bags.
Scope It is used for construction work in various areas of the national economy.
Two-component polyurethane composition "Ureplen-Liquid Roof" TU 2294-001-51088901-02
General information
GOST, TU TU 2294-001-51088901-02
Manufacturers OOO Zashchita Konstruktsii-M
OKP code 5772464002-002
Characteristics
Description Protective and decorative roofing. It has high water repellency, resistance to impact and tear from bird beaks and natural phenomena, such as hail. Tinted. Consumption for a coating of 6 layers is, on average, 1.2 l / m2 of surface.
Scope It is used to create seamless roofing with a service life without repair of more than 20 years and for the installation of an exploited roof of any geometry.
Technical characteristics Tensile strength - 13-14.5 MPa. Relative elongation - 350-500%. Residual elongation - 5-10%. Shore A hardness - 30-90 arb. units Electric durability - 10-24 Kv/mm. Adhesion to concrete - 1.3-1.8 MPa. Resilience to rebound - 25-30%. Operating temperature from -75°С to +100°С.
Method of application The composition is applied in several layers with a roller, brush, airless spray, airbrush. The use of open fire (gas burners, etc.) is not required.
Mastic bituminous roofing hot MBK-G
General information
Brand (type) MBK-G
GOST, TU TU 5775-017-72746455-2008
Manufacturers TechnoNIKOL (Minvody-Krovlya LLC)
OKP code 577521
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Softening temperature - not lower than 95°С. Needle penetration depth at 25°C, 0.1 mm - no more than 22. Adhesion strength with concrete - no less than 0.1 MPa, with metal - no less than 0.1 MPa. The shear strength of the adhesive joint is at least 4 kN/m.
Description Represents the homogeneous mass consisting of bitumen and a filler. Packing: mastic has the form of a briquette in a polyethylene film and a paper bag.
Scope of application It is used for gluing rolled bituminous roofing and waterproofing materials, for installing mastic roofs reinforced with fiberglass, as a coating waterproofing and anti-corrosion coating for metal, concrete, reinforced concrete, wood and other building structures. It can be used in all climatic regions according to SNiP 23-01.
Mastic bituminous roofing hotMBK-G-65, MBK-G-75,MBK-G-85 GOST 2889-80
General information
Brand (type) MBK-G-75
GOST, TU GOST 2889-80
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ
OKP code 5775210002-002
Characteristics
Technical characteristic Softening temperature according to Kish - 78-82°С. Mass fraction of water - traces. Heat resistance for 5 hours - not less than 75°C. Flexibility on a bar with a radius of 20 mm - 18°C. The content of pulverized filler is 25-30% by weight.
Description Represents the homogeneous mass consisting of bituminous knitting and a filler. Used hot. Packed in paper bags with anti-adhesion layer.
Scope Intended for the installation of rolled and mastic roofs, reinforced with glass materials.
Mastic bitumen-polymer MBP-90, MBP-100 TU 5775-004-00287912-2007
General information
Brand (type) MBP-100
GOST, TU TU 5775-004-00287912-2007
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ
OKP code 5775311002-002
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Softening temperature - not lower than 100°С. The depth of penetration of the needle at 25°C, 0.1 mm - 25-50. Adhesion strength to the base at t=20°C: with concrete - 0.1 MPa, with steel - 0.15 MPa. Adhesion strength between layers: roll material-roll - not less than 0.15 MPa, roll material-concrete - not less than 0.1 MPa. The shear strength of the adhesive joint is at least 1000 N/m. Water absorption within 24 hours, by weight - not less than 1.5%.
Description Represents the multicomponent mass consisting of SBS of the modified oil bitumen and a filler. Used when hot.
Mastic bitumen-polymer cold application MBP-X-90, MBP-X-100 TU 5775-005-00287912-2007
General information
Brand (type) MBP-X-100
GOST, TU TU 5775-005-00287912-2007
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ
OKP code 5775311002-004
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Softening temperature - not lower than 100°С. The depth of penetration of the needle at 25°C, 0.1 mm - 25-50. Adhesion strength with the base at t=20°C: with concrete - 0.1 MPa, with steel - 0.15 MPa. Adhesion strength between layers: roll material-roll - not less than 0.15 MPa, roll material-concrete - not less than 0.1 MPa. The shear strength of the adhesive joint is at least 1000 N/m. Water absorption within 24 hours by weight - no more than 1.5. Mass fraction of non-volatile substances - not less than 50%. Drying time of one layer - 12-24 hours.
Description Represents the multicomponent mass consisting of SBS of the modified roofing oil bitumen and organic solvent.
Scope Intended for installation and repair of rolled mastic roofs reinforced with glass materials, as well as for waterproofing underground structures.

Mastic bitumen-rubber insulating MBR-65, MBR-75, MBR-90, MBR-100 GOST 15836-79
General information
Brand (type) MBR-65
GOST, TU GOST 15836-79
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ
OKP code 5775240004
Characteristics
Specifications Depth of penetration of the needle at 25°C, 0.1 mm - 40. Softening temperature according to KISH - not less than 65°C. Extensibility at 25°С - not less than 4 cm. Flash point - not less than 240-300°С. Water saturation for 24 hours - no more than 0.2%.
Description Represents the multicomponent mass consisting of oil bitumen, a filler and plasticizer. Packed in paper bags with anti-adhesion coating. Used hot and cold.
Scope Intended for the installation of rolled roofs, insulation of underground steel pipelines and other structures in order to protect them from soil corrosion. It can be used for reinforced roofs, car underbody coatings as an anti-corrosion and anti-noise agent. It surpasses roofing hot mastic in quality and can be used not only for sticking roofing felt and for installing mastic roofing, but also for waterproofing foundations, basements and other reinforced concrete structures.

Mastic bitumen-rubber insulating cold MBR-X TU 5775-001-00287912-2005
General information
Brand (type) MBR-X
GOST, TU TU 5775-001-00287912-2005
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ
OKP code 5775240005
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Content a.d.v. at the request of the consumer - at least 50%, 60%. Drying time at t=(20±2°С) - no more than 24 hours. Drying time at t=(75±5°С) - no more than 5 hours.
Description It is a multicomponent mass consisting of petroleum bitumen, filler, plasticizer and solvent. Depending on the softening temperature, mastics are divided into brands: MBR-X-65, MBR-X-75, MBR-X-90, MBR-X-100. Consumption of mastic for priming concrete bases and laying roofing materials - 0.8-1.2 kg / m2; for anticorrosive protection threw. surfaces - 0.3-0.9 kg / m2.
Scope Intended for the device of rolled roofs, waterproofing of steel and concrete structures in order to protect them from soil corrosion and atmospheric moisture. It can be used to cover the bottoms of cars as an anti-corrosion and anti-noise agent. With a large margin of quality, it replaces hot roofing mastic and can be used not only for sticking roofing material, but also for waterproofing foundations, basements, and other reinforced concrete structures.
Mastic bitumen-rubber polymer MBRP-80, MBRP-85 TU 5775-003-00287912-2008
General information
Brand (type) MBRP-80
GOST, TU TU 5775-003-00287912-2008
Manufacturers CJSC MPK KRZ
OKP code 577500
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Softening temperature - not lower than 80°С. Depth of needle penetration at 25°C, 0.1 mm - 27. Extensibility at 25°C - not less than 4 cm. Water saturation in 24 hours - no more than 0.2%.
Description It is a homogeneous mass of black color, consisting of SBS modified roofing oil bitumen and rubber crumb, used in a hot state. Combustibility group - G4. Consumption: average consumption of mastic with a layer thickness of 2 mm - 2.2 kg/m2, for insulation of vertical concrete or brick surfaces - 2.4 kg/m2.
Scope Sealing of seams and cracks in cement and asphalt concrete pavements of highways. Protection of metal structures from corrosion damage under atmospheric influences and under the influence of various aggressive media (salt, slightly acidic and slightly alkaline solutions). Waterproofing of internal and external surfaces of ground and underground structures and structures made of metal, concrete, reinforced concrete and other materials of any shape and size, including foundations, basements, bathrooms, trays, flyovers and other objects.
Roofing waterproofing mastic "Hydrolon" TU 5770-002-98310821-2007
General information
GOST, TU TU 5770-002-98310821-2007
Manufacturers Company "KrasKo"
OKP code 5775321002
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Material basis - urethane prepolymer. Appearance films - a uniform semi-gloss surface. Conditional viscosity - not less than 45-55 sec. Drying time at (20±0.5)°C - no more than 24 hours. Pot life after mixing - no less than 60 minutes. Relative elongation at break - not less than 700%. Application temperature from +5°С to +30°С.
Description Hydrolon is a two-component urethane mastic based on polyester compounds with the addition of plasticizers, fillers and targeted additives. Forms an elastic waterproof membrane on the surface. Possibility of subsequent staining. Consumption: 1 kg/m2 with a thickness of 1 mm.
Scope It is used for the installation of new and reconstruction of old roofs (liquid roof), used for sealing and protecting tiles, slate, galvanized, roofing felt, for waterproofing pools and water tanks, waterproofing and sealing reinforced concrete, metal and other structures.
Method of application Roofing mastic is applied to a clean and dry surface. Add the contents of the container with component B to the container with component A and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous mass is obtained. The components are mixed in a container using a low-speed drill with a stirring nozzle. The mastic is applied with a roller or brush to a layer thickness of 0.5-0.7 mm, followed by drying for 24 hours and applying a second layer with a thickness of 0.5-0.7 mm.

Hot roofing mastic TECHNONICOL No. 41 (Eureka) TU 5775-010-17925162-2003
General information
GOST, TU TU 5775-010-17925162-2003
Manufacturers LLC "Minvody-Krovlya"
OKP code 5775310011
Characteristics
Technical characteristics Softening temperature - not lower than 105°C. Depth of needle penetration at 25°C - no more than 50. Bonding strength between layers: rolled material-rolled material - not less than 0.15 MPa, rolled material-concrete - not less than 0.15 MPa. The shear strength of the adhesive joint is at least 4 kN/m. Water absorption within 24 hours - no more than 1% by weight. Conditional strength - not less than 0.2 MPa. Relative elongation at break - not less than 1100%. Adhesion strength with concrete at t=(20±5)°C - not less than 0.2 MPa, with steel - not less than 0.25 MPa. Adhesion strength with concrete at t=(minus 20±5)°C - not less than 0.80 MPa, with steel - not less than 1 MPa. Flexibility on a bar with a radius of 5 mm - not higher than -15°C
Description Mastic bitumen-polymer roofing and waterproofing "Eureka" is made of bitumen modified with styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) and mineral fillers. Packing: 30 kg bags with anti-adhesive inner layer of siliconized paper.
Scope It is applied at repair and the device of roofs and a waterproofing. Roofing: gluing bituminous and bitumen-polymer roll materials to the base; leveling the base (sealing cracks and chips in the base of a cement-sand screed, concrete slabs, asphalt screeds, filling surfaces with potholes, leveling saucers and stagnant zones up to 5 mm deep); installation of mastic and repair of all types of roofs; installation of protective layers of the roof; when installing drain funnels; at the junction of the roofing carpet to the roof structures. Waterproofing: coating of steel structures and concrete blocks, columns in contact with the ground; mastic waterproofing of building structures, including pipelines.
Method of application The mastic is heated to a temperature of 160-180°C with constant stirring and applied in liquid form on a base preliminarily primed with a bituminous primer using a spatula, brush, or poured and leveled. After hardening forms a strong elastic covering.
From:
SNiP III-A.11-70
Decree N 226 / P9-4
OST 18-114-73
Annex 3
OST 38-7-25-73
TU 382-01-170-74
TU 113-08-586-86
TU 113-08-587-86
5. REPUBLICATION. January 1995
This standard applies to bitumen roofing hot mastic, which is a homogeneous mass, consisting of a bituminous binder and filler, and is used in a hot state.
Mastic can be made with additives of antiseptics and herbicides.
Mastic is intended for the installation of rolled roofs, as well as mastic roofs reinforced with glass materials.
The scope of the mastic is given in Appendix 1.
1. STAMPS
1. STAMPS
1.1. Mastic, depending on heat resistance, is divided into grades indicated in Table. one.
Table 1
Heat resistance, °С |
1.2. The conventional designation of mastic brands consists of its name - hot bituminous roofing mastic and a number indicating the heat resistance of a mastic of a certain brand.
In the designation of brands of mastic with additives of antiseptics or herbicides, after the designation of heat resistance, the letter A or G is added, respectively.
An example of a symbol for mastic with a heat resistance of 55 ° C:
MBK-G-55
The same, with the addition of an antiseptic:
MBK-G-55A
The same, with the addition of herbicides:
MBK-G-55G
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Mastic must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Depending on the brand, the mastic must meet the requirements of Table. 2.
table 2
Name | Norm for brand mastic |
||||
indicator | |||||
1. Heat resistance for 5 hours, °C, not less | |||||
2. Softening temperature according to the "ring and ball" method, °С | |||||
3. Flexibility at a temperature of (18±2) °С on a rod with a diameter, mm | |||||
fibrous | |||||
pulverized | |||||
2.3. In appearance, the mastic should be homogeneous, without foreign inclusions and particles of filler, antiseptic or herbicide, not covered with bitumen.
On a mastic cut with an area of 50 sq. cm, there should not be more than two unimpregnated particles of filler, antiseptic or herbicide larger than 0.4 mm.
2.4. Mastic must firmly glue rolled materials. When testing samples of glassine glued with mastic, rupture and splitting of the samples should occur along the glassine.
2.5. Mastic should be easy to apply: at a temperature of 160 - 180 ° C, mastic weighing 10 g should freely spread over the surface of glassine with dimensions of 50 x 100 mm in an even layer 2 mm thick.
2.6. When transporting the mastic in a hot state, the filler may settle. In this case, the amount of filler (at different levels of the vehicle) may differ from that indicated in Table. 2, respectively, for fibrous filler by no more than 3%, and for pulverized filler - 10%.
2.7. Requirements for materials for the preparation of mastics
2.7.1. bituminous binder
2.7.1.1. As a binder for the preparation of mastic, oil roofing bitumen that meets the requirements of GOST 9548 and their alloys, as well as oil road bitumen according to GOST 22245 and their alloys with roofing bitumen grade BNK 90/30 (BNK 90/40) should be used.
2.7.1.2. To reduce the sedimentation of fillers, surfactants should be added to the bituminous binder.
Anionic or cationic substances should be used as surfactants.
The list of products used as surfactants is given in Appendix 3.
2.7.1.3. In the bituminous binder used for the manufacture of mastics in winter conditions, one should introduce: coal oil for impregnating wood according to GOST 2770, shale oil for impregnating wood according to GOST 10835 or kukersol varnish according to specifications approved in the prescribed manner.
2.7.1.4. The softening temperature and brittleness of the bituminous binder for the manufacture of mastics of different grades must meet the requirements of Table. 3.
Table 3
Mastic brand | Bituminous binder softening temperature according to the "ring and ball" method, degrees C | Bituminous binder brittleness temperature, deg.С, not higher |
MBK-G-55 | ||
MBK-G-65 | ||
MBK-G-75 | ||
MBK-G-100 | ||
Note. With the introduction of plasticizing additives in the bituminous binder, its softening temperature can be 3-5°C lower. |
||
2.7.2. Filler
2.7.2.1. For the preparation of mastic, fibrous or dusty fillers should be used.
Chrysotile asbestos of the 7th grade according to GOST 12871 should be used as a fibrous filler.
Finely ground talc or talcomagnesite according to GOST 21235, shale rocks, limestones, dolomites, tripoli or chalk should be used as a pulverized filler according to specifications approved in the prescribed manner.
2.7.2.2. To reduce the sedimentation of the filler during its grinding, a surfactant based on synthetic fatty acids specified in Appendix 3 can be introduced. In this case, the surfactant is not added to the bituminous binder.
Note. In the case when shale rocks are used as a filler, surfactants are not introduced.
2.7.2.3. The filler for the manufacture of mastic must meet the requirements of Table. four.
Table 4
Name of indicator | ||||
1. Density (specific gravity), kg/cu.m., (g/cu.cm), no more | ||||
2. Humidity of the filler, % by weight, not more than: | ||||
fibrous | ||||
pulverized | ||||
3. Grain composition of the filler: | ||||
fibrous | Passes completely through a sieve with mesh N 04 | |||
pulverized | Passes completely through a sieve with mesh N 02, and the residue on a sieve with mesh N 009 is no more than 10% | |||
2.7.3. Antiseptics and herbicides
2.7.3.1. Sodium silicofluoride according to TU 113-08-587 or sodium fluoride according to TU 113-08-586 should be used as antiseptic additives.
An antiseptic is not added to mastics with plasticizing additives.
2.7.3.2. As herbicides, simazine according to GOST 15123 or the amine (sodium) salt of dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4D) should be used according to the specifications approved in the prescribed manner.
The amount of antiseptics and herbicides in the composition of the mastic must comply with the requirements of SNiP II-26.
3. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
3.1. Mastic is a combustible material with a flash point of 240-300°C. In the manufacture and use of mastics, the requirements of chapter SNiP III-A.11 must be observed.
3.2. In the production, draining, pouring and sampling of mastics, overalls and personal protective equipment should be used in accordance with the "Typical industry standards for the free issuance of overalls, safety shoes and safety devices", with an addition to them, approved by a resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor and Social Affairs and the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions July 6, 1978 No. 226/P9-4.
3.3. In case of ignition of small amounts of mastic, the fire should be extinguished with sand, felt mat, special powders, foam fire extinguisher; developed fires - foam jet or water from fire monitors.
4. ACCEPTANCE RULES
4.1. The mastic must be accepted by the technical control of the manufacturer.
Acceptance and delivery of mastic is carried out in batches.
The batch size is set in the amount of shift production of mastic prepared according to the same recipe, technology and from the same components.
4.2. To check the compliance of the mastic with the requirements of this standard, 3% is taken from each lot, but not less than three packing places, while the mass of each sample taken at three different levels must be at least 0.5 kg. When transported by special vehicles, a sample is taken before loading into the vehicle in the amount of 1.5 kg.
4.3. All selected samples are fused at a temperature of 120-130 ° C, thoroughly mixed and divided into two equal parts. One of these parts is tested, the other is labeled and stored in a clean tightly closed container in a dry and cool room for routine testing.
All tests are carried out on 3 samples.
4.4. Acceptance of mastic is carried out by carrying out acceptance control on the following indicators: appearance, heat resistance, softening point and flexibility.
4.5. The manufacturer is obliged to conduct periodic tests of the mastic for the following indicators:
4.6. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out for this indicator of a double amount of mastic selected from the same batch.
The results of the retests are final.
4.7. The consumer has the right to carry out a control check of the mastic in accordance with the requirements of this standard.
5. TEST METHODS
5.1. Checking the appearance (homogeneity of the mastic, the presence of foreign inclusions and particles of filler, antiseptic or herbicide not covered with bitumen) is carried out visually.
5.2. Determination of heat resistance
5.2.1. Equipment and accessories
Drying laboratory cabinet with perforated shelves, ventilated, allowing automatic control of the set temperature.
Plate metal flat dimensions 50x100x2 mm.
5.2.2. Preparing for the test
To determine the heat resistance, a glassine sample with dimensions of 50x100 mm is applied with a uniform layer of 8 - 10 g of mastic, preheated to a temperature of 140 - 160 ° C. A piece of glassine of the same size is placed on top and pressed with a load of 2 kgf for 2 hours. The load is applied through a flat metal a plate measuring 50x100x2 mm.
The drying cabinet is heated, depending on the brand of mastic, to the temperature indicated in Table. 2.
5.2.3. Conducting a test
After 2 hours of exposure, samples with mastic grades MBK-G-55 or MBK-G-65 are placed in a heated oven on an inclined stand (20%), and with mastic grades MBK-G-75, MBK-G-85, MBK- G-100 - on an inclined stand (100% at an angle of 45 °).
The samples are kept in a cabinet for 5 hours at a given temperature, after which the samples are removed and inspected.
The mastic is considered to have passed the test if it does not flow and does not begin to slide.
5.3. Flexibility Definition
The method is based on bending a glassine sample with mastic applied to it along a semicircle of a rod of a certain diameter at a given temperature.
5.3.1. Equipment and accessories
Thermometer according to GOST 28498.
Rods with a diameter of 10, 15, 20, 30, 40 mm.
Vessel for water.
5.3.2. Preparing for the test
8-10 g of mastic, preheated to 140-160°C, is applied in a uniform layer on a sample of glassine with dimensions of 50x100 mm.
After that, the sample is kept for 2 hours at a temperature of (18 ± 2) °C in air. Then water is poured into the vessel, the temperature of which should be (18±2) °C.
The samples and the rod are placed in this vessel with water and kept in it for 15 minutes.
5.3.3. Conducting a test
After soaking in water, the sample is slowly bent along the semicircle of the rod for 5 s with the front surface (mastic) up. The time from the moment of removing the sample from the water and bending it along the semicircle of the rod should not exceed 15 s.
The mastic is considered to have passed the test if no cracks form on the surface of the specimen.
5.4. Determination of the adhesive properties of mastic
The essence of the method is to determine the load required to break two glued samples of a certain length and width.
5.4.1. Equipment and accessories
Breaking machine brand RT-250M-2 or similar machines with a working part of the scale from 0 to 100 kgf with a division value of not more than 0.2 kgf, with an allowable error of readings within the working scale +/-1%.
Laboratory drying cabinet with perforated shelves, ventilated, allowing automatic temperature control.
The plate is metal.
5.4.2. Preparation of samples for testing
Two samples of glassine 50x140 mm in size, cut from a roll in the longitudinal direction, are glued together with mastic on an area of 50x60 mm. Mastic heated to 140-160 °C in the amount of 4-6 g is applied to the surface of both samples so that one end of each sample remains uncovered with mastic. The glued samples are pressed with a weight of 1 kg through a metal plate and incubated for 2 hours at a temperature of (20±2)°C. 3 samples are prepared for testing.
5.4.3. Conducting a test
2 hours after gluing, the samples are placed in the clamps of the tensile testing machine without distortion.
The specimen is tested at a constant moving jaw speed of 50 mm/min until rupture is to occur against the glassine.
5.5. Determination of filler content after heating
The content of the filler is determined by the combustion method according to GOST 2678 with the following addition. The mastic sample is poured into a split cylinder 20 mm in diameter and 150 mm high, which is placed in an oven, heated to a temperature of 160°C (when using surfactants up to 130°C) and kept at this temperature for 5 hours.
After cooling to room temperature, the mastic is removed from the cylinder and samples (from the bottom and in the middle of the cylinder) are taken, each weighing at least 1 g. The test results must comply with the requirements of clause 2.6.
5.6. Determination of the softening point of the mastic - according to GOST 11506.
5.7. Determination of the filler content - according to GOST 2678.
5.8. Determination of water content in mastic - according to GOST 2477.
6. PACKAGING, LABELING, TRANSPORT AND STORAGE
6.1. Mastic can be packed in steel barrels with a removable bottom, in wooden barrels or drums, paper bags with an anti-adhesive layer.
Mastic should be transported to construction sites located near centralized manufacturing sites heated to 160-180°C in special vehicles equipped with mixers. Travel time should not exceed 3 hours.
6.2. On the packaging of the mastic must be indicated with indelible paint:
Brand of mastic;
The name of the filler;
Party number.
6.3. Each shipped batch of mastic must be accompanied by a document certifying the quality, which indicates:
- name or trademark of the manufacturer;
The number of seats in the party and their mass;
Brand of mastic;
Name of fillers and their percentage in mastic;
- the name of the antiseptic or herbicide and their percentage in the mastic;
- test results;
Designation of this standard.
6.4. Packed mastic can be transported by any type of transport.
6.5. Mastic should be stored separately by brands indoors.
7. MANUFACTURER WARRANTY
7.1. The manufacturer guarantees the compliance of the mastic with the requirements of this standard, subject to the conditions of transportation and storage.
Warranty period of storage of mastic - one year from the date of production. After the expiration of the warranty period of storage before use, the mastic must be checked for compliance with its requirements of this standard.
1. The scope of mastic, depending on the construction area and the slope of the roof, is indicated in the table.
Construction area | Mastic for the device |
|||
roofs with slope, % | ||||
2.5 - less than 10 | junctions |
|||
1. North of the geographic latitude of 50 degrees. for European and 53 deg. for the Asian part of the USSR | ||||
2. South of these areas | ||||
2. Mastics of the MBK-G-55 and MBK-G-65 brands should be used for gluing antiseptic roofing material, glass roofing felt and roofing materials, and mastics of the MBK-G-55A and MBK-G-65A brands - for gluing non-antiseptic roofing material; mastic brands MBK-G-55G and MBK-G-65G - for the installation of a protective layer on roofs.
APPENDIX 2 (recommended). RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE COMPOSITION AND PREPARATION OF BITUMEN ROOFING HOT MASTICS
1. Mastics should be prepared in the factory (for example, at asphalt concrete plants), at centralized installations of building trusts in heated tanks equipped with agitators. It is allowed to manufacture mastics in construction conditions.
2. The process of preparation of bituminous binder consists in dehydration and melting of bitumen, in fusion of bitumen, in the introduction of surfactants and plasticizing additives into bitumen or alloy.
3. Initially, low-melting bitumen is loaded into the tank, which is dehydrated at a temperature of 105-110 degrees C, then bitumen of the BNK 90/30 (BNK 90/40) brand is loaded and, with the mixer constantly running, the temperature of the bituminous binder is adjusted to 160 - 180 degrees. FROM.
4. The amount of roofing bitumen grade BNK 90/30 (BNK 90/40), introduced into the molten low-melting bitumen, depends on the softening temperature of the mixed bitumen and is determined by the formulas:
where Bt is the content in the alloy of more refractory bitumen (grade BNK 90/30),%;
Bm is the content of low-melting bitumen in the alloy, %;
t is the softening temperature of the bituminous binder for the preparation of mastics, assigned in accordance with the table. 3 of this standard;
tt, tm - softening temperature, respectively, of refractory and low-melting bitumen.
5. To prevent foaming of bitumen when heated, defoamer grade SKTN-1 should be added at the rate of 0.01 g (2-3 drops) per 1 ton of bitumen.
6. Surfactant additives, introduced to reduce the sedimentation of the filler during the transportation of mastics at a temperature not exceeding 130 degrees C, should be added directly to the bituminous binder or with the filler.
Surfactants are introduced into the bituminous binder in the amount of 1.5 - 2% by weight of the bituminous binder.
Surfactants are introduced into the filler during grinding in the amount of 0.15 - 0.2% by weight of the filler.
7. By agreement with the consumer, for work in winter conditions, it is allowed to introduce plasticizing additives in the amount of 3-8% by weight of the bituminous binder. With the introduction of plasticizing additives, surfactants should not be introduced into the bituminous binder.
8. After sampling and determining the softening point of the bituminous binder, the filler is introduced in separate portions with constant stirring.
9. The amount of loaded filler in each portion should be 1/3 -1/4 of the required calculated amount. With an intensive rise of the foam, the introduction of the filler is stopped until the level of the foam drops, after which the backfilling of the filler is resumed.
10. After loading the last portion of the filler, mastic cooking is continued at a temperature of 160 - 180 C with constant stirring until a homogeneous mixture is obtained and the foam is completely settled.
11. Antiseptic additives in the amount of 4 - 5% or herbicides in the amount of: simazine 0.3 - 0.5%, amine (sodium) salt 2.4D 1 - 1.5% by weight of the bituminous binder is administered in separate portions in 2 -3 reception with constant stirring before the end of the preparation of the mastic.
APPENDIX 3 (informative). LIST OF PRODUCTS USED AS surfactants
APPENDIX 3
Reference
Product name | Regulatory document |
1. Anionic types of higher carboxylic acids: | |
Gossypol resin (cotton tar) | |
Fat tar | |
Synthetic fatty acids C(17) - C(20) | |
2. Cationic: | |
Type of higher aliphatic amines (BP-Z) | |
Type of four substituted ammonium bases (alkyltrimethylammonium chloride) |
The text of the document is verified by:
official publication
M.: Publishing house of standards, 1995
To protect the roofs of residential and industrial buildings, along with modern means of waterproofing - deep penetration impregnations, polypropylene films, membranes and coatings - bitumen-based materials are still actively used. Builders are well aware of hot bituminous roofing mastic, which allows you to create elastic seamless waterproof coatings for roofs that have a strictly horizontal or minimally inclined position.
When choosing products from a manufacturer or a company that sells waterproofing, they are guided by the official standard introduced back in 1982 - GOST 2889-80. It regulates technical characteristics, product requirements, scope and conditions of use, features of storage and transportation.
Composition, types and labeling
The material that serves as the basis for other components is a binder - petroleum roofing or road bitumen and their alloys.
Appearance of containers for bituminous mixtures
In order for the composition to retain elasticity and strength for a long time, to spread when heated and quickly harden, the following components are added to the base:
- fillers of various types (pulverized, fibrous) - chrysotile asbestos, talcomagnesite, talc, slate, tripoli, dolomite, chalk;
- Surfactants cationic, anionic - to minimize the sedimentation of inclusions;
- antiseptics - sodium silicofluoride or fluoride;
- herbicides - sodium salt, simazine.
If the mixture is intended for use in the winter season, it must necessarily include oils (shale, coal - impregnating for wood) or kukersol varnish.
There are 5 types of mastic, which differ in heat resistance (from 55ºС to 100ºС). For example, the MBK-G-55 brand has a heat resistance of 55ºС, and the MBK-G-85 brand has a heat resistance of 85ºС, respectively. Some components are also indicated in the labeling: herbicides with the letter "G", antiseptics with the letter "A". If you want to purchase a product with a heat resistance of 100ºС and antiseptic protection, you need to look for products labeled MBK-G-100 A.
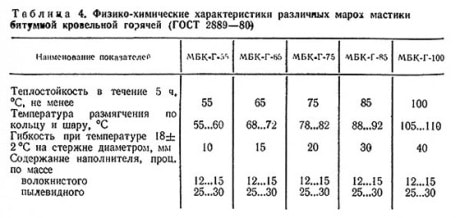
quality requirements
In order for the finished coating to fully comply with the operating conditions, it is necessary to verify the quality of MBK-G. Visually, you can determine the uniformity of the mass, the absence of foreign particles. Components included in the regulation (for example, antiseptics) must be completely covered with bitumen.
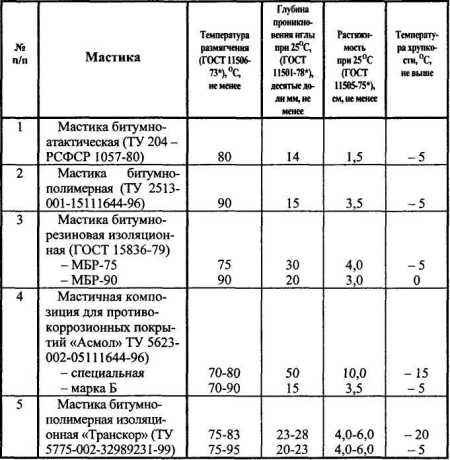
Technical characteristics of mastic various kinds
The quality of stickiness is determined by interaction with rolled materials. The frozen bituminous mass is usually stronger: when checking for a gap, glassine should delaminate. The ease of application depends on the fluidity: if at a temperature of 170ºС the mass reaches a consistency that allows it to spread with a layer of 2 mm, then the product is of high quality.
Storage and transportation
In the factory, the mastic is packed in containers that are convenient for storage and transportation:
- drums and barrels made of wood;
- paper bags;
- steel barrels.
Barrels are equipped with a removable bottom for ease of use, and paper bags are equipped with special anti-adhesive liners.

Each package is stamped, the imprint contains the following information:
- manufacturer information;
- brand of goods;
- the name of the filler;
- batch number.
The quality certificates, which are accompanying documents for each batch, indicate the manufacturer, brand of goods, total weight, number of seats, detailed information about the components, test data.
Transportation can be carried out by any mode of transport. Closed rooms, hangars and warehouses are used as storage facilities. In some cases, products are delivered to the construction site directly from the place of production in a special vehicle, in a heated state. In this case, the filler may precipitate (data on the content of inclusions will differ from those declared by 3-10%).
The purpose declared by the manufacturer is the waterproofing of flat and sloped roofs, as well as junctions that cause difficulties in fixing alternative materials. Products are recommended to be used only for roofs with a slope of not more than 25%, and the choice of brand depends on the slope indicators. For example, if the slope is less than 2.5%, MBK-G-55 (in the northern regions) or MBK-G-65 (in the southern regions) is suitable, for a slope of 10-25% - MBK-G-75 and MBK-G -85 respectively.

For sticking roofing felt, glass of roofing material and roofing material with antiseptic impregnation, it is recommended to use grades with a thermal conductivity of 55-65ºС. Ordinary roofing material is glued with a mixture with an antiseptic, and if protection is needed, with a herbicide. Hot bituminous mastic MBK-G-75 is diluted with kerosene (white spirit) and the surfaces are primed with the resulting solution before gluing the rolls.
In addition to its direct purpose, the waterproofing agent is also effectively used for other construction areas, for example, for protecting underground structures, foundations, pipelines, buried tanks, piles, tunnels, concrete structures, etc. Cracks in the roadway are poured with a hot solution, metal parts of buildings are insulated.

Foundation treated with hot bituminous mastic
Mastic roofing technology
Flat mastic roofing equipment is the main purpose of MBK-G, but more often it has to be used for hydroprotection of inclined planes. When pouring sloped surfaces, there is a possibility that the layer will have an uneven thickness. The advantage of the cured film is the absence of joints and seams. Consider how to properly pour the hot mass manually, glue the rolls and use sprayed waterproofing.
The order of applying the material
Previously, even if the roof is horizontal, without a slope, preparation should be made. It is necessary to clean the surface from debris, dirt, dust, chemical and greasy spots.

The further course of action is as follows:
- Primer primer.
- Application of the first layer, heated to the desired temperature. The mass should be distributed evenly, with a layer of the same thickness (from 2 mm to 4 mm).
- Laying a reinforcing layer using fiberglass, geotextile or fiberglass.
- Application of 2 and 3 layers with subsequent reinforcement.
The final stage is the slate topping, which is necessary to protect the monolithic coating from ultraviolet radiation and thermal shocks. Instead of slate, bitumen-aluminum mastics with a reflective effect are often used.
Features of the spraying method
In addition to the manual method, for which doctor blades, rollers and brushes are used, the spray method is used. The mechanized process of applying a thin layer of material is provided by an airless sprayer operating at a pressure of 150 bar and resembling a paint spray gun. When working with a sprayer, you must take precautions - wear protective clothing and goggles (or a mask).

Recently, cold roofing mastic has been increasingly used. It also has a second name, common among builders - "liquid rubber". The smallest drops of bituminous solution fit well on concrete, wooden, metal bases, enveloping them with a thin impermeable film. Spraying - the best option to protect the old roofing, as it penetrates into all cracks and smoothes deformations. This type of waterproofing is more suitable for mechanized application.
How to properly stack rolls
Due to technical characteristics, hot roofing bituminous mastic became a connecting element between rolled materials containing bitumen and bases different type. A suitable level of heat resistance allows increased adhesion and creates a reliable, almost monolithic coating. On the hot solution well "sits down" as rolled roofing material or glassine, and shingles. The type of base does not matter much, it can be concrete, wood, metal, brick.

It is enough to heat one-component compositions with an open flame, two-component compositions must first be mixed using the instructions from the manufacturer.
Operating procedure:
- preparation of the base (elimination of large defects with putty, garbage collection, cleaning);
- primer with a special primer or diluted binder solution;
- uniform distribution hot (heated to a temperature of 160-180 ºС) mass over the processing area;
- laying of roll material.
When installing roofing material, it is necessary to avoid the appearance of cavities, air bubbles, and irregularities. Having rolled out the canvas, it must be pressed tightly so that the solution protrudes along the edges. Rollers are used to remove air. The procedure should be performed in dry weather, at air temperatures above 0ºС (in some cases - up to -5ºС).
Functional Differential Benefits
Many are interested in the question: why is it necessary to kindle fires, heat the mass, fiddle with the burning solution, if there are many types of cold analogues that are safer and more convenient to use? The answer lies in the capabilities of the heated solution and the quality of the finished coating.

Distribution of the bituminous mixture with a roller
Here are the benefits that experienced roofers note:
- deeper penetration of the hot composition into the structure of the base (for example, porous concrete or wood);
- excellent adhesion with various types of bases, including old ones;
- high curing speed;
- the possibility of waterproofing adjunctions and joints, the creation of a monolithic coating.
Well, another advantage that is of great importance in the field of budget construction is the low cost of production. The price range is from 10 rubles/kg to 55 rubles/kg.
Brief overview of popular manufacturers
Almost all well-known domestic manufacturers of roofing waterproofing produce a hot version of the mastic. On the market you can find products of the following companies:
- Hydroisol;
- TechnoNikol (Eureka #41);
- Izhora;
Professionals note the high quality of the Polish mixture "Titan".

Bitumen for concrete surfaces
There are many varieties with the addition of rubber, rubber, polymers, however, cold counterparts are still slowly replacing MBK-G - they are easier to apply, you do not need to order propane and make a fire (or rent special equipment to transport a hot solution).
Thematic videos
Thematic videos will help to present the process of preparation and use of MBK-G
Video instruction for preparing hot mass:
Video review of TechnoNikol products:
Modern alternative to MBK-G:
The process of laying the built-up roofing material:
You can cover a flat roof with waterproofing (utility rooms in the country house, garage, gazebos, terraces) on your own using MBK-G, however, it is much easier for beginners to work with another type of bituminous material - cold. It is sold in full ready-made, and the MBK-X application technology resembles the painting process.



